What are noncancerous tumors called?
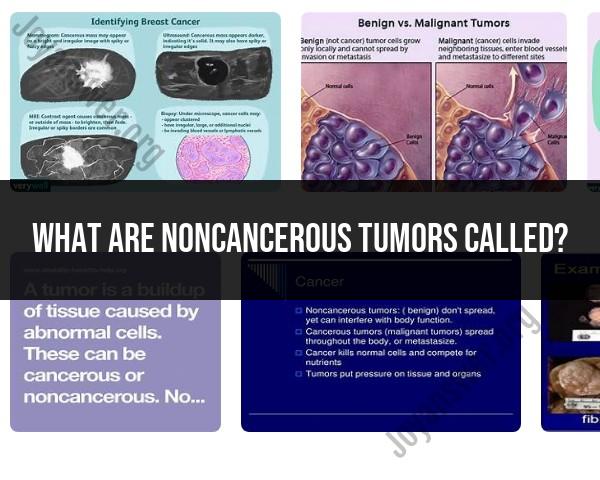
Noncancerous tumors are typically referred to as "benign tumors." The term "benign" indicates that these tumors are not cancerous and do not have the ability to invade nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body. Benign tumors are characterized by slow growth, a well-defined border, and cells that closely resemble normal cells.
There are various types of benign tumors, and the terminology used to describe them can vary based on the tissue or organ from which they arise. Here are some common terms for benign tumors in specific tissues:
Adenoma:
- A benign tumor that originates from glandular tissues. Adenomas can occur in various organs, such as the colon, pituitary gland, or thyroid gland.
Fibroma:
- A benign tumor of fibrous or connective tissue. Fibromas can develop in the breast, uterus, or other connective tissue-rich areas.
Lipoma:
- A benign tumor composed of fatty tissue. Lipomas are often found just beneath the skin and are soft to the touch.
Neuroma:
- A benign tumor of nerve tissue. Neuromas can develop in various nerves throughout the body.
Osteoma:
- A benign tumor of the bone. Osteomas can occur in the bones of the skull or other skeletal structures.
Chondroma:
- A benign tumor of cartilage. Chondromas can develop in cartilaginous tissues, such as those found in joints or the ribs.
Hemangioma:
- A benign tumor composed of blood vessels. Hemangiomas can occur in various tissues and organs, including the skin and liver.
Myoma:
- A benign tumor of muscle tissue. Myomas can develop in the uterus (uterine fibroids) or other muscles.
Papilloma:
- A benign tumor that grows on the surface of tissues and often has a wart-like appearance. Papillomas can occur in various organs, including the skin, bladder, or throat.
It's important to note that while benign tumors are not cancerous, they can still cause health issues depending on their size, location, and potential impact on surrounding tissues. In many cases, benign tumors are detected incidentally during medical examinations or imaging studies conducted for unrelated reasons. If a benign tumor is causing symptoms or concerns, medical professionals may recommend monitoring, removal, or other interventions based on the specific characteristics of the tumor and its potential impact on the individual's health.
Sure, here is a comprehensive analysis of benign tumors, their characteristics, classification, common types, and differentiation from malignant tumors:
Benign tumors: Understanding the characteristics and classification of noncancerous tumors
Benign tumors, also known as noncancerous tumors, are abnormal masses of cells that do not invade surrounding tissues or spread to distant sites. They differ from malignant tumors, also known as cancers, in their localized nature and lack of metastatic potential. While benign tumors can cause discomfort or functional impairments depending on their location and size, they do not pose a direct threat to life.
Characteristics of Benign Tumors:
Localized growth: Benign tumors remain confined to their original location, surrounded by a distinct capsule that separates them from normal tissues.
Lack of metastasis: Benign tumors do not spread to distant sites through the bloodstream or lymphatic system, preventing the formation of secondary tumors.
Slow growth: Benign tumors typically grow slowly over time, often taking years or even decades to reach a noticeable size.
Well-defined borders: Benign tumors usually have distinct boundaries, making them easy to distinguish from surrounding normal tissues.
Normal cell appearance: Benign tumors are composed of cells that closely resemble the normal cells from which they originated, maintaining their typical structure and function.
Classification of Benign Tumors:
Benign tumors are classified according to the type of tissue they originate from. Some common examples include:
Adenomas: Benign tumors of glandular tissue, such as polyps in the colon or uterus.
Lipomas: Benign tumors of fat tissue, often appearing as soft, painless lumps under the skin.
Fibromas: Benign tumors of connective tissue, such as skin tags or uterine fibroids.
Hemangiomas: Benign tumors of blood vessels, often appearing as red or purple birthmarks.
Osteomas: Benign tumors of bone tissue, typically asymptomatic and slow-growing.
Common types of benign tumors: Exploring various examples of noncancerous tumors
Benign tumors can occur in various parts of the body, and each type has its own characteristics and potential impact. Here are some common examples:
Skin tumors: Benign skin tumors include moles, skin tags, and lipomas. These tumors are typically harmless and may only cause cosmetic concerns.
Uterine tumors: Benign uterine tumors include fibroids and polyps. These tumors are common in women of reproductive age and may cause irregular bleeding or discomfort.
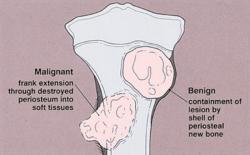
Bone tumors: Benign bone tumors include osteomas and enchondromas. These tumors are often asymptomatic and may be discovered incidentally during imaging tests.
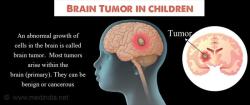
Brain tumors: Benign brain tumors include meningiomas and acoustic neuromas. These tumors can cause neurological symptoms depending on their location and size.
Distinguishing between benign and malignant tumors: Identifying key differences and diagnostic criteria
Differentiating between benign and malignant tumors is crucial for determining the appropriate course of treatment and patient prognosis. Here are some key differences:
| Feature | Benign Tumors | Malignant Tumors |
|---|---|---|
| Growth pattern | Localized growth | Invasive growth, invading surrounding tissues |
| Metastasis | No metastasis | Metastasis, spreading to distant sites |
| Growth rate | Slow growth | Rapid growth |
| Cellular appearance | Normal cell appearance | Abnormal cell appearance, with irregular shape and size |
| Borders | Well-defined borders | Irregular borders |
| Capsules | Surrounded by a distinct capsule | Lack of a distinct capsule |
Diagnosing benign tumors often involves a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and biopsies. The specific diagnostic approach depends on the location and suspected type of benign tumor.
Conclusion:
Benign tumors are a diverse group of noncancerous growths that can occur in various parts of the body. While they typically do not pose a direct threat to life, they may cause discomfort, functional impairments, or cosmetic concerns. Understanding the characteristics, classification, and common types of benign tumors is essential for accurate diagnosis, appropriate management, and patient reassurance.