How did Ethiopia become a center of Christianity?
Ethiopia's role as a center of Christianity has deep historical roots and is closely tied to the ancient Kingdom of Aksum. The adoption of Christianity in Ethiopia is traditionally associated with several key events and historical figures:
Queen of Sheba and King Solomon:
- According to Ethiopian tradition and biblical accounts, the Queen of Sheba (sometimes identified with Makeda) visited King Solomon in Jerusalem. The two are said to have had a son named Menelik I. Legend holds that Menelik I later visited his father in Jerusalem, where he received the Ark of the Covenant and brought it back to Ethiopia.
The Ark of the Covenant in Aksum:
- The presence of the Ark of the Covenant, Ethiopia's most sacred religious relic, is an integral part of Ethiopian Christian tradition. Legend suggests that it was brought to Aksum by Menelik I and has been housed in the Church of St. Mary of Zion.
St. Frumentius and the Nine Saints:
During the 4th century CE, St. Frumentius, a Christian from the Eastern Roman Empire, arrived in Aksum. He played a crucial role in the conversion of the Aksumite kingdom to Christianity. After the ruler's death, Frumentius acted as a regent for the young heir, Ezana, and continued to spread Christianity.
Around the same time, a group of Christian missionaries, often referred to as the Nine Saints, arrived in Aksum and further contributed to the establishment and growth of the Christian faith.
King Ezana's Conversion:
- King Ezana of Aksum, who ruled in the 4th century, is credited with officially adopting Christianity as the state religion. The conversion of Ezana played a pivotal role in the establishment of Christianity as a dominant force in the kingdom.
The Aksumite Church:
- The Aksumite Church, later known as the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church, emerged as a distinct Christian tradition. It developed its own liturgy and practices, and its leaders played a central role in both religious and political matters.
Axum as a Christian Center:
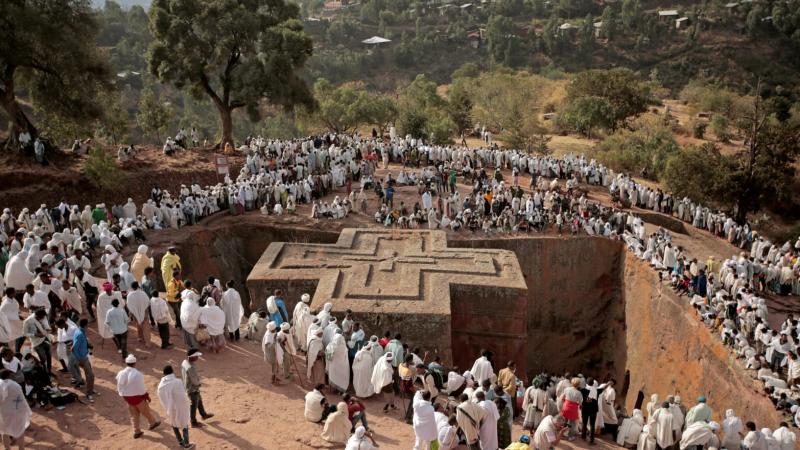
- Axum, the capital of the Aksumite Kingdom, became a significant center of Christianity in the region. The city's obelisks and rock-hewn churches, such as those in Lalibela, are enduring symbols of Ethiopia's Christian heritage.
Continuity of Christianity:
- Despite various challenges, including the rise and fall of different dynasties and external pressures, Christianity remained a central and enduring aspect of Ethiopian culture and identity.
The adoption of Christianity in Ethiopia reflects a combination of local traditions, biblical narratives, and the influence of early Christian missionaries. The history of Christianity in Ethiopia is integral to the country's cultural and religious identity, and it has played a significant role in shaping the nation's history and heritage.
Historical transformation: The journey of Ethiopia to a center of Christianity
Ethiopia is one of the oldest Christian countries in the world, with a history of the faith that dates back to the first century AD. The country's transformation into a center of Christianity was a complex and multifaceted process, but it was largely driven by the efforts of the Axumite Empire, which ruled over Ethiopia and much of the surrounding region from the fourth to the sixth century AD.
Axumite Empire: The foundation of Christianity in ancient Ethiopia
The Axumite Empire was a powerful and influential kingdom that played a major role in the spread of Christianity throughout Africa and the Middle East. The empire's conversion to Christianity began in the fourth century AD under the reign of King Ezana. Ezana was initially a pagan ruler, but he converted to Christianity after defeating the Meroitic Kingdom, a powerful pagan kingdom in southern Egypt.
Ezana's conversion had a profound impact on the development of Christianity in Ethiopia. The king actively promoted the new faith, building churches and monasteries throughout the empire and sending missionaries to neighboring regions. He also made Christianity the official religion of the Axumite Empire.
Religious influence: How Ethiopian Christianity shaped the region
The Axumite Empire's conversion to Christianity had a major impact on the region. Ethiopia became a center of Christian learning and scholarship, and Ethiopian missionaries played a key role in the spread of Christianity to other parts of Africa, including Nubia, Somalia, and Eritrea.
Ethiopian Christianity also developed its own unique character. The Ethiopian Church is one of the few Oriental Orthodox churches, and it has its own unique liturgy, traditions, and beliefs. The Ethiopian Church has also been a major force for cultural unity and identity in Ethiopia.
Cultural continuity: Ethiopia's enduring Christian identity
Despite the many challenges that Ethiopia has faced over the centuries, Christianity has remained a central part of the country's culture and identity. Today, over 60% of Ethiopians are Orthodox Christians. The Ethiopian Church plays a major role in Ethiopian society, and it is involved in a wide range of activities, including education, healthcare, and social welfare.
UNESCO World Heritage: Ethiopian sites preserving Christian heritage
Ethiopia is home to a number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites that preserve the country's rich Christian heritage. Some of the most notable of these sites include:
Lalibela Rock-Hewn Churches: This complex of 11 rock-hewn churches is one of the most important Christian pilgrimage sites in Ethiopia. The churches were built by King Lalibela in the 12th century AD and are considered to be among the most impressive examples of rock-cut architecture in the world.
Aksumite Obelisks: These massive obelisks were erected by the Aksumite kings in the fourth and fifth centuries AD. They are considered to be among the most important symbols of Ethiopia's ancient Christian heritage.
Fasil Ghebbi: This complex of palaces, churches, and other structures was built by the Gondarine kings in the 17th and 18th centuries AD. It is considered to be one of the best-preserved examples of medieval African architecture in the world.
These are just a few of the many Ethiopian sites that preserve the country's rich Christian heritage. Ethiopia is a fascinating country with a long and rich history, and its Christian heritage is an important part of its story.
Summary
Ethiopia's journey to a center of Christianity was a long and complex process, but it was largely driven by the efforts of the Axumite Empire. The empire's conversion to Christianity had a profound impact on the region, and Ethiopian Christianity has played a major role in shaping the country's culture and identity.