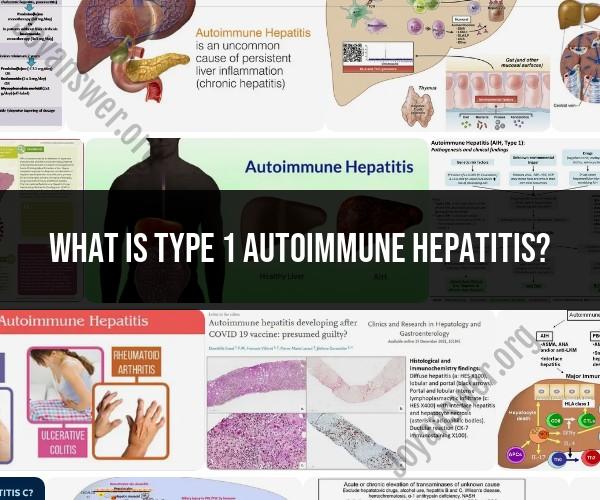
What is type 1 autoimmune hepatitis?
Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic liver disease characterized by inflammation and damage to the liver tissue due to an autoimmune response. In autoimmune hepatitis, the body's immune system mistakenly identifies the liver cells as foreign invaders and attacks them, leading to ongoing liver inflammation. Here are some key points about type 1 autoimmune hepatitis:
Autoimmune Response: In autoimmune hepatitis, the exact cause of the immune system's attack on the liver is not fully understood. It is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. Certain genetic predispositions may increase the risk of developing autoimmune hepatitis, but it often requires a trigger, such as a viral infection or exposure to certain toxins, to activate the autoimmune response.
Chronic Inflammation: The immune system's attack on the liver leads to chronic inflammation, which, if left untreated, can cause scarring of the liver tissue (fibrosis) and eventually progress to cirrhosis, a condition in which the liver becomes severely scarred and loses its ability to function properly.
Symptoms: The symptoms of type 1 autoimmune hepatitis can vary in severity and may include fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), abdominal discomfort, joint pain, itching, and flu-like symptoms. Some individuals may not experience noticeable symptoms, and the condition may be discovered through routine blood tests.
Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to assess liver function and detect specific antibodies associated with autoimmune hepatitis. A liver biopsy may also be performed to assess the extent of liver damage and confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment: The primary treatment for type 1 autoimmune hepatitis is immunosuppressive therapy. This involves medications like corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone) and immunosuppressants (e.g., azathioprine) to suppress the autoimmune response and reduce liver inflammation. Treatment aims to control the disease, prevent further liver damage, and induce remission.
Monitoring: Individuals with autoimmune hepatitis require ongoing medical monitoring and management. Blood tests and liver function tests are regularly performed to assess the response to treatment and monitor for any potential side effects of medications.
Long-Term Outlook: With appropriate treatment and monitoring, many individuals with type 1 autoimmune hepatitis can achieve remission and maintain stable liver function. However, the condition is typically lifelong, and relapses can occur. In severe cases, or if the disease progresses to advanced cirrhosis, a liver transplant may be considered.
It's essential for individuals diagnosed with autoimmune hepatitis to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan and receive regular follow-up care. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for managing the condition effectively and preserving liver health.
Autoimmune Hepatitis Type 1: Understanding the Disease and Its Impact
Autoimmune hepatitis type 1 (AIH-1) is a chronic liver disease that occurs when the body's immune system attacks the liver cells. This can cause inflammation and damage to the liver. AIH-1 is the most common type of autoimmune hepatitis, accounting for about 80% of cases.
The exact cause of AIH-1 is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. AIH-1 can occur at any age, but it is most common in young women.
The impact of AIH-1 can vary from person to person. Some people may have only mild symptoms, while others may develop severe liver damage. In severe cases, AIH-1 can lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and even death.
A Closer Look at Type 1 Autoimmune Hepatitis: Symptoms and Diagnosis
The most common symptoms of AIH-1 include:
- Fatigue
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Dark-colored urine
- Light-colored stools
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Itching
- Joint pain
- Rash
In some cases, AIH-1 may not cause any symptoms, and it may only be diagnosed during a routine blood test.
To diagnose AIH-1, doctors will typically perform a blood test to look for elevated liver enzymes and antibodies. They may also order an imaging test, such as an ultrasound or biopsy, to get a better look at the liver.
Managing Type 1 Autoimmune Hepatitis: Treatment and Lifestyle
The goal of treatment for AIH-1 is to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation in the liver. The most common treatment for AIH-1 is a medication called prednisone. Other medications, such as azathioprine and mycophenolate, may also be used.
In some cases, a liver transplant may be necessary if the liver damage is severe.
In addition to medication, there are a number of lifestyle changes that people with AIH-1 can make to manage their condition. These changes include:
- Eating a healthy diet
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding alcohol
- Exercising regularly
- Getting regular checkups from a doctor
By following their treatment plan and making healthy lifestyle changes, people with AIH-1 can often live long and healthy lives.