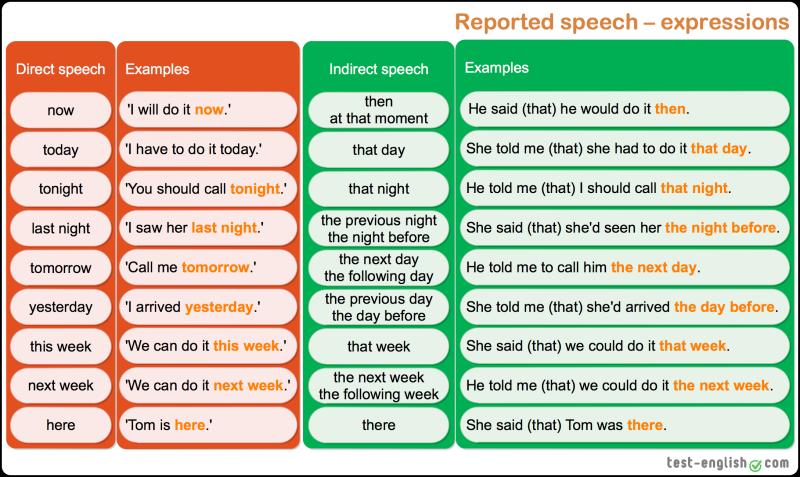
What is procedural law in your own words?
Procedural law refers to the set of rules and processes that govern how legal cases are handled within a legal system. It outlines the methods and steps to be followed in resolving disputes or enforcing rights. Unlike substantive law, which defines rights and duties, procedural law focuses on the procedures and mechanisms involved in legal proceedings. This includes aspects such as filing lawsuits, gathering evidence, presenting arguments, and the overall conduct of a legal case from start to finish. Essentially, procedural law ensures that legal proceedings are fair, consistent, and conducted in an organized manner.
Explaining procedural law in simpler terms
Here's a simple explanation of procedural law, using some everyday analogies:
Imagine the law as a big game:
- Substantive law is the rulebook that tells you what's allowed and what's not (like "no running with the ball" or "no stealing bases").
- Procedural law is the instruction manual that explains how to play the game (like "how to start a play" or "how to challenge a call").
Think of it like a recipe:
- Substantive law is the list of ingredients you need (like flour, sugar, eggs).
- Procedural law is the step-by-step instructions on how to mix those ingredients together to make a cake.
Here are some key points about procedural law:
- It outlines the steps involved in legal proceedings, from starting a lawsuit to appealing a decision.
- It covers things like:
- How to file documents (like a complaint or a motion)
- How to gather evidence (like taking depositions or requesting documents)
- How to present arguments in court
- How to appeal a decision
- It helps ensure that legal proceedings are fair and orderly.
- It protects the rights of all parties involved.
Here are some examples of procedural law in action:
- Criminal cases: Rules for arresting suspects, conducting trials, and sentencing offenders.
- Civil cases: Rules for filing lawsuits, conducting discovery, and trying cases.
- Administrative law: Rules for government agencies to make decisions and enforce regulations.
Key takeaways:
- Procedural law is the "how" of the legal system.
- It provides a roadmap for resolving legal disputes.
- It's essential for ensuring fairness and protecting rights.
Important note: Procedural law can vary depending on the jurisdiction (state or federal court). It's always best to consult with an attorney if you have specific questions about procedural law in a particular case.