What is the hierarchy of Management?
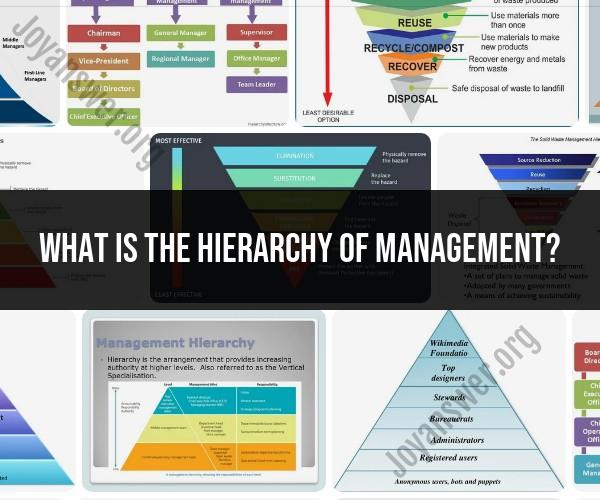
The hierarchy of management refers to the levels of authority and responsibility within an organization, typically arranged in a pyramid-like structure. Each level has a specific role and set of responsibilities, and individuals at different levels of the hierarchy are accountable for different aspects of the organization's operations. The specific names and number of management levels can vary depending on the organization's size, industry, and structure, but the following is a common representation of the hierarchy of management:
Top-Level Management (Strategic Management):
- Board of Directors: The highest level of authority in a corporation, responsible for setting the organization's overall strategic direction, making major decisions, and representing the interests of shareholders.
- CEO (Chief Executive Officer): The top executive responsible for the overall management of the organization, making strategic decisions, and overseeing other top-level executives.
Senior Management (Tactical Management):
- C-Suite Executives: These are top executives who oversee specific functional areas of the organization, such as the Chief Financial Officer (CFO), Chief Operating Officer (COO), Chief Marketing Officer (CMO), Chief Technology Officer (CTO), etc. They play a key role in implementing the strategic decisions made by the top-level management.
- Vice Presidents (VPs): These executives are responsible for specific departments or divisions within the organization, such as HR, Sales, Marketing, or Operations. They report to the C-Suite executives.
Middle Management (Operational Management):
- Department Managers: Responsible for the day-to-day operations of specific departments within the organization, such as Production Manager, Marketing Manager, or HR Manager.
- Team Leaders or Supervisors: They oversee teams or groups of employees within their respective departments, ensuring that tasks are carried out efficiently and effectively.
Frontline Management (Supervisory Management):
- Supervisors or Team Leaders: These are typically the first-level managers responsible for directly managing the work of front-line employees.
- Frontline Employees: These are the employees who directly produce goods or deliver services to customers. They may include workers, customer service representatives, salespeople, and others who perform the core tasks of the organization.
The hierarchy of management serves to provide a clear chain of command, facilitate communication and decision-making, allocate responsibilities, and ensure that the organization's goals and strategies are effectively implemented throughout the organization. It's important to note that in some organizations, particularly in flatter structures or startups, the hierarchy may be less pronounced, and individuals may have broader and more cross-functional roles.
The Leadership Ladder: Understanding the Hierarchy of Management
The leadership ladder, also known as the management hierarchy, is the organizational structure of a business or organization. It shows the different levels of management and how they relate to each other. The higher up the ladder, the more authority and responsibility a manager has.
There are three main levels of management:
- Top-level management: This is the highest level of management and consists of the CEO, CFO, COO, and other senior executives. They are responsible for setting the overall direction of the organization and making long-term decisions.
- Middle-level management: This level of management is responsible for implementing the plans and policies set by top-level management. They also oversee the work of lower-level managers.
- Lower-level management: This is the lowest level of management and consists of supervisors and foremen. They are responsible for the day-to-day operations of the organization and supervising the work of non-management employees.
Organizational Authority: Exploring the Levels in Management Hierarchy
Organizational authority is the power that managers have to make decisions and give orders. It flows from top to bottom in the management hierarchy. Top-level managers have the most authority, while lower-level managers have the least.
Managers at all levels of the hierarchy have different responsibilities. Top-level managers are responsible for setting the overall direction of the organization, while middle-level managers are responsible for implementing those plans. Lower-level managers are responsible for the day-to-day operations of the organization and supervising the work of non-management employees.
Climbing the Management Hierarchy: Roles and Responsibilities
As managers climb the management hierarchy, their roles and responsibilities change. Top-level managers are more focused on strategic planning and decision-making, while lower-level managers are more focused on operational tasks and supervising the work of others.
Here is a more detailed overview of the roles and responsibilities of each level of management:
Top-level management:
- Set the overall vision and strategy for the organization
- Make long-term decisions about resource allocation, product development, and market expansion
- Represent the organization to the public and to investors
- Oversee the performance of middle-level managers
Middle-level management:
- Implement the plans and policies set by top-level management
- Develop and manage budgets
- Oversee the work of lower-level managers
- Serve as a liaison between top-level management and lower-level management
Lower-level management:
- Supervise the work of non-management employees
- Ensure that employees are meeting their goals and objectives
- Train and develop employees
- Identify and resolve employee problems
Managers at all levels of the hierarchy play an important role in the success of an organization. By understanding the different levels of management and the roles and responsibilities of each level, managers can be more effective in their jobs and help their organizations to achieve their goals.