Why are used cars so expensive?
Used cars can be expensive for several reasons, and the pricing dynamics of the used car market are influenced by various factors. Here are some key reasons why used cars can be expensive:
High Demand: A significant factor driving up used car prices is high demand. This demand can result from various factors, including economic conditions, supply chain disruptions, and consumer preferences. In some cases, a strong demand for used cars can lead to increased competition among buyers, pushing prices higher.
Supply Constraints: The supply of used cars can be limited due to various factors, such as a decrease in new car production, reduced lease returns, or decreased trade-ins. When supply is constrained, it can drive up prices as buyers compete for the available vehicles.
Delayed New Car Purchases: During economic downturns or uncertain times, some consumers delay purchasing new cars and opt for used cars instead. Increased demand for used cars in such situations can lead to higher prices.
Shortages of Specific Models: Certain used car models may experience shortages in the market due to factors like discontinued production, popularity, or limited availability. When demand for these specific models is high, their prices can rise significantly.
Economic Factors: Economic conditions, such as changes in interest rates, employment levels, and consumer confidence, can influence the demand for both new and used cars. Economic stability can encourage people to buy used cars, contributing to higher prices.
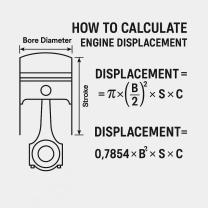
Increased Vehicle Complexity: Modern cars often come equipped with advanced technology and features, making them more expensive to repair and maintain. As a result, older used cars may command higher prices because of their simpler designs and lower long-term maintenance costs.
Vehicle Age and Mileage: The age and mileage of a used car significantly affect its price. Cars with lower mileage and those that are relatively new tend to be more expensive than older, higher-mileage vehicles.
Dealer Markup: Dealerships often add a markup to the prices of used cars to cover their expenses and earn a profit. This markup can vary depending on the dealership's pricing strategy and operating costs.
Consumer Preferences: Consumer preferences, including a preference for SUVs and trucks over sedans or a demand for specific brands and models, can affect the pricing of used cars. Popular models may command higher prices.
Vehicle Condition and History: Well-maintained used cars with clean histories and documented service records often fetch higher prices due to their perceived reliability and condition.
Warranty and Certification: Used cars that come with a warranty or are certified pre-owned (CPO) by manufacturers often have higher price tags because of the added peace of mind they offer to buyers.
Scarcity of Used Parts: Availability of used or aftermarket parts for certain cars can impact their resale value. Cars with readily available and affordable parts tend to be more attractive to buyers.
Regional Variations: Used car prices can vary significantly by region due to factors like climate, local preferences, and supply. Urban areas and regions with harsh winters may see higher prices for specific types of vehicles.
It's important to recognize that the pricing of used cars is influenced by a combination of these factors, and prices can fluctuate over time. Additionally, the used car market can be influenced by external events, such as economic recessions, natural disasters, and supply chain disruptions, which can further impact pricing dynamics.
The Used Car Conundrum: Why Prices Are on the Rise
Used car prices have been rising steadily in recent years, and for good reason. There are a number of factors that are contributing to this trend, including:
- The global chip shortage: The global chip shortage has disrupted the production of new cars, which has led to a decrease in supply. This has driven up the prices of both new and used cars.
- Supply chain disruptions: The COVID-19 pandemic has caused supply chain disruptions that have impacted the production of cars and car parts. This has also contributed to the shortage of new cars and the rising prices of used cars.
- Increased demand: The demand for used cars has increased in recent years, due to a number of factors, including the rising cost of new cars and the increasing popularity of car ownership. This increased demand has also put upward pressure on used car prices.
Market Dynamics: Understanding the Factors Behind Expensive Used Cars
The market dynamics that are driving up used car prices are complex, but they can be summarized as follows:
- Supply and demand: The basic laws of supply and demand are at play in the used car market. When the supply of used cars is low and the demand is high, prices will go up.
- Consumer behavior: Consumer behavior is also playing a role in the rising prices of used cars. More people are choosing to buy used cars instead of new cars, due to the high cost of new cars and the increasing popularity of car ownership.
- Government policies: Government policies, such as fuel efficiency standards and emissions standards, can also impact the used car market. For example, fuel efficiency standards can make older cars less desirable, which can drive up the prices of newer used cars.
The Economics of Used Car Buying: Exploring the High Price Trend
The high price trend of used cars is a complex issue with no easy solutions. However, there are a few things that consumers can do to protect themselves:
- Do your research: Before you buy a used car, research the market value of the car you are interested in. You can use online tools such as Kelley Blue Book and Edmunds to get an estimated value.
- Get a pre-purchase inspection: Before you buy a used car, have it inspected by a qualified mechanic. This will help you identify any potential problems with the car and give you an idea of how much it will cost to fix them.
- Negotiate: Don't be afraid to negotiate on the price of a used car. Most sellers are willing to negotiate, especially if you are willing to pay cash.
It is also important to keep in mind that the used car market is cyclical. Prices will eventually come down, but it is difficult to say when that will happen. In the meantime, consumers should be prepared to pay a premium for used cars.
Conclusion
The rising prices of used cars is a complex issue with no easy solutions. However, by understanding the factors that are driving up prices and taking steps to protect themselves, consumers can minimize their financial burden.