What is land tax assessment?
Land tax assessment, also known as property tax assessment, is a process by which the value of a piece of land is determined for taxation purposes. Property tax is a tax levied on the value of real estate, including the land and any structures or improvements on the land. The assessment of land for tax purposes is essential for local governments to generate revenue that can be used to fund public services, infrastructure, and other community needs.
Here are key components and considerations related to land tax assessment:
1. Assessment Authority:
- Land tax assessments are typically conducted by a government agency or assessment authority at the local or municipal level. The specific authority responsible for property tax assessments can vary by jurisdiction.
2. Valuation Methods:
- Various methods may be used to determine the value of land for tax assessment purposes. Common valuation methods include:
- Market Value: The estimated price the land would fetch in the open market under normal conditions.
- Comparable Sales: Comparing the land in question to similar properties that have recently been sold.
- Cost Approach: Estimating the cost to replace the land with a similar one, minus depreciation.
3. Frequency of Assessment:
- The frequency of land tax assessments can vary. In some jurisdictions, assessments are conducted annually, while in others, they may occur less frequently. Regular assessments help ensure that property values are kept up-to-date.
4. Appeals Process:
- Property owners typically have the right to appeal their land tax assessments if they believe the assessed value is inaccurate. The appeals process allows property owners to present evidence supporting their claim of an inaccurate assessment.
5. Tax Rates and Revenue Collection:
- Once the land is assessed, local governments apply a tax rate to the assessed value to determine the property tax owed by the owner. The collected property taxes contribute to local government revenue.
6. Use of Property Tax Revenues:
- Property tax revenues are used by local governments to fund various public services and projects, including schools, roads, public safety, parks, and other community needs.
7. Exemptions and Deductions:
- Some jurisdictions may offer exemptions or deductions that reduce the taxable value of certain properties. Common exemptions include those for homesteads, agricultural land, or properties owned by certain nonprofit organizations.
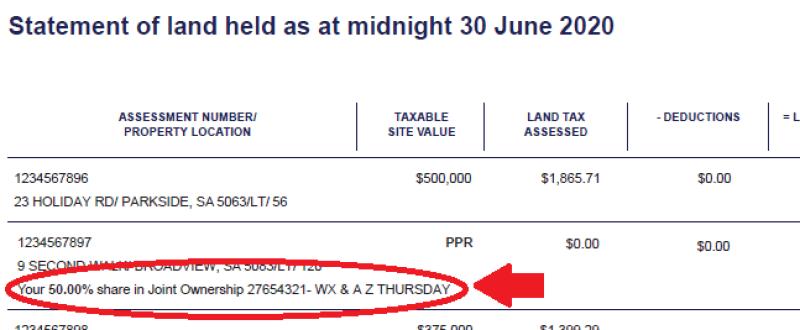
8. Assessment Notices:
- Property owners typically receive assessment notices that provide details about the assessed value of their land, the applicable tax rate, and the resulting property tax amount. This information is crucial for property owners to understand their tax obligations.
Importance of Land Tax Assessment:
- Equitable Taxation: Land tax assessments aim to ensure that property owners contribute to local government funding in a manner that reflects the value of their real estate holdings.
- Revenue Generation: Property taxes are a significant source of revenue for local governments, supporting essential services and community development.
- Fairness and Transparency: An effective assessment process promotes fairness and transparency in property taxation, ensuring that similar properties are taxed at similar rates.
It's important for property owners to be aware of the land tax assessment process in their jurisdiction, including how values are determined and the avenues available for appeal. Property tax laws and assessment practices can vary, so understanding the local regulations is crucial for property owners and real estate investors.
What is involved in the assessment of land for tax purposes?
The assessment of land for tax purposes is the process of determining the value of a piece of land for taxation purposes. This process is typically carried out by local government officials, such as assessors or appraisers.
The assessment of land for tax purposes typically involves the following steps:
Data collection: Assessors gather information about the property, such as its size, location, zoning, and improvements.
Valuation analysis: Assessors use various methods to determine the value of the property, such as the comparable sales approach, the cost approach, and the income approach.
Classification and assessment: The property is classified based on its use, such as residential, commercial, or agricultural. The assessed value is determined based on the classification and the valuation analysis.
Review and appeal: Property owners have the opportunity to review the assessment and appeal it if they believe it is inaccurate.
How is land tax assessment different from property tax assessment?
Land tax assessment and property tax assessment are two similar processes, but there are some key differences between the two.
Scope: Land tax assessment only considers the value of the land itself, while property tax assessment considers the value of both the land and the improvements on the land.
Valuation methods: The valuation methods used for land tax assessment and property tax assessment may vary. For example, the comparable sales approach is commonly used for both land tax assessment and property tax assessment, but the cost approach and the income approach may be used more frequently for property tax assessment.
Tax rates: Land tax rates and property tax rates are typically set by different entities. Land tax rates are typically set by state or local governments, while property tax rates are typically set by local governments.
Can land tax assessments vary based on land use?
Yes, land tax assessments can vary based on land use. This is because different types of land have different values and generate different levels of income. For example, residential land is typically valued higher than agricultural land, and commercial land is typically valued higher than residential land.
In some jurisdictions, land tax assessments may also be based on the zoning of the property. For example, land that is zoned for commercial use may be assessed at a higher rate than land that is zoned for residential use.