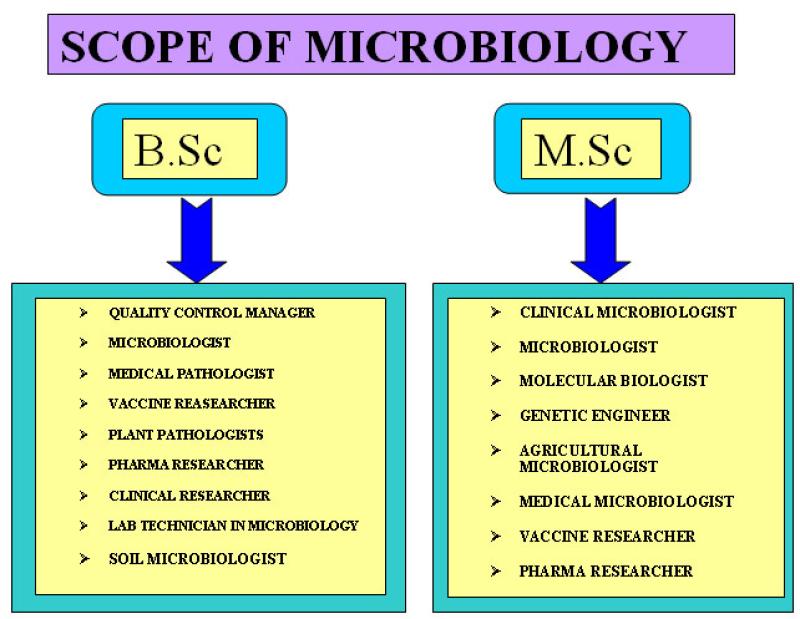
Is microbiology a medical course?
Microbiology is not exclusively a medical course, but it is a foundational and integral component of many medical and healthcare-related disciplines. Microbiology is a scientific field that encompasses the study of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and algae. While microbiology itself is a broader discipline, its applications in medicine are significant and far-reaching.
Here are some ways in which microbiology is applied in the medical field:
Medical Microbiology: This is a specialized branch of microbiology that specifically focuses on microorganisms that cause human diseases. Medical microbiologists study the characteristics, identification, and mechanisms of pathogenic microorganisms. They play a crucial role in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of infectious diseases.
Immunology: Immunology, a branch of microbiology, is dedicated to the study of the immune system. Immunologists investigate how the immune system responds to infections, the development of vaccines, and the understanding of autoimmune diseases.
Clinical Microbiology: Clinical microbiologists work in clinical laboratories where they analyze patient samples (such as blood, urine, and swabs) to identify and characterize microorganisms causing infections. This information is crucial for physicians to prescribe appropriate treatments.
Infectious Diseases: Microbiology is fundamental to the study of infectious diseases. Researchers in this field work on understanding the epidemiology, transmission, and control of infectious agents. They also contribute to the development of antimicrobial drugs.
Epidemiology: Microbiologists, particularly in the field of epidemiology, study the distribution and determinants of diseases in populations. They play a crucial role in tracking and controlling outbreaks of infectious diseases.
Virology: Virologists study viruses and their impact on human health. This includes researching viral diseases, developing vaccines, and understanding the molecular mechanisms of viral infections.
Antimicrobial Resistance Research: Microbiologists contribute significantly to the study of antimicrobial resistance, helping to identify mechanisms by which bacteria and other pathogens develop resistance to antibiotics and other drugs.
Public Health Microbiology: Microbiology plays a vital role in public health, including surveillance of infectious diseases, development of vaccination strategies, and implementation of control measures to protect communities.
While microbiology is not exclusively a medical course, many universities offer microbiology programs with specializations or concentrations in medical microbiology. Students interested in pursuing careers in medicine, public health, or healthcare often take microbiology courses as part of their education to gain a better understanding of the role microorganisms play in health and disease. Additionally, microbiologists contribute valuable knowledge and expertise to medical research, drug development, and public health initiatives.
1. Is Microbiology Solely Medical-Focused?
No, microbiology is not solely a medical-focused course. While medical applications are prominent and vital, the field of microbiology encompasses a much broader scope. It delves into the vast world of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and algae, exploring their diversity, structure, function, interactions with the environment, and their roles in various aspects of life.
2. Extending Beyond Medical Studies
Here are some ways microbiology extends beyond medical studies:
- Environment: Microbes play essential roles in nutrient cycling, decomposition, bioremediation, and maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Understanding these processes is crucial for environmental sustainability and addressing issues like climate change and pollution.
- Agriculture: Microbes contribute to soil fertility, plant growth, and disease control. Applying microbiological knowledge helps improve agricultural practices, increase crop yields, and reduce reliance on chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
- Food Science: Microbes are involved in food fermentation, preservation, and spoilage. Understanding their activity allows for developing safe and nutritious food products, extending shelf life, and preventing foodborne illnesses.
- Industrial Applications: Microbes are utilized in various industrial processes like biofuel production, bioremediation, wastewater treatment, and the manufacture of chemicals, enzymes, and other products.
- Biotechnology: Microorganisms are vital tools in genetic engineering, protein production, drug development, and the creation of new technologies for various sectors.
- Energy Production: Studying microbial metabolism and biofuels holds promise for developing alternative and sustainable energy sources.
- Forensic Science: Microbiological analysis plays a crucial role in criminal investigations by analyzing DNA evidence and identifying the presence or absence of specific microorganisms in crime scenes.
3. Industries and Fields Benefiting from Microbiology
Here are some industries and fields that benefit from knowledge in microbiology:
- Agriculture: Crop production, soil management, disease control, and biofertilizers.
- Food and beverage industry: Food safety, fermentation processes, spoilage prevention, and development of novel foods.
- Pharmaceutical industry: Drug discovery, antibiotic development, vaccine production, and biopharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Environmental sector: Bioremediation, wastewater treatment, pollution control, and waste management.
- Energy industry: Biofuel production, renewable energy sources, and bioremediation of contaminated sites.
- Biotechnology and bioengineering: Genetic engineering, protein production, biomaterials development, and synthetic biology.
- Forensic science: DNA analysis, criminal investigations, and identification of microorganisms.
- Cosmetics and personal care industry: Microbial fermentation for cosmetic ingredients, probiotic products, and antimicrobial applications.
- Textile industry: Enzyme-based biofinishing of textiles, bio-based fibers, and microbial production of dyes.
- Mining and metals industry: Bioleaching of metals, microbial enhanced oil recovery, and bioremediation of mining wastes.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of microbiology beyond medical studies. The field continues to expand and evolve, offering promising solutions to various challenges in different sectors.