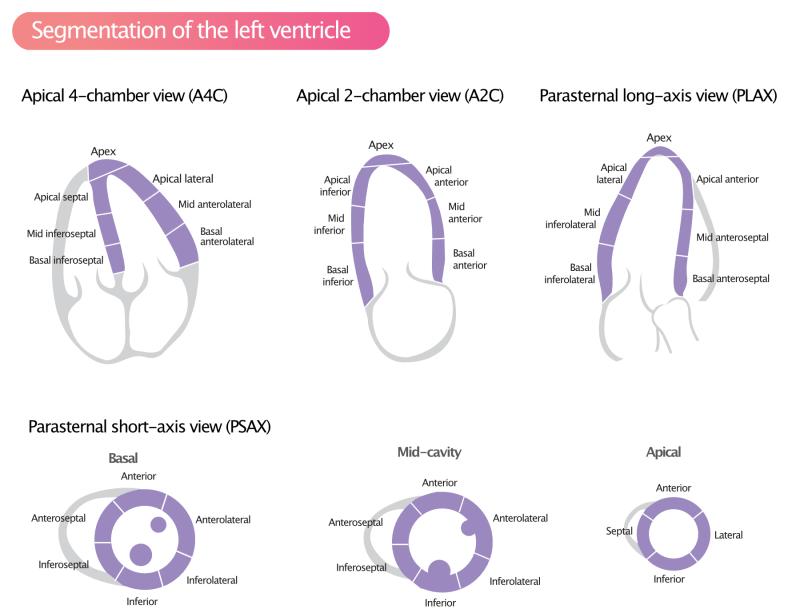
What is normal thickness of left ventricular wall?
The normal thickness of the left ventricular wall can vary depending on factors such as age, gender, and overall heart health. Generally, cardiac measurements are expressed in terms of wall thickness and chamber size. The left ventricle is a muscular chamber of the heart responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
Normal values for the thickness of the left ventricular wall can be described in terms of diastole and systole. Diastole refers to the phase when the heart is relaxed and filling with blood, while systole is the phase when the heart contracts to pump blood.
Here are approximate normal ranges for the thickness of the left ventricular wall:
End-Diastolic Thickness (EDT): This is the thickness of the left ventricular wall during diastole.
- Normal range: 0.6 to 1.1 centimeters (cm)
End-Systolic Thickness (EST): This is the thickness of the left ventricular wall during systole.
- Normal range: 1.0 to 1.5 cm
It's important to note that these are general guidelines, and individual variations can occur. Also, variations may be influenced by factors such as age, gender, body size, and ethnicity. Additionally, medical professionals often use imaging techniques like echocardiography or cardiac MRI to assess the thickness of the ventricular walls and overall heart function.
If you have specific concerns about the thickness of your left ventricular wall or if you are undergoing cardiac assessments, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized information based on your medical history, test results, and other relevant factors.
What is the typical thickness of the left ventricular wall in the heart?
The typical thickness of the left ventricular wall in the heart varies depending on the specific region of the ventricle and the measurement technique used. However, in general, the average thickness of the left ventricular wall is between 7 and 11 millimeters.
How does the thickness of the left ventricular wall affect heart function?
The thickness of the left ventricular wall plays a crucial role in the heart's ability to pump blood effectively. When the left ventricular wall is too thin, it may not be able to generate enough force to adequately pump blood throughout the body, leading to a condition called left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Conversely, when the left ventricular wall is too thick, it may become stiff and less compliant, making it difficult for the heart to fill properly with blood during diastole, a condition known as left ventricular diastolic dysfunction.
Are there medical conditions related to variations in left ventricular wall thickness?
Yes, there are several medical conditions that can affect the thickness of the left ventricular wall. These conditions include:
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM): HCM is a genetic disorder characterized by an abnormally thickened left ventricular wall.
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): LVH is a condition in which the left ventricular wall thickens due to various factors, such as high blood pressure, chronic kidney disease, or aortic valve stenosis.
Left ventricular dilation: This condition occurs when the left ventricular wall becomes stretched and enlarged, often as a result of a heart attack or other cardiac damage.
How is the thickness of the left ventricular wall measured in medical assessments?
The thickness of the left ventricular wall can be measured using various imaging techniques, including:
Echocardiography: This noninvasive ultrasound imaging method allows for detailed visualization of the heart's structures, including the thickness of the left ventricular wall.
Cardiac MRI: Cardiac MRI provides high-resolution images of the heart, enabling accurate measurements of left ventricular wall thickness.
Chest X-ray: While not as precise as echocardiography or MRI, chest X-rays can provide a general indication of left ventricular wall thickness.
Can variations in left ventricular wall thickness indicate cardiac health issues?
Yes, variations in left ventricular wall thickness can indeed indicate cardiac health issues. As mentioned earlier, abnormal wall thickness can be a sign of conditions like HCM, LVH, or left ventricular dilation, which can affect the heart's pumping function and lead to various complications if left untreated.
Monitoring left ventricular wall thickness is an important aspect of cardiac assessments, particularly for individuals with risk factors for heart disease. Early detection of abnormal wall thickness allows for timely intervention and management of underlying conditions, improving patient outcomes.