What are some examples of psychological traits?
Psychological traits refer to enduring patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that distinguish individuals from one another. These traits are relatively stable over time and across different situations. There are various models and theories that attempt to describe and categorize psychological traits. Here are examples of some commonly discussed psychological traits:
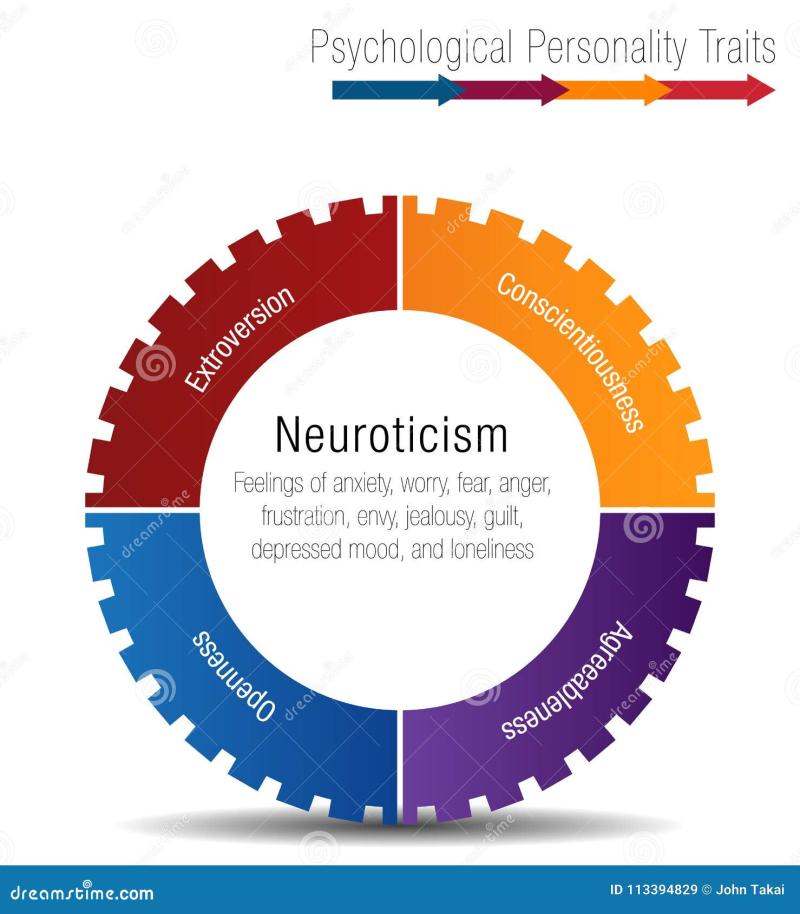
The Big Five Personality Traits:
- Openness to Experience: Reflects the degree of intellectual curiosity, creativity, and preference for novelty.
- Conscientiousness: Involves being organized, responsible, and goal-oriented.
- Extraversion: Pertains to the extent of sociability, assertiveness, and enthusiasm.
- Agreeableness: Describes one's tendency to be cooperative, empathetic, and compassionate.
- Neuroticism (Emotional Stability): Reflects the degree of emotional stability, anxiety, and moodiness.
Intelligence:
- General Cognitive Ability (G): The overall capacity to learn, reason, and solve problems.
- Verbal Intelligence: Proficiency in language-related tasks.
- Spatial Intelligence: Ability to visualize and manipulate spatial information.
- Logical-Mathematical Intelligence: Aptitude for logical reasoning and mathematical problem-solving.
Emotional Intelligence:
- Self-awareness: Understanding one's own emotions.
- Self-regulation: Managing and controlling one's emotions.
- Social Awareness: Recognizing and understanding others' emotions.
- Relationship Management: Building and maintaining healthy relationships.
Self-Esteem:
- The overall evaluation and perception an individual has about themselves.
Locus of Control:
- Internal Locus of Control: The belief that one has control over their own life and outcomes.
- External Locus of Control: The belief that external factors, like luck or fate, determine life events.
Trait Anxiety:
- The tendency to experience anxiety in different situations.
Risk-Taking Propensity:
- The degree to which an individual is willing to take risks.
Resilience:
- The ability to bounce back from adversity or cope effectively with stress.
Self-Monitoring:
- The extent to which individuals regulate their behavior based on social cues and adapt to different social situations.
Need for Achievement:
- The drive to excel and accomplish challenging goals.
Altruism:
- The tendency to selflessly help and care for others.
Sensation-Seeking:
- The pursuit of novel and intense experiences.
It's important to note that these traits are not mutually exclusive, and individuals may exhibit a combination of various traits. Additionally, psychological traits can be influenced by genetic, environmental, and cultural factors. Different psychological theories may emphasize different traits, and researchers continue to explore and refine our understanding of human personality and behavior.
Can you provide examples of psychological characteristics or traits commonly studied in psychology?
- Personality traits:
- The Big Five is a widely used model that identifies five broad traits that encompass most aspects of personality: Openness to Experience, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, and Neuroticism (OCEAN).
- Cognitive traits:
- Intelligence is a broad term that encompasses various mental abilities, including problem-solving, reasoning, learning, and memory.
- Attention refers to the ability to focus and select relevant information from the environment.
- Creativity involves the ability to generate new and original ideas.
- Decision-making is the process of selecting a course of action from among several alternatives.
- Emotional traits:
- Neuroticism is characterized by a tendency to experience negative emotions, such as anxiety, fear, and sadness.
- Extraversion is characterized by a tendency to be outgoing, sociable, and energized by social interaction.
- Agreeableness is characterized by a tendency to be cooperative, helpful, and compassionate.
- Conscientiousness is characterized by a tendency to be organized, responsible, and planful.
- Motivational traits:
- Achievement motivation refers to the desire to set and achieve challenging goals.
- Power motivation refers to the desire to have control and influence over others.
- Affiliation motivation refers to the desire to form close relationships and be accepted by others.
- Curiosity refers to the desire to explore and learn new things.
- Behavioral traits:
- Aggression refers to behavior intended to harm or injure another person.
- Altruism refers to behavior that benefits others without expectation of reward.
- Compliance refers to the tendency to follow the instructions or commands of others.
- Risk-taking refers to the tendency to engage in activities with uncertain or potentially negative outcomes.
It is important to note that these traits are not fixed and can be influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, environment, and personal experiences.