What can you say about two parents with autosomal dominant traits?
When both parents have autosomal dominant traits, it can have implications for their offspring's genetic inheritance. Autosomal dominant traits are those in which a single copy of the dominant allele (variant) is sufficient to express the trait, overriding the presence of the recessive allele. Here's what you can generally say about two parents with autosomal dominant traits:
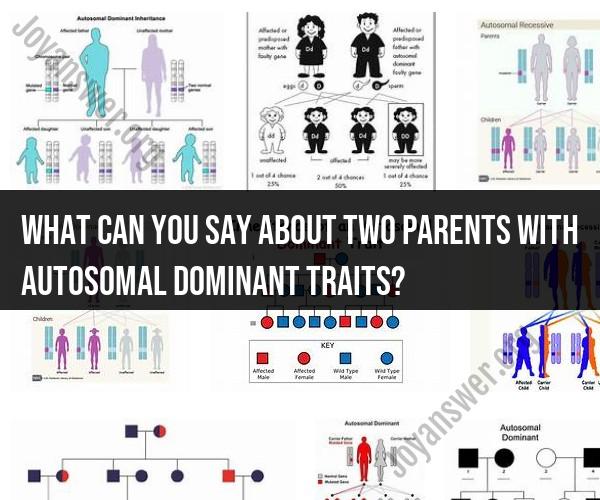
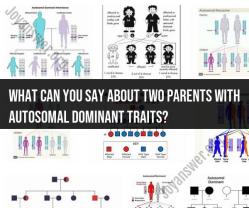
Offspring Inheritance: If both parents have autosomal dominant traits, they each carry at least one dominant allele for the respective trait. Therefore, each parent has a 50% chance of passing on the dominant allele to their offspring.
Heterozygous Offspring: If both parents are heterozygous for the same autosomal dominant trait (meaning they each carry one dominant allele and one recessive allele), their offspring have a 25% chance of inheriting two dominant alleles (homozygous dominant), a 50% chance of inheriting one dominant and one recessive allele (heterozygous, expressing the dominant trait), and a 25% chance of inheriting two recessive alleles (homozygous recessive).
Phenotype Expression: Offspring who inherit at least one dominant allele from one or both parents will typically express the dominant trait. The presence of one dominant allele is usually sufficient to manifest the trait, and it will override the presence of a recessive allele if one is also inherited.
Risk of Homozygous Dominant: There is a 25% chance that the offspring will inherit two dominant alleles (homozygous dominant) for the trait. In this case, they will express the dominant trait strongly. However, being homozygous dominant for a trait does not necessarily mean it will be more severe or significant than when expressed by a heterozygous individual.
Risk of Homozygous Recessive Offspring: There is also a 25% chance that the offspring will inherit two recessive alleles (homozygous recessive) for the trait. In this scenario, the offspring will not express the dominant trait and will not exhibit the associated phenotype.
It's important to note that the specific implications and outcomes can vary depending on the nature of the autosomal dominant traits involved and whether the parents carry different dominant alleles or the same one. Additionally, other genetic factors and inheritance patterns may come into play if multiple traits are considered.
When considering the genetic implications of two parents with autosomal dominant traits, it's advisable to consult with a genetic counselor or healthcare professional who can provide a more detailed analysis and assessment of the specific traits involved and their potential effects on offspring.