Can a Rh negative person receive Rh positive blood?
In general, an Rh-negative person can receive Rh-positive blood in a transfusion, but it is not an ideal or preferred match. The Rh factor (Rhesus factor) is one of the factors that are considered when matching blood types for transfusions, and it's important to minimize any potential adverse reactions.
Here's how Rh-negative individuals and Rh-positive blood compatibility typically work:
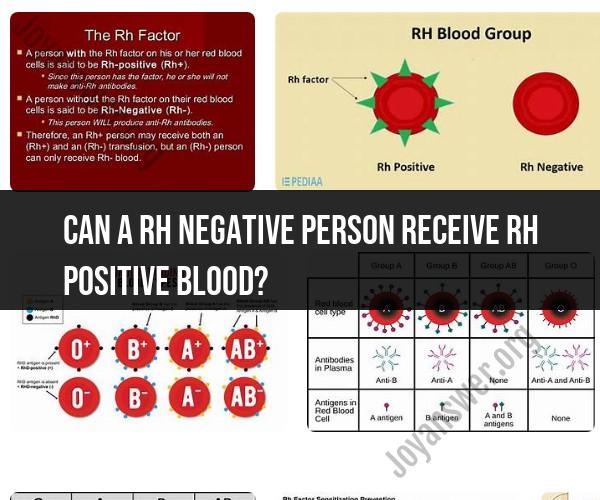
Rh Status: People can be classified as Rh-positive or Rh-negative based on the presence or absence of the Rh antigen (D antigen) on the surface of their red blood cells. Rh-positive individuals have the Rh antigen, while Rh-negative individuals do not.
Blood Transfusions: Ideally, blood transfusions should match both the ABO blood type (e.g., A, B, AB, O) and the Rh factor (positive or negative) to minimize the risk of transfusion reactions.
Rh-Negative Receivers: Rh-negative individuals can safely receive Rh-negative blood because there is no Rh antigen present to cause a reaction.
Rh-Positive Blood to Rh-Negative Receivers: While it is possible for Rh-negative individuals to receive Rh-positive blood in certain situations, it is generally avoided when Rh-negative blood is available. The reason for this is that if an Rh-negative person is exposed to Rh-positive blood, their immune system may develop antibodies against the Rh antigen. Subsequent exposures to Rh-positive blood can lead to hemolytic transfusion reactions, which can be severe and potentially life-threatening.
In emergency situations where Rh-negative blood is not readily available, healthcare providers may provide Rh-positive blood to an Rh-negative individual while closely monitoring for any adverse reactions. However, this is considered a temporary solution until Rh-negative blood can be obtained.
To minimize the risk of complications, medical professionals prioritize matching the Rh factor when selecting blood for transfusions. Rh incompatibility can also be a concern during pregnancy when an Rh-negative mother is carrying an Rh-positive fetus, which can lead to sensitization and hemolytic disease of the newborn. In such cases, preventive measures and treatment, such as Rh immunoglobulin (RhoGAM), are often used to reduce the risk of sensitization.
It's important to note that blood transfusions are typically administered under the supervision of healthcare professionals who consider the individual's specific medical history and needs to ensure safe and appropriate transfusion practices.
Rh-Negative Individuals and Rh-Positive Blood: Compatibility and Concerns
The Rh factor is a protein that can be found on the surface of red blood cells. If your blood cells have this protein, you are Rh positive. If your blood cells do not have this protein, you are Rh negative.
Rh incompatibility can occur when a pregnant woman is Rh negative and her fetus is Rh positive. This can happen if the father of the fetus is Rh positive. If the Rh factor of the mother and fetus are different, the mother's immune system may produce antibodies against the fetus's blood cells. These antibodies can cross the placenta and attack the fetus's red blood cells. This can lead to a condition called hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN).
HDN can cause a variety of health problems in the fetus, including anemia, jaundice, and brain damage. In severe cases, HDN can be fatal.
There are a number of things that can be done to prevent HDN, including:
- Administering Rho(D) immune globulin (RhIg) to Rh-negative women. RhIg is a medication that can help to prevent the mother's immune system from producing antibodies against the fetus's blood cells. RhIg is typically administered at 28 weeks of pregnancy and again after delivery if the baby is Rh positive.
- Monitoring the mother and fetus for signs of HDN. Prenatal tests, such as the Coombs test, can be used to monitor the mother's blood for antibodies against the fetus's blood cells. If antibodies are detected, the fetus can be monitored for signs of HDN, such as anemia and jaundice.
- Treating HDN if necessary. If the fetus is diagnosed with HDN, there are a number of treatments that can be used, such as blood transfusions and phototherapy.
Can Rh-Negative People Receive Rh-Positive Blood?
Rh-negative people can receive Rh-negative blood. However, they cannot receive Rh-positive blood unless they have been previously exposed to the Rh factor. If an Rh-negative person receives Rh-positive blood, their immune system will produce antibodies against the Rh factor. These antibodies can destroy Rh-positive red blood cells, which can lead to serious health problems.
Blood Type Compatibility: Understanding Rh Factors in Transfusions
Blood type compatibility is important for blood transfusions. When a person receives a blood transfusion, their blood is mixed with the blood of the donor. If the blood types are not compatible, the recipient's immune system may attack the donor's red blood cells. This can lead to a serious condition called a transfusion reaction.
The Rh factor is one of the most important factors to consider when determining blood type compatibility. Rh-negative people can only receive Rh-negative blood. Rh-positive people can receive either Rh-negative or Rh-positive blood.
In addition to the Rh factor, there are other factors to consider when determining blood type compatibility, such as the ABO blood group. The ABO blood group is the most common blood type system. There are four ABO blood groups: A, B, AB, and O.
People with the same ABO blood group are compatible with each other. For example, people with type A blood can receive blood from people with type A blood. People with type O blood are universal donors, meaning that they can donate blood to people with any ABO blood group.
If you are considering a blood transfusion, it is important to talk to your doctor about blood type compatibility. Your doctor will be able to determine the best type of blood for you to receive.