How to test a 220 volt circuit breaker?
Testing a 220-volt circuit breaker should be done with caution to ensure safety. Here are the steps to test a 220-volt circuit breaker:
Important Safety Precautions:Before you start, prioritize safety:
Turn Off Power: Ensure that the main power to the circuit breaker panel is turned off. This is essential to prevent electrical shocks or accidents.
Wear Safety Gear: Wear safety goggles and appropriate electrical safety gear to protect yourself.
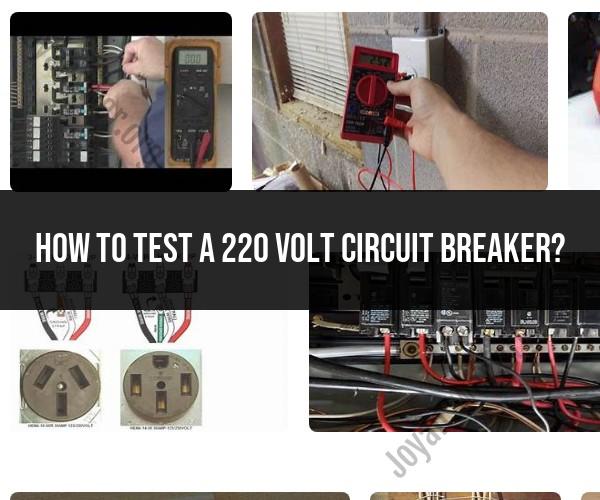
Use the Right Tools: Use a digital multimeter (DMM) or voltage tester for accurate readings.
Now, you can proceed with testing the circuit breaker:
Locate the Circuit Breaker: Identify the circuit breaker in the electrical panel that you want to test. This is the one responsible for controlling the 220-volt circuit you're interested in.
Visually Inspect: First, visually inspect the circuit breaker. Look for any signs of damage, wear, or loose wires. If you notice any issues, do not proceed with testing and consult a professional electrician for repairs.
Set Up the Multimeter:
- If you're using a digital multimeter (DMM), set it to the voltage testing mode (AC voltage).
- Choose an appropriate voltage range. For a 220-volt circuit, select a range that covers at least 220 volts.
Test for Voltage:
- Turn on the main power supply to the electrical panel.
- Carefully and with all safety precautions in mind, test for voltage by placing the DMM probes on the terminals of the circuit breaker. Place one probe on the terminal where the incoming power (hot wire) connects, and the other probe on the terminal where the outgoing power (load) connects.
- The DMM should read approximately 220 volts. If you get a voltage reading close to 0 or significantly lower than 220 volts, it may indicate a problem with the circuit breaker.
Reset the Circuit Breaker:
- If the voltage reading is low or 0, reset the circuit breaker by turning it off and then back on. Sometimes, a tripped breaker can cause a loss of voltage.
Test for Continuity (Optional):
- In some cases, you may want to test the continuity of the circuit breaker using the DMM's continuity mode. This checks if the breaker is able to conduct electricity when closed.
- With the circuit breaker in the OFF position, set the DMM to continuity mode (the symbol often looks like a sound wave).
- Place one probe on the terminal where the incoming power (hot wire) connects and the other probe on the terminal where the outgoing power (load) connects. If the circuit breaker is in good condition, you should hear a beep or see a reading indicating continuity.
Record and Document: Make a record of your test results, including voltage readings and continuity if tested. This information can be useful if you need to consult an electrician or replace the circuit breaker.
Secure the Electrical Panel: After testing, securely close and fasten the electrical panel cover to prevent unauthorized access.
If you are unsure about any aspect of testing the circuit breaker or if you encounter any irregularities during the testing process, it's strongly recommended to consult a licensed electrician. Electrical work can be dangerous, and it's essential to prioritize safety and seek professional help when needed.
Testing a 220-Volt Circuit Breaker: Step-by-Step Instructions
- Turn off the main power to the circuit breaker. This can usually be done by flipping the main breaker switch to the "OFF" position.
- Disconnect the circuit breaker from the power source. This can be done by removing the wires from the circuit breaker terminals.
- Use a multimeter to test the voltage across the circuit breaker terminals. The multimeter should be set to the AC voltage setting.
- If the voltage reading is 0, the circuit breaker is working properly. If the voltage reading is not 0, the circuit breaker is faulty and needs to be replaced.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with 220-Volt Breakers
One of the most common issues with 220-volt breakers is tripping. This can happen for a variety of reasons, such as:
- Overload: If the circuit is overloaded, the breaker will trip to prevent the circuit from overheating.
- Short circuit: If there is a short circuit on the circuit, the breaker will trip to protect the circuit from damage.
- Ground fault: If there is a ground fault on the circuit, the breaker will trip to protect the people on the circuit from electric shock.
If your 220-volt breaker is tripping, you can try the following to troubleshoot the problem:
- Check for overloads: Disconnect any unnecessary appliances or devices from the circuit. If the breaker stops tripping, then you know that the circuit is overloaded.
- Check for short circuits: If you are familiar with electrical work, you can use a multimeter to check for short circuits. If you find a short circuit, you will need to repair it before you can use the circuit again.
- Call an electrician: If you are not comfortable troubleshooting electrical problems, it is best to call an electrician.
When and How to Replace a Faulty 220-Volt Circuit Breaker
If your 220-volt circuit breaker is faulty, it is important to replace it as soon as possible. A faulty circuit breaker can be a fire hazard.
To replace a faulty 220-volt circuit breaker, you will need to:
- Turn off the main power to the circuit breaker.
- Disconnect the circuit breaker from the power source.
- Remove the old circuit breaker.
- Install the new circuit breaker.
- Connect the circuit breaker to the power source.
- Turn on the main power to the circuit breaker.
- Test the circuit breaker to make sure it is working properly.
If you are not comfortable replacing a circuit breaker yourself, it is best to call an electrician.
Safety Precautions
When working with electricity, it is important to take safety precautions. Here are some safety tips:
- Always turn off the main power to the circuit breaker before working on it.
- Use insulated tools to work on electrical circuits.
- Be aware of your surroundings and avoid working on electrical circuits near water or other conductive materials.
- If you are not comfortable working with electricity, it is best to call an electrician.