What is the difference between metric and imperial units?
Metric and Imperial units are two systems of measurement that are used to quantify various physical quantities. While both systems serve the same purpose, they differ in terms of their base units, conversions, and widespread usage. Here's an overview of the key differences between Metric and Imperial units:
Metric System:
- Origin: The metric system, also known as the International System of Units (SI), is based on the decimal system and was developed in France during the late 18th century.
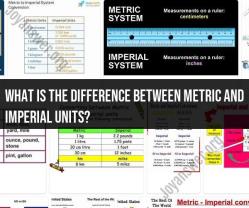
- Base Units: The metric system uses a set of base units, including the meter (length), kilogram (mass), second (time), ampere (electric current), kelvin (temperature), mole (amount of substance), and candela (luminous intensity).
- Decimal Prefixes: The metric system employs decimal prefixes (e.g., kilo-, centi-, milli-) to represent multiples or fractions of the base units. This makes conversions between units straightforward.
- Widespread Usage: The metric system is the dominant system of measurement worldwide, used by most countries for scientific, industrial, and everyday purposes.
- Advantages: Its decimal nature and ease of conversion make the metric system more intuitive for calculations and conversions.
Imperial System:
- Origin: The Imperial system, also known as the British Imperial system, has its roots in various historical systems of measurement and was once widely used in the British Empire.
- Base Units: The Imperial system does not have a consistent set of base units like the metric system. Instead, it uses units such as the inch (length), pound (mass), second (time), degree Fahrenheit (temperature), and others.
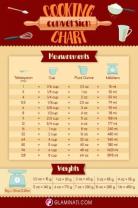
- Complex Conversions: Converting between Imperial units can be more complex due to the lack of a uniform decimal structure. For example, there are 12 inches in a foot and 3 feet in a yard.
- Usage: The Imperial system is still used in some countries, including the United States, for certain applications such as everyday measurements, construction, and manufacturing.
- Advantages: People who are accustomed to the Imperial system may find it more familiar for certain practical tasks.
Key Differences:
- The metric system is based on a decimal structure, while the Imperial system often uses fractions and non-decimal conversions.
- The metric system uses a consistent set of base units, while the Imperial system employs a mix of units.
- Conversions between metric units are generally easier due to decimal prefixes, whereas Imperial unit conversions can be more complex.
- The metric system is more widely used internationally and is the standard system for scientific measurements.
- The choice between Metric and Imperial often depends on historical tradition, geographical location, and specific applications.
In summary, the metric system offers a more consistent and intuitive approach to measurements, while the Imperial system may be more familiar to those who have grown up using it. The choice between the two systems often depends on factors such as the country's historical background and the specific context of measurement.