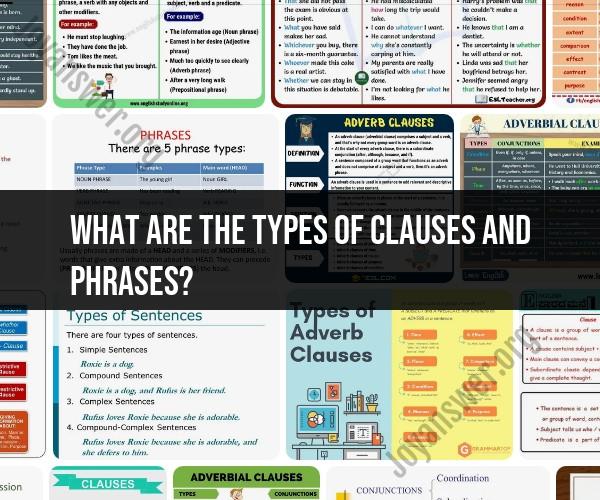
What are the types of clauses and phrases?
In grammar, clauses and phrases are essential components that make up sentences. They serve different functions and contribute to the structure of a sentence. Here are the main types of clauses and phrases:
Clauses:
Independent Clause:
- An independent clause (also known as a main clause) is a group of words that forms a complete thought and can stand alone as a sentence.
- Example: "She went to the store."
- An independent clause (also known as a main clause) is a group of words that forms a complete thought and can stand alone as a sentence.
Dependent Clause:
- A dependent clause (also known as a subordinate clause) is a group of words that does not express a complete thought and cannot stand alone as a sentence. It relies on an independent clause to make sense.
- Example: "Although she was tired," (This clause is dependent and needs more information to complete the thought.)
- A dependent clause (also known as a subordinate clause) is a group of words that does not express a complete thought and cannot stand alone as a sentence. It relies on an independent clause to make sense.
Adjective Clause:
- An adjective clause is a dependent clause that functions as an adjective in a sentence, providing more information about a noun.
- Example: "The book that she recommended is excellent."
- An adjective clause is a dependent clause that functions as an adjective in a sentence, providing more information about a noun.
Adverbial Clause:
- An adverbial clause is a dependent clause that functions as an adverb in a sentence, providing information about the verb, adjective, or adverb.
- Example: "After she finished her homework, she went to bed."
- An adverbial clause is a dependent clause that functions as an adverb in a sentence, providing information about the verb, adjective, or adverb.
Phrases:
Noun Phrase:
- A noun phrase is a group of words centered around a noun, which may include modifiers and determiners.
- Example: "The big, red apple on the table."
- A noun phrase is a group of words centered around a noun, which may include modifiers and determiners.
Verb Phrase:
- A verb phrase consists of a main verb and its auxiliary (helping) verbs, if any.
- Example: "She has been studying for hours."
- A verb phrase consists of a main verb and its auxiliary (helping) verbs, if any.
Adjective Phrase:
- An adjective phrase is a group of words centered around an adjective, providing more information about a noun.
- Example: "The weather was very cold."
- An adjective phrase is a group of words centered around an adjective, providing more information about a noun.
Adverb Phrase:
- An adverb phrase is a group of words centered around an adverb, providing more information about a verb, adjective, or other adverbs.
- Example: "He ran extremely quickly."
- An adverb phrase is a group of words centered around an adverb, providing more information about a verb, adjective, or other adverbs.
Prepositional Phrase:
- A prepositional phrase consists of a preposition, its object (usually a noun or pronoun), and any modifiers.
- Example: "In the morning, she goes for a run."
- A prepositional phrase consists of a preposition, its object (usually a noun or pronoun), and any modifiers.
Infinitive Phrase:
- An infinitive phrase consists of an infinitive verb (to + base form of the verb) along with any accompanying modifiers or objects.
- Example: "To learn a new language is my goal."
- An infinitive phrase consists of an infinitive verb (to + base form of the verb) along with any accompanying modifiers or objects.
Gerund Phrase:
- A gerund phrase consists of a gerund (an -ing form of a verb) along with any accompanying modifiers or objects.
- Example: "Swimming in the pool is her favorite activity."
- A gerund phrase consists of a gerund (an -ing form of a verb) along with any accompanying modifiers or objects.
Understanding the distinctions between these types of clauses and phrases is crucial for constructing clear and grammatically correct sentences. It allows for more effective communication and writing.
Delving into the world of clauses and phrases is like exploring the building blocks of language. Let's unlock their secrets and understand how they shape meaning and expression:
1. Types of Clauses and Phrases:
Clauses:
- Independent Clauses: Can stand alone as complete sentences with a subject and verb (e.g., "The sun shines.").
- Dependent Clauses: Need to be attached to an independent clause to make complete sense (e.g., "Although it rained, they enjoyed the picnic.").
- Noun Clauses: Act as nouns within a sentence (e.g., "What I want most is a good book.").
- Adjective Clauses: Modify nouns or pronouns (e.g., "The book I recommended was fascinating.").
- Adverb Clauses: Modify verbs or other adverbs (e.g., "She studied diligently after she heard the news.").
Phrases:
- Noun Phrases: Function as a noun within a sentence (e.g., "The red balloon soared high.").
- Verb Phrases: Contain a verb and any modifiers (e.g., "She will have walked for miles by sunset.").
- Adjective Phrases: Modify nouns or pronouns (e.g., "A house decorated with flowers stands on the hill.").
- Adverb Phrases: Modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs (e.g., "She spoke confidently in front of the crowd.").
- Prepositional Phrases: Begin with a preposition and modify nouns, pronouns, or verbs (e.g., "The cat leaped on top of the table.").
2. Sentence Structure and Meaning:
- Clauses and phrases form the skeletal structure of sentences, determining their flow and emphasis.
- Independent clauses express complete ideas, while dependent clauses add depth and detail.
- Different types of clauses and phrases introduce nuance, create suspense, and guide the reader's understanding.
3. Categories and Classifications:
- Clauses are further classified based on the type of verb they contain (e.g., main clauses, subordinate clauses).
- Phrases are categorized by their function and grammatical structure (e.g., infinitive phrases, participial phrases).
- Understanding these categories helps with proper sentence construction and analysis.
4. Clarity and Expressiveness:
- Mastering clauses and phrases allows for precise and vivid communication.
- Varying clause and phrase lengths adds rhythm and interest to writing.
- Using specific types of clauses and phrases can create different tones and emotions (e.g., using complex sentences for formality, using simpler phrases for informality).
5. Identifying and Using Clauses and Phrases:
- Actively reading and analyzing different texts can help identify and understand different types of clauses and phrases.
- Using online resources and grammar guides can provide additional explanation and examples.
- Pay attention to sentence structure, word order, and punctuation clues to differentiate clauses and phrases.
- Practice incorporating different types of clauses and phrases in your own writing to enhance clarity and expressiveness.
Remember, clauses and phrases are not just grammatical terms; they are the tools that allow us to build intricate and meaningful language structures. By understanding their various forms and functions, you can unlock the power to craft expressive and impactful communication in both written and spoken word. So, explore, experiment, and let your sentences sparkle with the diverse tapestry of clauses and phrases!