What does it mean when someone has in IEP?
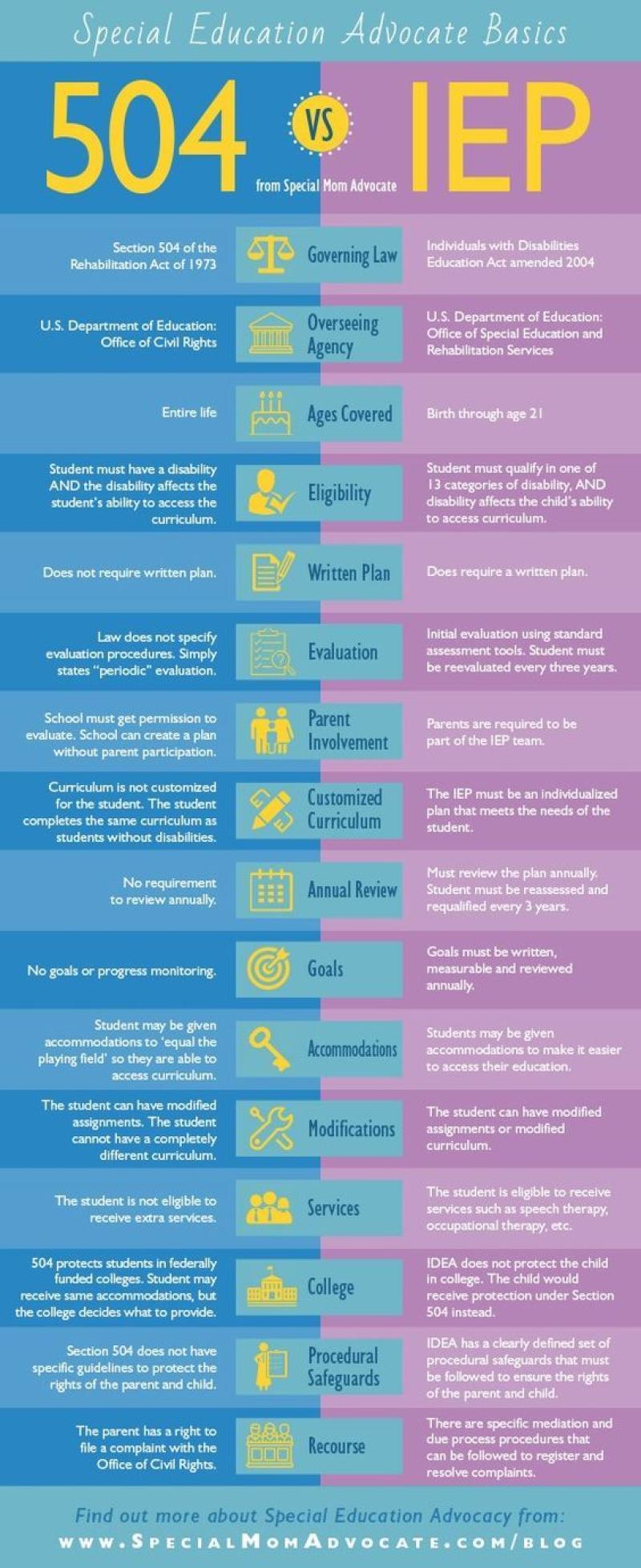
Having an Individualized Education Program (IEP) signifies that an individual, typically a student with a disability, is entitled to receive special education services tailored to their unique needs. An IEP is a legal document that outlines the educational goals, services, and accommodations designed to support the student's learning and academic success. Here are key points about the significance of having an IEP:
Personalized Education Plan:
- An IEP is highly individualized, taking into account the specific strengths, challenges, and learning styles of the student. It is developed through collaboration among educators, parents, and other relevant professionals.
Legal Entitlement:
- In the United States, the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) mandates that eligible students with disabilities are entitled to receive a free appropriate public education (FAPE). The IEP is a key component of ensuring that students receive the specialized education and services they need.
Identification of Disability:
- To qualify for an IEP, a student must have a disability that adversely affects their educational performance. The IEP identifies the specific disability or disabilities, whether it's a learning disability, speech impairment, autism spectrum disorder, or another qualifying condition.
Educational Goals and Objectives:
- The IEP includes measurable academic and functional goals that are tailored to the student's current abilities and future needs. These goals are designed to help the student make progress in the general education curriculum.
Specialized Services and Supports:
- The IEP specifies the specialized services and supports the student will receive. This may include accommodations, modifications, related services (such as speech therapy or occupational therapy), assistive technology, and more.
Regular Review and Updates:
- The IEP is a dynamic document that is reviewed and updated regularly, typically at least annually. This allows for adjustments based on the student's progress and changing needs.
Parental Involvement:
- Parents play a crucial role in the IEP process. They are involved in the development, review, and modification of the IEP. Their input is valued, and the IEP team considers their perspective when making decisions about the student's education.
Transition Planning:
- For students approaching adulthood, the IEP includes transition planning to help them prepare for post-secondary life. This may involve setting goals related to employment, further education, independent living, and community participation.
Procedural Safeguards:
- IDEA provides procedural safeguards to protect the rights of students and their parents in the IEP process. This includes the right to be informed, participate in meetings, and resolve disputes through due process if necessary.
Inclusion in General Education Settings:
- Whenever possible, the IEP aims to promote inclusion by ensuring that students with disabilities have access to and participate in the general education curriculum and activities alongside their non-disabled peers.
Having an IEP is a commitment to providing an inclusive and supportive educational environment for students with disabilities. It reflects a collaborative effort to address each student's unique needs and maximize their potential for academic and personal success.
An Individualized Education Program (IEP) is a legal document that outlines the special education services and accommodations that a student with a disability needs to succeed in school. Having an IEP signifies that the student's disability significantly impacts their ability to learn and function in a typical classroom setting. The IEP is designed to ensure that the student receives the necessary support to access the general education curriculum and make meaningful progress towards their educational goals.
Here are some of the key implications of having an IEP:
Specialized Instruction: An IEP provides the student with access to specialized instruction and teaching methods that are tailored to their specific learning needs and abilities. This may include individualized teaching strategies, modified lesson plans, or assistive technology.
Accommodations and Modifications: An IEP may include accommodations or modifications to help the student overcome barriers to learning. Accommodations provide support for the student to access the curriculum without changing the content or expectations. Modifications may involve altering the content or expectations to better suit the student's abilities.
Additional Support Services: An IEP may also include additional support services, such as speech-language therapy, occupational therapy, or physical therapy, to address specific developmental needs or impairments.
Regular Monitoring and Progress Tracking: An IEP is a dynamic document that is reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that it is meeting the student's changing needs and progress. The IEP team, including the student, parents, and educators, monitors the student's progress and makes adjustments as needed.
Access to Educational Opportunities: An IEP ensures that students with disabilities have equal access to educational opportunities and can participate fully in the learning process. It helps bridge the gap between their unique needs and the general education curriculum, promoting their academic, social, and emotional development.
In summary, having an IEP signifies that a student with a disability requires specialized instruction, accommodations, and support services to succeed in school. It is a valuable tool that ensures equitable access to education and promotes the student's overall development.