What is the difference in the treatment between a STEMI and NSTEMI?
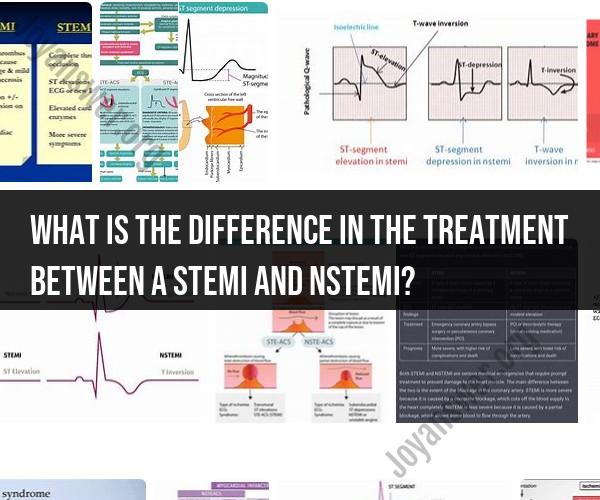
STEMI (ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction) and NSTEMI (non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction) are both types of heart attacks, but they have differences in their treatment approaches due to variations in their clinical presentation and severity. Here's an overview of the key differences in treatment:
Treatment for STEMI (ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction):
Immediate Reperfusion Therapy: STEMI is considered a medical emergency, and the primary goal is to quickly restore blood flow to the blocked coronary artery. This is typically done using one of the following methods:
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): Also known as angioplasty and stent placement, PCI involves threading a catheter with a balloon and stent into the blocked artery to open it up and keep it open.
- Thrombolytic Therapy: If PCI is not available or cannot be performed promptly, thrombolytic drugs (clot-busting drugs) may be administered intravenously to dissolve the blood clot in the coronary artery.
Antiplatelet and Anticoagulant Medications: Patients with STEMI are given medications to prevent further blood clotting and reduce the risk of complications. This includes drugs like aspirin, clopidogrel, and heparin.
Pain Management: Pain relief, typically with nitroglycerin and/or opioids, is provided to alleviate chest pain and discomfort.
Monitoring and Observation: After reperfusion therapy, patients with STEMI are closely monitored in the hospital's coronary care unit (CCU) or intensive care unit (ICU) to assess their cardiac function and watch for potential complications.
Treatment for NSTEMI (Non-ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction):
Risk Stratification: NSTEMI patients are evaluated to assess their risk of further cardiac events. This often involves the use of various clinical and diagnostic tools, including cardiac biomarkers, electrocardiograms (ECGs), and clinical assessment.
Medication Management: Medications are a key component of NSTEMI treatment. Common medications include:
- Antiplatelet Medications: Aspirin and other antiplatelet drugs are given to reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Anticoagulant Medications: Drugs like heparin or low molecular weight heparin are used to prevent further clotting.
- Pain Relief: Nitroglycerin or other pain relievers may be administered for chest pain relief.
- Beta-Blockers: These medications can help reduce the workload on the heart.
- Statins: Cholesterol-lowering drugs like statins may be prescribed to manage risk factors.
Cardiac Catheterization: Depending on the patient's clinical status and risk factors, cardiac catheterization (angiography) may be performed to assess the extent and location of coronary artery disease. If significant blockages are identified, PCI or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) may be considered.
Lifestyle and Risk Factor Management: Patients with NSTEMI are often advised to make lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing risk factors like hypertension and diabetes.
The treatment approach for both STEMI and NSTEMI is focused on reducing myocardial damage, preventing complications, and improving long-term outcomes. The key difference lies in the urgency and method of reperfusion therapy, with STEMI requiring more immediate intervention due to the characteristic ST-segment elevation on the ECG, indicating complete coronary artery occlusion. NSTEMI patients receive a more comprehensive evaluation to determine the best course of action based on their individual risk profile.
STEMI vs. NSTEMI: Differences in Heart Attack Treatment
STEMI and NSTEMI are two types of heart attacks, both caused by a blockage in a coronary artery. However, they differ in the severity of the blockage and the resulting damage to the heart muscle.
STEMI stands for ST-elevation myocardial infarction. It is a more severe type of heart attack that occurs when a complete blockage in a coronary artery prevents blood flow to a portion of the heart muscle. This causes the heart muscle to die, resulting in permanent damage.
NSTEMI stands for non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction. It is a less severe type of heart attack that occurs when a partial blockage in a coronary artery reduces blood flow to the heart muscle. This can cause damage to the heart muscle, but it is usually not as severe as the damage caused by a STEMI.
The main difference in treatment between STEMI and NSTEMI is that STEMI patients need immediate medical attention to restore blood flow to the heart muscle. This can be done with a procedure called angioplasty and stenting, in which a thin tube with a balloon on the end is inserted into the blocked artery and inflated to open it. A stent, a small metal mesh tube, is then placed in the artery to keep it open.
NSTEMI patients may also need angioplasty and stenting, but they may be able to wait a few days or weeks before the procedure. In the meantime, they will be treated with medications to prevent blood clots and reduce the workload on the heart.
In addition to angioplasty and stenting, both STEMI and NSTEMI patients may be treated with the following medications:
- Anticoagulants: These medications prevent blood clots from forming.
- Antiplatelet agents: These medications thin the blood and make it less likely to clot.
- Beta-blockers: These medications slow down the heart rate and reduce the workload on the heart.
- Statins: These medications lower cholesterol levels.
Cardiac Care: Distinct Approaches for STEMI and NSTEMI Patients
The distinct approaches to cardiac care for STEMI and NSTEMI patients reflect the different underlying causes of these two types of heart attacks.
STEMI is caused by a complete blockage in a coronary artery, which is usually caused by a blood clot. The blood clot can form around a plaque buildup in the artery. Plaque is a fatty substance that can accumulate in the arteries over time.
NSTEMI is caused by a partial blockage in a coronary artery, which is usually caused by inflammation. Inflammation can damage the lining of the artery and make it more likely to form a blood clot.
The different underlying causes of STEMI and NSTEMI lead to different approaches to cardiac care.
STEMI patients need immediate medical attention to restore blood flow to the heart muscle. This is because the heart muscle is dying without oxygen. If the blockage is not opened within a few hours, the patient may suffer permanent heart damage or even death.
NSTEMI patients may not need immediate medical attention, but they do need close monitoring. This is because they are at risk for developing a STEMI if the partial blockage in their coronary artery becomes complete.
Managing Heart Attacks: Tailoring Treatment to STEMI and NSTEMI Cases
The management of heart attacks is tailored to the individual needs of each patient. However, there are some general principles that apply to both STEMI and NSTEMI patients.
All heart attack patients should be hospitalized for observation and treatment. They should also be monitored for complications, such as arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) and heart failure.
STEMI patients are typically admitted to the coronary care unit (CCU), where they can be closely monitored and treated. NSTEMI patients may be admitted to the CCU or to a regular hospital ward.
The goals of treatment for both STEMI and NSTEMI patients are to:
- Restore blood flow to the heart muscle
- Prevent further damage to the heart muscle
- Reduce the risk of future heart attacks and strokes
Treatment for STEMI and NSTEMI patients may include:
- Medications: Medications are used to prevent blood clots, reduce the workload on the heart, and control blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Angioplasty and stenting: Angioplasty and stenting is a minimally invasive procedure that is used to open blocked arteries.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG): CABG surgery is a more invasive procedure that is used to bypass blocked arteries.
The best treatment for a heart attack depends on the individual patient's needs and circumstances.