What is a member of a gene pair that determines a trait?
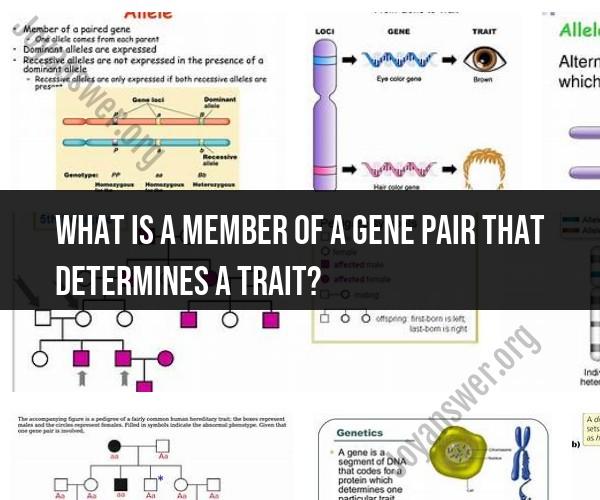
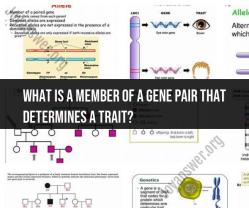
In the context of genetics, a member of a gene pair that determines a trait is referred to as an "allele." Alleles are alternative versions of a gene found at the same location (locus) on a chromosome. Each individual inherits two alleles for most genes, one from each parent.
Here's how alleles work in determining traits:
Gene Locus: A specific gene is located at a particular locus on a chromosome. This gene encodes instructions for a specific trait, such as eye color or blood type.
Two Alleles: At that gene locus, an individual has two alleles—one inherited from their mother and one from their father. These alleles may be the same (homozygous) or different (heterozygous).
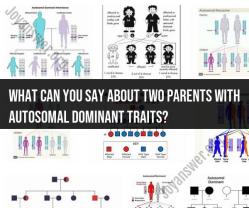
Dominance and Recessiveness: Alleles can be dominant or recessive. Dominant alleles are expressed, or "seen," when an individual carries one or two copies of that dominant allele. Recessive alleles are only expressed when an individual carries two copies of that recessive allele.
Trait Expression: The combination of alleles an individual carries at a particular gene locus determines their genotype for that trait. The genotype, in turn, determines the observable characteristics, or phenotype, of the trait.
For example, consider the gene for eye color. There are multiple alleles for this gene, but let's focus on two common ones: a dominant allele for brown eye color (B) and a recessive allele for blue eye color (b).
- If an individual inherits two copies of the dominant allele (BB), they will have brown eyes because the dominant allele is expressed.
- If an individual inherits one dominant and one recessive allele (Bb), they will still have brown eyes because the dominant allele is expressed.
- Only if an individual inherits two copies of the recessive allele (bb) will they have blue eyes because the recessive allele is expressed when no dominant allele is present.
So, in this example, the alleles (B and b) form the gene pair that determines the trait of eye color, and the specific combination of alleles (genotype) determines the observed eye color (phenotype).
It's important to note that not all traits are determined by a single gene with only two alleles; many traits are influenced by multiple genes, each with its set of alleles. Understanding the genetics of traits involves considering the interactions of these genes and alleles.