What is microeconomics in simple words?
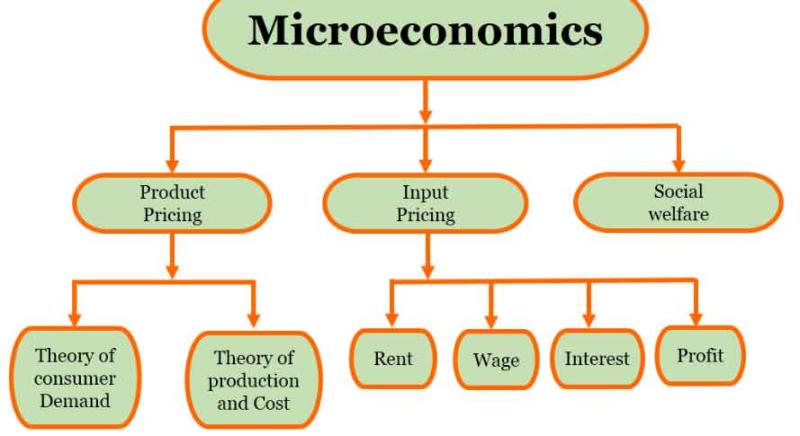
Microeconomics, in simple terms, is the study of how individuals and businesses make decisions about using limited resources. It focuses on understanding the small-scale components of the economy, such as individual consumers, firms, and markets for specific goods and services.
Here are the key points about microeconomics:
Individual Choices: Microeconomics examines how individuals and households make decisions about what to buy, how much to buy, and how to allocate their income among different goods and services based on their preferences and constraints, like budget limitations.
Supply and Demand: It analyzes how the quantity of goods or services supplied by producers and the quantity demanded by consumers interact to determine prices and quantities bought and sold in markets. This interaction forms the basis of market equilibrium.
Market Structures: Microeconomics explores different types of markets, such as perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly, and monopolistic competition. Each structure has distinct characteristics that influence pricing, production, and market behavior.
Production and Costs: It delves into how firms produce goods and services, examining concepts like production functions, costs (fixed and variable), and factors affecting production decisions.
Resource Allocation: Microeconomics looks at the efficient allocation of scarce resources. It studies how resources like labor, capital, and land are used and distributed among different industries and sectors to maximize overall welfare.
Consumer and Producer Behavior: It studies consumer preferences, utility maximization, profit maximization for firms, and how these behaviors influence market outcomes.
Market Failures: Microeconomics identifies instances where markets might not allocate resources efficiently due to factors like externalities, public goods, information asymmetry, or market power, leading to the need for government intervention.
In essence, microeconomics provides a framework for understanding how individual choices and behaviors shape the interactions in markets, influencing prices, quantities, and resource allocation in an economy.
How would you define microeconomics in layman's terms or in a simple manner?
Imagine life as a giant marketplace, where everyone's buying and selling something, whether it's pizza for lunch, your time playing video games, or the skills you use at your job. Microeconomics is like zooming in on a tiny corner of that marketplace, focusing on how individuals and small groups make choices about what to buy, sell, or do.
Here's the breakdown:
- Individuals: Microeconomics looks at how you decide what to spend your money on, how much you're willing to work, or how you use your free time.
- Small Groups: It also studies how small businesses set prices, decide how much to produce, and compete with each other.
- Choices: It's all about understanding the "why" behind these choices. Why do you choose one burger over another? Why do companies offer discounts? Microeconomics explores the forces that influence these decisions.
Think of it this way:
- Macroeconomics is like looking at the whole market from a helicopter, seeing the big trends and movements.
- Microeconomics is like stepping down into that marketplace, observing how individuals and businesses interact, and understanding the reasons behind their actions.
It's all about the intricate dance between supply and demand, figuring out why things cost what they do, and how choices in one corner of the market can ripple out and affect others.
And just like that bustling marketplace is always changing, microeconomics is constantly evolving to understand the new ways we interact and make choices in an ever-connected world.