What were the 13 colonies of America?
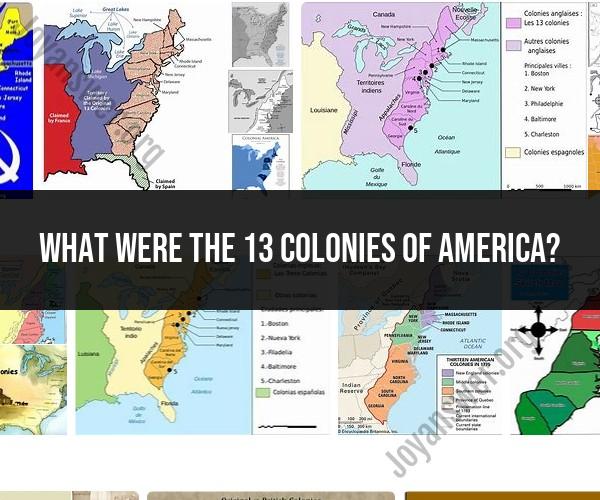
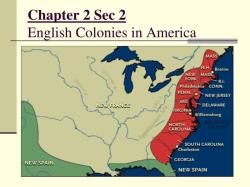
The 13 Colonies were a group of British colonies on the eastern coast of North America that eventually formed the basis for the original United States of America. They were established over a period of about 150 years, starting in the early 17th century and leading up to the American Revolution. Here is a list of the 13 original colonies, along with their founding dates:
1. Virginia (1607):
- Jamestown, Virginia, was the first permanent English colony in North America, founded by the Virginia Company.
2. Massachusetts (1620):
- The Plymouth Colony was founded by the Pilgrims aboard the Mayflower in 1620. The Massachusetts Bay Colony, including settlements like Salem and Boston, was established in 1630.
3. New Hampshire (1623):
- New Hampshire was settled in 1623 by English fishermen and became a royal colony in 1679.
4. Maryland (1634):
- Maryland was founded in 1634 by Lord Baltimore as a haven for Catholics seeking religious freedom.
5. Connecticut (1636):
- The Connecticut Colony was established in 1636 by Thomas Hooker and others, with settlements in Hartford, Windsor, and Wethersfield.
6. Rhode Island (1636):
- Roger Williams founded the colony of Rhode Island in 1636 as a place of religious tolerance and separation of church and state.
7. Delaware (1638):
- The first European settlement in Delaware was established by the Swedes and Finns in 1638. Later, it was taken over by the Dutch and then the English.
8. North Carolina (1653):
- The first permanent English settlement in North Carolina was established in the 1650s, and it later became a royal colony.
9. South Carolina (1670):
- The English established the colony of South Carolina in 1670, primarily for economic reasons.
10. New York (1664):- New York was originally settled by the Dutch in 1624 as New Amsterdam but was captured by the English in 1664 and renamed New York.
11. New Jersey (1664):- The English acquired New Jersey from the Dutch in 1664. It was initially divided into East Jersey and West Jersey.
12. Pennsylvania (1682):- Pennsylvania was founded by William Penn in 1682 as a Quaker colony, known for its religious tolerance.
13. Georgia (1733):- The last of the 13 colonies, Georgia, was founded in 1733 by James Oglethorpe as a haven for debtors and a buffer against Spanish Florida.
These 13 colonies played a significant role in the early history of the United States and were the primary participants in the American Revolution against British rule, which ultimately led to the founding of the United States in 1776.
The 13 Original Colonies That Formed the United States
The 13 original colonies that formed the United States are:
- New Hampshire
- Massachusetts Bay
- Rhode Island and Providence Plantations
- Connecticut
- New York
- New Jersey
- Pennsylvania
- Delaware
- Maryland
- Virginia
- North Carolina
- South Carolina
- Georgia
Regional Differences Among the First 13 Colonies
The 13 original colonies can be divided into three main regions:
- New England colonies: The New England colonies were located in the northeastern part of North America. They were founded by Puritans and other religious dissenters who were seeking religious freedom. The New England colonies were characterized by a strong emphasis on education and religion.
- Middle colonies: The Middle colonies were located in the middle part of North America. They were founded by a variety of European groups, including Dutch, English, and Swedes. The Middle colonies were characterized by a diverse population and a thriving economy.
- Southern colonies: The Southern colonies were located in the southeastern part of North America. They were founded by English settlers who were seeking economic opportunity. The Southern colonies were characterized by a plantation economy and a reliance on slave labor.
Events Leading to American Independence from Britain
There were a number of events that led to American independence from Britain. Some of the most important events include:
- The French and Indian War (1754-1763): The French and Indian War was a major conflict between Britain and France for control of North America. The war ended with a British victory, but it also left Britain heavily in debt. To help pay off its debt, Britain began to impose new taxes on the American colonists.
- The Stamp Act (1765): The Stamp Act was a tax on all printed materials in the American colonies. The colonists were outraged by the Stamp Act, and they protested against it. The Stamp Act was eventually repealed, but it set a precedent for future taxes on the colonies.
- The Boston Tea Party (1773): In protest of a new tax on tea, a group of colonists disguised as Native Americans boarded British ships in Boston Harbor and dumped the tea into the water. The Boston Tea Party was a major escalation of the conflict between the colonists and Britain.
- The First Continental Congress (1774): The First Continental Congress was a meeting of representatives from the American colonies. The Congress met to discuss the conflict with Britain and to coordinate their response.
- The Second Continental Congress (1775): The Second Continental Congress met after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress declared independence from Britain on July 4, 1776.
The American Revolutionary War ended with a British defeat in 1783. The United States of America was officially recognized as an independent nation in the Treaty of Paris.