What are linguistic concepts?
Linguistic concepts are fundamental ideas and principles that form the basis of the study of language and its various components. Linguistics is the scientific study of language, and linguistic concepts help linguists, language researchers, and students understand, analyze, and describe how languages work. Here are some key linguistic concepts:
Phonetics: Phonetics is the study of the physical properties of speech sounds (phonemes) and how they are produced, transmitted, and perceived. It deals with the articulation (how sounds are produced), acoustic properties (sound waves), and auditory perception (how sounds are heard and interpreted) of speech sounds.
Phonology: Phonology focuses on the abstract, mental representations of speech sounds within a particular language or languages. It explores the sound patterns, rules, and structures that govern how sounds function in a given language. Phonology helps explain why certain sound combinations are allowed in a language while others are not.
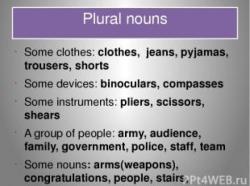
Morphology: Morphology is the study of the structure and formation of words. It deals with morphemes, which are the smallest units of meaning in language. Linguists analyze how morphemes combine to form words and how word forms can change to convey different meanings (e.g., adding "-ed" to verbs in English to indicate past tense).
Syntax: Syntax is the study of sentence structure and how words are combined to form grammatical sentences. It explores the rules governing word order, sentence structure, and the relationships between words within sentences.
Semantics: Semantics examines the meaning of words, phrases, sentences, and discourse. It explores how words and expressions convey meaning, how meanings can be composed to create complex meanings, and how context influences interpretation.
Pragmatics: Pragmatics focuses on the use of language in context and how speakers convey meaning beyond the literal interpretation of words. It deals with speech acts, implicature, presupposition, and the ways people use language effectively in communication.
Sociolinguistics: Sociolinguistics explores the relationship between language and society. It examines how language varies and changes based on factors like social class, ethnicity, region, and gender. Dialectology and language variation are important subfields of sociolinguistics.
Psycholinguistics: Psycholinguistics investigates the psychological processes involved in language production, comprehension, and acquisition. It explores how the brain processes language and how humans learn and use language.
Principles and Parameters: This is a theoretical framework in linguistics that proposes that all languages share a common set of principles (universal grammar) but vary in specific parameters that are set differently in each language.
Language Acquisition: The study of how humans acquire their native language(s) and learn to use language for communication. It includes first language acquisition in children and second language acquisition in adults.
Historical Linguistics: Historical linguistics examines how languages change over time and how they are related to each other through linguistic reconstruction. It helps trace the evolution of languages and language families.
Cognitive Linguistics: Cognitive linguistics explores the relationship between language and cognition, emphasizing the role of mental processes in language use and understanding. Concepts like metaphor and conceptual framing are central to cognitive linguistics.
These are just a few of the many linguistic concepts that linguists use to analyze and describe language. Linguistics is a diverse field with various subfields and theoretical frameworks, all contributing to our understanding of how languages function, evolve, and shape human communication.
Essential Linguistic Concepts: Exploring Language Fundamentals
Language is a complex system of communication that is used by humans to express themselves and to interact with others. It is made up of a set of rules and conventions that govern how words are used to form sentences and to convey meaning.
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. Linguists study all aspects of language, from its structure and sound system to its meaning and use.
Here are some essential linguistic concepts:
- Phonology: Phonology is the study of the sound system of a language. It includes the study of the individual sounds (phonemes) that make up a language, as well as the rules that govern how these sounds are combined to form words.
- Morphology: Morphology is the study of word structure. It includes the study of how words are formed from smaller units of meaning (morphemes).
- Syntax: Syntax is the study of sentence structure. It includes the study of how words are combined to form sentences, and the rules that govern how these sentences are interpreted.
- Semantics: Semantics is the study of meaning. It includes the study of the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences.
- Pragmatics: Pragmatics is the study of how language is used in context. It includes the study of the factors that influence how we use language, such as our relationship with the person we are speaking to, the purpose of the conversation, and the setting in which the conversation is taking place.
These are just a few of the many essential linguistic concepts. By understanding these concepts, we can gain a deeper understanding of how language works and how it can be used to communicate effectively.
Language and Communication: Key Linguistic Concepts
Language is essential for human communication. It allows us to share our thoughts and ideas, to build relationships, and to coordinate our activities.
Here are some key linguistic concepts that are important for understanding language and communication:
- Reference: Reference is the relationship between language and the world. When we use language, we are referring to things in the world around us. For example, the word "dog" refers to the animal that we call a dog.
- Sense: Sense is the meaning of a word or phrase. The sense of a word can be determined by its context, such as the other words in the sentence and the situation in which the word is used. For example, the word "bank" can refer to a financial institution or to the side of a river.
- Presupposition: Presuppositions are the assumptions that we make when we use language. For example, when we say "I'm hungry," we are presupposing that there is food available.
- Implicature: Implicatures are the meanings that we convey indirectly, through the use of language. For example, if we say "It's cold in here," we may be implying that we would like someone to close the window.
By understanding these key linguistic concepts, we can become more effective communicators.
Building Blocks of Language: Understanding Linguistic Concepts
Language is made up of a number of building blocks, including:
- Sounds: The smallest units of sound in a language are called phonemes. Phonemes are combined to form words. For example, the English language has 26 phonemes.
- Morphemes: Morphemes are the smallest units of meaning in a language. Morphemes can be combined to form words. For example, the English word "dog" is made up of the morphemes "dog" (which means "canine animal") and "s" (which means "plural").
- Words: Words are the basic units of language. Words can be used to form phrases and sentences. For example, the English words "dog," "cat," and "bird" can be used to form the phrase "the dog, the cat, and the bird."
- Sentences: Sentences are the largest units of language. Sentences are made up of words and phrases. For example, the English sentence "The dog chased the cat" is made up of the words "dog," "chased," and "cat."
By understanding the building blocks of language, we can gain a deeper understanding of how language works and how to use it effectively.
Conclusion
Language is a complex and fascinating system of communication that is essential to human life. By understanding essential linguistic concepts, we can gain a deeper understanding of how language works and how it can be used to communicate effectively.