Life Expectancy After Retirement: Factors and Considerations
January 24, 2024 by JoyAnswer.org, Category : Retirement
What is the average life expectancy after retirement? Explore factors and considerations affecting life expectancy after retirement. This article provides insights into planning for a fulfilling and healthy retirement.
What is the average life expectancy after retirement?
The average life expectancy after retirement can vary based on several factors, including individual health, lifestyle, socioeconomic status, and access to healthcare. It's important to note that "retirement" can happen at different ages for different people, so the post-retirement life expectancy may vary.
I can provide some general information, but you should be aware that these figures may have changed, and it's advisable to consult more recent sources for the latest data.
Global Averages:
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the global average life expectancy was around 72.6 years in 2019.
- Life expectancy varies significantly by country, with some nations having higher or lower averages.
Post-Retirement Life Expectancy:
- In many developed countries, it's common for individuals to live well into their 80s and beyond.
- Advances in healthcare and improvements in living conditions have contributed to increased life expectancy.
Factors Influencing Life Expectancy After Retirement:
- Health Status: The state of one's health plays a crucial role. Those in good health at retirement may have a longer life expectancy.
- Lifestyle Choices: Factors such as diet, exercise, and overall lifestyle can impact longevity.
- Financial Security: Adequate financial planning and security can influence access to healthcare and overall well-being.
- Social Support: Strong social connections and support networks can contribute to a healthier and longer life.
- Access to Healthcare: Availability and quality of healthcare services can affect life expectancy.
Retirement Age:
- The age at which individuals retire can impact post-retirement life expectancy. Those who retire earlier may have longer retirement periods.
Gender Differences:
- In many populations, women tend to have a longer life expectancy compared to men.
It's essential to recognize that these are general trends, and individual experiences may vary widely. Additionally, improvements in healthcare and lifestyle factors could impact life expectancy trends over time. For the most current and accurate information, consulting recent demographic and health statistics or seeking advice from experts in the field is recommended.
1. Average Life Expectancy and Influencing Factors:
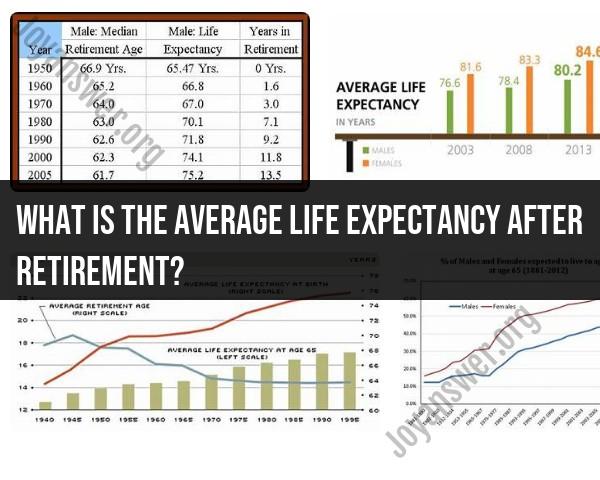
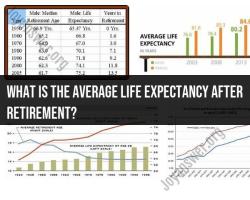
Average life expectancy after retirement:
- Varies significantly depending on age at retirement, health conditions, and other factors.
- In the US, for example, an average 65-year-old retiree can expect to live another 19.3 years (men) or 22.3 years (women).
- However, individual lifespans can be much shorter or longer than these averages.
Factors influencing life expectancy:
- Demographics: Gender (women generally live longer), race and ethnicity (socioeconomic disparities affect health outcomes).
- Health: Existing health conditions, access to healthcare, healthy lifestyle choices (diet, exercise, smoking).
- Socioeconomic factors: Income, education level, social support network, quality of housing and environment.
2. Demographic, Health, and Lifestyle Considerations:
Demographics:
- Women's longer life expectancy means they need to plan for more extended retirements financially.
- Racial and ethnic disparities in health access and outcomes influence life expectancy differently across groups.
Health:
- Pre-existing chronic conditions like heart disease or diabetes can shorten life expectancy.
- Maintaining good health through preventive care, managing chronic conditions, and healthy lifestyle choices can significantly extend life.
Lifestyle:
- Healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol contribute to longevity.
- Social engagement, mental stimulation, and maintaining a sense of purpose can also add years to life.
3. Planning for Financial Security and Well-being:
- Financial planning: Estimating retirement income needs, maximizing Social Security benefits, saving and investing wisely, and managing debt are crucial.
- Healthcare planning: Consider long-term care needs and ensure medical insurance coverage for potential future health challenges.
- Housing: Planning for comfortable and affordable housing throughout retirement, considering potential mobility limitations in older age.
4. Trends and Changes in Retirement Patterns:
- Rising life expectancy leads to longer retirements, requiring more robust financial planning.
- Increased focus on healthy aging and active lifestyles can potentially extend life expectancy and improve quality of life.
- Trends towards phased retirement or flexible work arrangements are emerging, allowing for gradual transitions from full-time work.
5. Enhancing Quality of Life and Longevity:
- Stay active and engaged: Regular physical and mental activities improve health and well-being.
- Maintain social connections: Strong social ties contribute to both happiness and longevity.
- Focus on purpose and meaning: Having a sense of purpose and engaging in activities with meaning can boost life satisfaction and overall health.
- Manage stress and prioritize mental health: Addressing stress and promoting mental well-being can improve overall health and longevity.
- Seek professional help when needed: Don't hesitate to seek medical or financial advice to ensure a healthy and financially secure retirement.
Remember, these are general trends and considerations. Individual circumstances and choices will significantly impact life expectancy and quality of life during retirement. Planning, healthy habits, and proactive care are key to making the most of your retirement years.