How to become a Certified Financial modeling?
Becoming a Certified Financial Modeling Expert (CFME) or earning a financial modeling certification involves building technical skills in finance, accounting, Excel, and valuation, then completing a recognized certification program. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
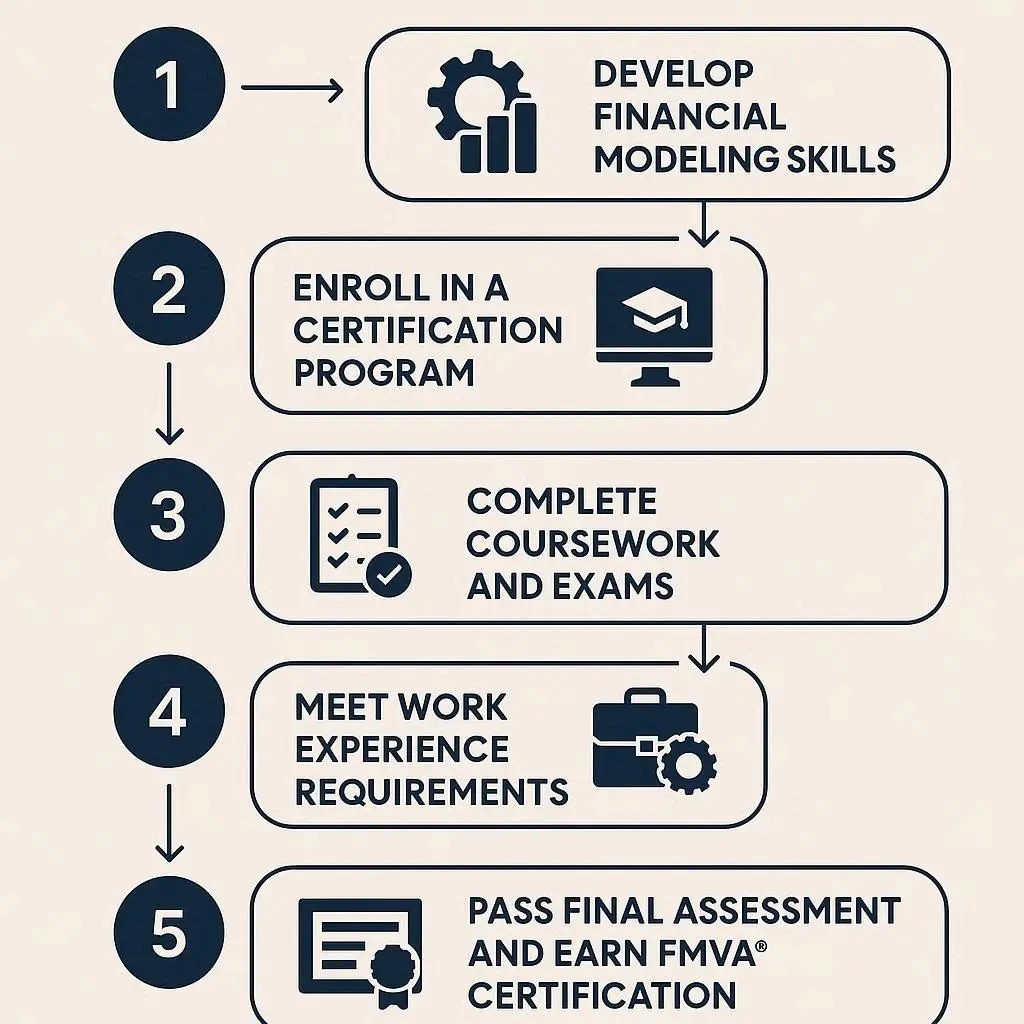
1. Build Your Foundational Knowledge
Finance & Accounting – Understand financial statements, corporate finance, and accounting principles.
Excel Skills – Learn advanced Excel functions, formulas, pivot tables, and VBA (optional).
Valuation & Investment Concepts – Get comfortable with DCF analysis, comparables, M&A models, and LBOs.
2. Choose a Recognized Certification
Several organizations offer respected financial modeling certifications:
CFM™ (Certified Financial Modeler) – Offered by the Global Academy of Finance and Management.
FMVA® (Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst) – Offered by the Corporate Finance Institute (CFI), very popular globally.
AFM (Advanced Financial Modeler) – From the Financial Modeling Institute (FMI).
Wall Street Prep or Training The Street – Industry-recognized programs (not always formal “certifications”).
The FMVA® and AFM are currently the most recognized worldwide.
3. Complete the Program Requirements
Enroll in the chosen program.
Study online modules or attend live workshops.
Complete practical assignments (often building valuation, M&A, or forecasting models).
Pass the certification exam, which may involve:
Case studies,
Multiple-choice tests,
Or hands-on model building.
4. Gain Practical Experience
Apply your skills in internships, investment banking, corporate finance, or consulting roles.
Build and refine real-world models (budgets, forecasts, deal valuations).
5. Maintain & Upgrade Your Certification
Some programs require continuing education credits.
Stay updated with advanced topics (AI in finance, Power BI, Python for financial modeling).
Summary:
To become a Certified Financial Modeling Expert, strengthen your finance and Excel skills, pick a reputable certification (such as FMVA® or AFM), complete the required coursework and exams, and then apply your skills in real-world projects.
Here’s a detailed comparison of the top financial modeling certifications: FMVA®, AFM, and CFM™, to help you decide which best fits your goals:
1. FMVA® – Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (Corporate Finance Institute)
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Provider | Corporate Finance Institute (CFI) |
| Target Audience | Finance professionals, analysts, accountants, investment bankers |
| Focus | Practical financial modeling, Excel, valuation, budgeting, forecasting, M&A, LBOs |
| Format | Online, self-paced; includes video lectures, quizzes, and case studies |
| Prerequisites | None, but basic finance and Excel knowledge recommended |
| Exam | Online; requires completing all modules and passing assessments |
| Recognition | Highly recognized in investment banking, corporate finance, and FP&A roles |
| Cost | ~$497–$847 USD (varies by package and promotion) |
| Advantages | Practical, hands-on, widely used in real-world finance jobs |
| Drawbacks | Mostly self-paced; less formal “accreditation” compared to some institutes |
2. AFM – Advanced Financial Modeler (Financial Modeling Institute)
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Provider | Financial Modeling Institute (FMI) |
| Target Audience | Experienced finance professionals, consultants, analysts |
| Focus | High-level Excel modeling, financial analysis, valuation, scenario planning |
| Format | Online or in-person; rigorous exam including case study models |
| Prerequisites | Recommended: Intermediate finance knowledge and Excel skills |
| Exam | Hands-on financial model built under exam conditions |
| Recognition | Internationally recognized; emphasizes technical proficiency |
| Cost | ~$450–$700 USD per level (Levels 1–3) |
| Advantages | Focused on modeling excellence; globally recognized |
| Drawbacks | More challenging; less emphasis on soft skills or corporate context |
3. CFM™ – Certified Financial Modeler (Global Academy of Finance & Management)
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Provider | Global Academy of Finance and Management (GAFM) |
| Target Audience | Finance managers, analysts, professionals seeking certification in modeling and finance |
| Focus | Broad finance, accounting, and modeling knowledge; includes ethics and risk |
| Format | Online or in-person courses; exam-based |
| Prerequisites | Bachelor’s degree or equivalent experience in finance/accounting |
| Exam | Multiple-choice or case study exam |
| Recognition | Recognized globally but less specialized than FMVA or AFM |
| Cost | ~$1,000 USD (varies by country and program options) |
| Advantages | Comprehensive finance coverage; professional certification title |
| Drawbacks | Less practical/excel-focused; more theoretical than FMVA® |
Quick Comparison Summary
| Feature | FMVA® | AFM | CFM™ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Practical focus | High | Very High | Moderate |
| Global recognition | High | High | Medium |
| Excel/Hands-on | Strong | Very Strong | Moderate |
| Cost | $497–$847 | $450–$700 | ~$1,000 |
| Best For | Analysts, FP&A, investment banking | Expert modelers, consultants | Finance managers, broad certification seekers |
Recommendation
If you want practical, career-ready modeling skills: FMVA® is ideal.
If you want highly technical, expert-level modeling recognition: AFM is best.
If you want a formal professional title with broader finance knowledge: CFM™ is suitable.
Steps to Become a Certified Financial Modeler
Becoming a Certified Financial Modeler (CFM) typically involves a structured path of education, training, and examination. While there isn't one single "CFM" certification universally recognized, several reputable organizations offer credentials in financial modeling. The general steps often include:
Gaining Foundational Knowledge: Building a strong understanding of finance, accounting, and business principles. This usually comes from a relevant bachelor's degree.
Specialized Training: Enrolling in dedicated financial modeling courses or bootcamps that teach practical skills.
Hands-on Experience: Applying theoretical knowledge through real-world projects or practical exercises.
Passing a Certification Exam: Successfully completing an exam offered by a recognized financial modeling certification body.
Continuous Learning: Staying updated with industry best practices and software.
Courses and Training Required
To become proficient in financial modeling and pursue certification, specific courses and training are essential. These typically cover:
Core Finance and Accounting: Understanding financial statements (income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement), valuation techniques (DCF, multiples), and corporate finance concepts.
Excel Proficiency: Advanced Excel skills are fundamental, including functions (e.g., VLOOKUP, INDEX-MATCH, SUMIFS), pivot tables, data validation, and scenario analysis tools.
Modeling Best Practices: Learning structured approaches to building robust, flexible, and auditable financial models. This includes linking assumptions, building schedules (depreciation, amortization), and integrating statements.
Specific Model Types: Training often delves into various model types such as:
Three-Statement Models: Integrating income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
Valuation Models: Discounted Cash Flow (DCF), Leveraged Buyout (LBO), Merger & Acquisition (M&A) models.
Project Finance Models: For large-scale infrastructure projects.
Budgeting and Forecasting Models: For operational planning.
Many programs are offered by financial training institutions, universities, or online platforms, often culminating in their own proprietary certification.
Skills Needed for Financial Modeling
Beyond formal training, successful financial modelers possess a blend of technical, analytical, and soft skills:
Technical Skills:
Advanced Excel: Mastery of Excel is non-negotiable.
Accounting Knowledge: A deep understanding of how financial transactions impact statements.
Finance Theory: Strong grasp of valuation, capital budgeting, and corporate finance.
Database Management (Basic): Familiarity with data organization and retrieval can be helpful.
Analytical Skills:
Critical Thinking: Ability to dissect complex problems and synthesize information.
Problem-Solving: Developing logical and efficient solutions within a model.
Attention to Detail: Accuracy is paramount; even small errors can have large consequences.
Soft Skills:
Communication: Clearly explaining model assumptions, outputs, and limitations to non-technical stakeholders.
Time Management: Building complex models often under tight deadlines.
Adaptability: Adjusting models quickly based on new information or changing assumptions.
Curiosity: A desire to understand the underlying business and economic drivers.
Certification Exams and Study Tips
Certification exams for financial modeling typically test both theoretical knowledge and practical application, often involving a timed case study in Excel. Examples of well-known certifications include the Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA) by Corporate Finance Institute (CFI) or specialized certifications from Wall Street Prep or the CFA Institute (though the CFA is broader than just modeling).
Study Tips:
Master Excel Shortcuts: Efficiency is key in timed exams.
Practice Consistently: Build numerous models from scratch, not just modifying existing ones.
Understand the "Why": Don't just memorize formulas; understand the financial and accounting logic behind each step.
Review Financial Concepts: Be solid on accounting principles, valuation methodologies, and corporate finance.
Simulate Exam Conditions: Take practice exams under timed pressure to get comfortable with the format and pace.
Focus on Structure and Clarity: Build models that are easy to follow, audit, and debug.
Career Benefits of Certification
Obtaining a financial modeling certification can significantly enhance an individual's career trajectory:
Enhanced Credibility: Certifications demonstrate a proven level of expertise and commitment to the field.
Improved Job Prospects: Many employers in finance, consulting, and corporate development look for candidates with strong financial modeling skills, and a certification can make an applicant stand out.
Higher Earning Potential: Certified professionals often command higher salaries due to their specialized skills.
Career Advancement: It can open doors to more senior roles, such as financial analyst, investment banking analyst, private equity associate, corporate finance manager, or consultant.
Networking Opportunities: Many certification programs connect participants with a network of professionals in the finance industry.
Validation of Skills: It provides external validation of your ability to build robust, accurate, and impactful financial models, which are critical for strategic decision-making in businesses.