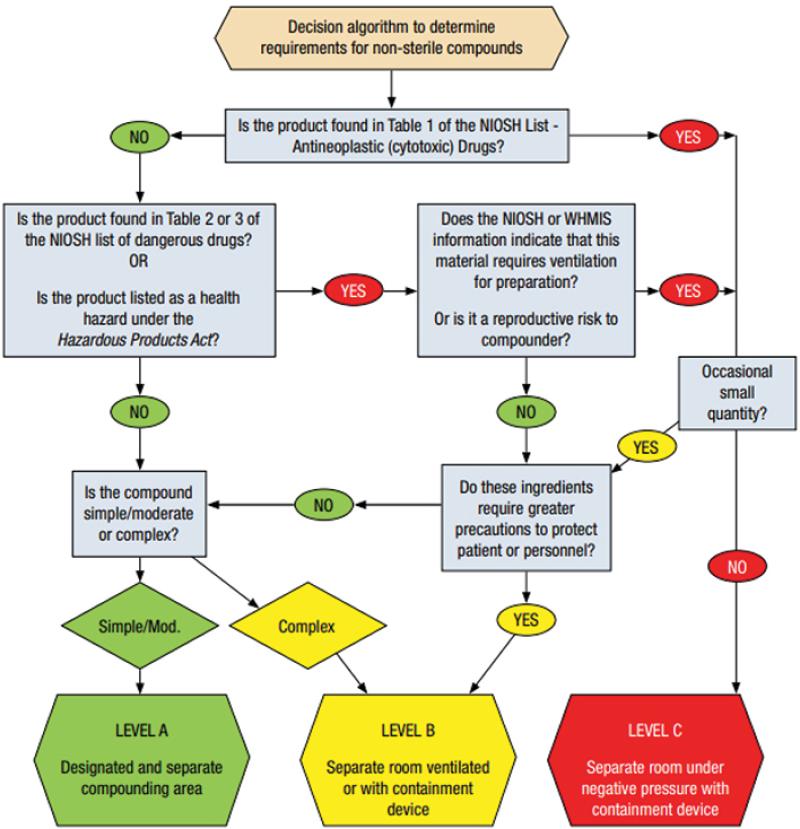
What are the policies and SOPs for non-sterile compounding?
The specific policies and standard operating procedures (SOPs) for non-sterile compounding can vary depending on the type of facility, regulatory requirements, and the nature of the compounding activities. Non-sterile compounding involves the preparation of medications that do not need to be sterile (free from microorganisms). It is important to follow established guidelines to ensure the quality, safety, and consistency of compounded products. Here are some general policies and SOPs that may be part of non-sterile compounding practices:
Facility Design and Environmental Controls:
- Establish guidelines for the design and layout of the compounding area to ensure cleanliness and minimize the risk of contamination.
- Define environmental controls, such as temperature and humidity requirements, for non-sterile compounding.
Personnel Training and Competency:
- Develop procedures for the training and ongoing competency assessment of personnel involved in non-sterile compounding.
- Specify the qualifications and responsibilities of compounding personnel.
Quality Assurance and Quality Control:
- Implement a quality assurance program to monitor and evaluate the quality of compounded products.
- Define procedures for quality control testing of raw materials and finished products.
Documentation and Record-Keeping:
- Establish documentation practices for recording all aspects of the compounding process, including formulations, calculations, and procedures.
- Maintain accurate and complete records of compounding activities, including batch records.
Formulation and Compounding Procedures:
- Develop SOPs for the formulation and compounding of non-sterile preparations, specifying ingredients, equipment, and procedures.
- Include detailed instructions for weighing, measuring, mixing, and packaging.
Labeling and Packaging:
- Define procedures for labeling compounded products, including required information such as ingredient names, strengths, and expiration dates.
- Establish packaging procedures to ensure the integrity and stability of the compounded products.
Cleaning and Sanitization:
- Develop cleaning and sanitization procedures for compounding equipment and the compounding area.
- Specify the frequency and methods for cleaning surfaces, utensils, and equipment.
Storage and Beyond-Use Dating:
- Define storage conditions for raw materials and finished compounded products.
- Determine beyond-use dates based on stability considerations and regulatory guidelines.
Adverse Event Reporting:
- Establish procedures for reporting and investigating adverse events or quality issues related to compounded products.
- Implement corrective and preventive actions based on the findings of investigations.
Regulatory Compliance:
- Ensure that all non-sterile compounding activities comply with applicable regulatory requirements, such as those set forth by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or other relevant regulatory bodies.
These policies and SOPs are intended to provide a framework for ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of non-sterile compounded products. It's essential for compounding facilities to stay informed about regulatory updates and industry best practices to continually improve and update their policies and procedures. Additionally, consultation with regulatory agencies and experts in compounding pharmacy can provide valuable guidance in developing and maintaining these policies.
Policies and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for Non-Sterile Compounding
Non-sterile compounding involves the preparation of medications outside a sterile environment. While not as stringent as sterile compounding, non-sterile compounding still requires careful procedures and adherence to specific policies and SOPs to ensure the safety and efficacy of the compounded products.
Key Policies for Non-Sterile Compounding
Personnel Requirements: Compounding personnel must have appropriate training and experience in non-sterile compounding techniques. They should be familiar with the principles of asepsis, cross-contamination prevention, and proper handling of hazardous materials.
Facility Requirements: The compounding area should be designated and maintained in a clean and organized manner. Surfaces should be non-porous, easily cleanable, and free from cracks or crevices. Proper ventilation and lighting are essential.
Equipment and Materials: Compounding equipment should be dedicated for non-sterile compounding and maintained in good working order. All materials used in compounding must be of appropriate quality and sourced from reputable suppliers.
Documentation and Recordkeeping: Detailed documentation of all compounding procedures should be maintained. This includes records of raw materials used, compounding steps, batch numbers, expiration dates, and any deviations from standard procedures.
Quality Control and Assurance: Regular quality control and assurance measures should be implemented to verify the accuracy, potency, and sterility of compounded products. This may involve testing of batches, audits of compounding procedures, and ongoing monitoring of product stability.
Protocols and Guidelines for Non-Sterile Compounding Procedures
Hand Hygiene: Proper hand hygiene is crucial to prevent contamination of the product and the compounding environment. Hand washing or alcohol-based hand sanitizers should be used before and after compounding activities.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use appropriate PPE, such as gloves, masks, and gowns, to minimize the risk of exposure to hazardous substances or potential contaminants.
Aseptic Techniques: Employ aseptic techniques to minimize the risk of introducing microorganisms into the compounded product. This includes using sterile techniques when opening vials, handling components, and transferring materials.
Cross-Contamination Prevention: Implement measures to prevent cross-contamination between different compounded products. This may involve using dedicated equipment and work surfaces for different medications, cleaning and disinfecting equipment between uses, and storing products appropriately.
Labeling and Packaging: Properly label compounded products with complete information, including the name of the medication, strength, dosage instructions, expiration date, storage instructions, and any special precautions. Use tamper-proof packaging to maintain product integrity.
Rules and Regulations Governing Non-Sterile Compounding Practices
Non-sterile compounding practices are regulated by various authorities, including:
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA): The FDA provides guidance and regulations for compounding pharmacies to ensure the safety and effectiveness of compounded products.
State Pharmacy Boards: Each state has its own pharmacy board that regulates the practice of pharmacy, including non-sterile compounding.
United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and National Formulary (NF): These compendia provide general guidance and standards for non-sterile compounding practices.
Accreditation Organizations: Organizations like the Pharmacy Compounding Accreditation Board (PCAB) provide accreditation standards for compounding pharmacies to ensure compliance with best practices.
Adherence to these policies, protocols, and regulations is essential for ensuring the safety and quality of compounded medications and protecting patient health.