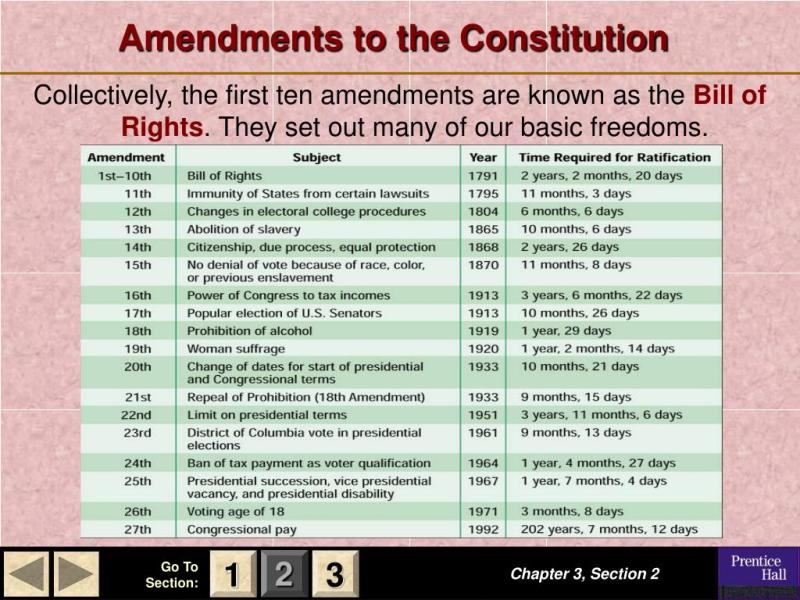
What are the main ideas of the amendments?
The United States Constitution has been amended several times to address various issues and ensure the protection of individual rights. Here are some key concepts within certain constitutional amendments:
First Amendment: Protects freedom of speech, religion, and the press. It also guarantees the right to assemble peacefully and petition the government.
Second Amendment: Protects the right to bear arms, allowing citizens to own firearms.
Fourth Amendment: Protects against unreasonable searches and seizures, ensuring that individuals have a right to privacy.
Fifth Amendment: Ensures due process of law and protection against self-incrimination. It also prohibits double jeopardy.
Sixth Amendment: Guarantees the right to a fair and speedy trial, including the right to legal counsel.
Eighth Amendment: Prohibits cruel and unusual punishment and excessive bail.
Fourteenth Amendment: Addresses citizenship rights and equal protection under the law. It prohibits states from depriving any person of life, liberty, or property without due process.
Nineteenth Amendment: Grants women the right to vote, ensuring suffrage regardless of gender.
Twenty-Sixth Amendment: Lowers the voting age to 18, ensuring that citizens 18 years and older have the right to vote.
These amendments, among others, play a crucial role in shaping the legal and social landscape of the United States by safeguarding individual liberties and promoting equality.
Summarizing the core principles or themes within constitutional amendments
Core Principles and Themes in Constitutional Amendments:
Summarizing the vast array of themes across all 27 amendments is a task requiring nuance, but here are some key threads woven throughout:
Individual Rights and Liberties:
- The Bill of Rights (Amendments 1-10): These foundational amendments guarantee freedoms like speech, religion, assembly, and due process, reflecting a core principle of individual liberty against government overreach.
- 13th & 14th Amendments: Abolishing slavery and extending citizenship and equal protection under the law solidified basic human rights for all.
- 15th, 19th, and 26th Amendments: Secured voting rights for formerly enslaved men, women, and 18-year-olds, respectively, expanding political participation and equality.
Federalism and Power Distribution:
- 10th Amendment: Reserves unenumerated powers for the states, upholding a core principle of federalism where power is shared between national and state governments.
- 16th & 17th Amendments: Established a federal income tax and direct election of senators, respectively, reflecting shifting power dynamics between the federal government and states/citizens.
Balance and Checks on Power:
- 11th Amendment: Limits federal court jurisdiction over suits against states, safeguarding state sovereignty and preventing excessive federal power.
- 22nd Amendment: Limits presidents to two terms, reflecting a concern about concentrated power and ensuring periodic transitions in leadership.
- 25th Amendment: Clarifies procedures for presidential succession and disability, ensuring continuity of government even during challenges.
Evolving Values and Adaptation:
- Many amendments reflect responses to specific historical contexts and societal changes, such as abolishing slavery (13th), enfranchising women (19th), or prohibiting alcohol (18th, later repealed by 21st).
- Ongoing debates and interpretations surrounding amendments like the 14th's Equal Protection Clause or the 2nd Amendment's right to bear arms demonstrate the Constitution's adaptability and the continuous evolution of its meaning.
It's important to remember:
- These are just some of the major themes, and individual amendments often encompass multiple principles.
- The specific interpretation and application of these themes through Supreme Court rulings and historical contexts also play a crucial role in understanding their impact.
Remember, delving deeper into specific amendments will reveal further nuances and complexities within these overarching themes. I hope this summary provides a starting point for your exploration of the core principles and themes within the U.S. Constitution's amendments.