What does transactional leadership mean?
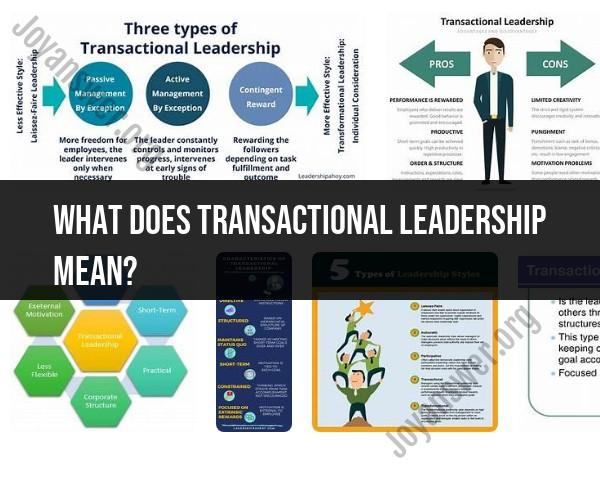
Transactional leadership is a style of management that focuses on the exchanges that occur between leaders and their followers. This approach is based on a system of rewards and punishments to achieve compliance and motivate employees to perform their tasks effectively. Here are the key characteristics and concepts of transactional leadership:
Key Characteristics
Clear Structure and Expectations: Transactional leaders establish clear rules, procedures, and expectations for their employees. They define roles and responsibilities clearly, ensuring that everyone knows what is expected of them.
Rewards and Punishments: This leadership style operates on a system of rewards and punishments. Positive performance and meeting targets are rewarded, often with bonuses, promotions, or other incentives. Conversely, failure to meet expectations can result in disciplinary actions or penalties.
Performance Monitoring: Transactional leaders closely monitor the performance of their subordinates. They provide feedback and corrective measures when necessary to ensure that employees stay on track.
Short-term Focus: This approach is typically more focused on short-term goals and tasks rather than long-term vision and innovation. It aims at maintaining the status quo and achieving specific, immediate objectives.
Standardization and Efficiency: Emphasis is placed on standardization of processes and efficiency in operations. This helps in maintaining consistency and predictability in performance.
Benefits of Transactional Leadership
- Efficiency: By clearly defining roles and expectations, transactional leadership can lead to high efficiency and productivity.
- Clarity: Employees understand exactly what is required of them and what they will receive in return, reducing ambiguity and confusion.
- Motivation through Rewards: The reward system can effectively motivate employees to meet and exceed their performance targets.
Limitations of Transactional Leadership
- Limited Creativity: This style does not encourage creativity or innovation, as it focuses more on following established procedures and achieving specific goals.
- Dependency on Leader: Employees may become overly dependent on their leader for direction and motivation, potentially stifling their ability to work independently.
- Short-term Focus: By concentrating on short-term goals, transactional leadership might neglect long-term strategic planning and development.
Examples in Practice
Transactional leadership is commonly seen in various industries and organizational settings, including:
- Military: Where strict adherence to rules and a clear chain of command are essential.
- Sales Teams: Where achieving sales targets can be directly rewarded with commissions and bonuses.
- Manufacturing: Where maintaining production efficiency and meeting output goals are crucial.
References
For further reading on transactional leadership, you can refer to:
- MindTools on Transactional Leadership
- Indeed Career Guide on Transactional Leadership
- Verywell Mind on Transactional Leadership
Transactional leadership is effective in environments where structured processes and clear guidelines are necessary, but it may need to be complemented with other leadership styles to foster innovation and long-term growth.
What is the definition and significance of transactional leadership?
Transactional leadership is a leadership style characterized by an exchange-based relationship between leaders and followers. Here's a breakdown of its definition and significance:
Definition:
- Focuses on clear short-term goals and structured tasks.
- Leaders provide rewards and punishments to motivate followers.
- Emphasizes efficiency and productivity in achieving pre-defined objectives.
- Relies on established rules and regulations to maintain order.
Significance:
- Provides stability and clarity: In environments with well-defined tasks and procedures, transactional leadership offers clear expectations and a structured approach, promoting stability and efficiency.
- Motivates through incentives: By offering rewards for achieving goals and meeting performance standards, transactional leaders can motivate employees to deliver consistent results.
- Maintains order and control: The emphasis on rules and regulations helps maintain order and control within a team or organization.
Here are some limitations to consider:
- Limited innovation and creativity: The focus on established procedures can stifle creativity and hinder innovation within a team.
- Extrinsic motivation only: This style relies solely on external rewards and punishments, which may not lead to long-term commitment or high morale.
- Limited development of followers: Transactional leaders may not prioritize developing their followers' skills and knowledge for future growth.
Overall, transactional leadership can be effective in well-defined environments that require clear direction, stability, and short-term results. However, it may not be the most suitable approach for fostering long-term engagement, innovation, or employee development.