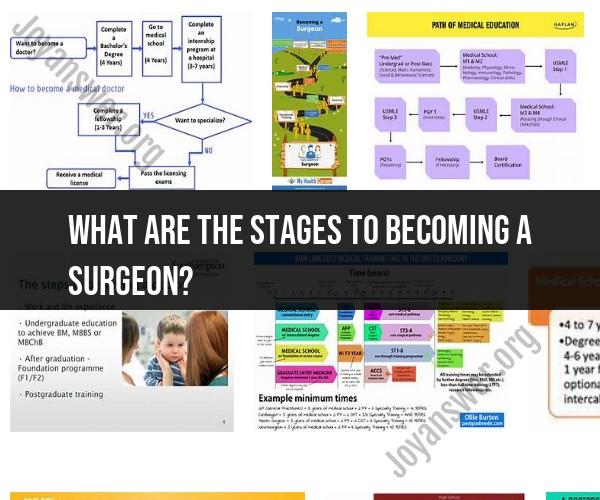
What are the stages to becoming a surgeon?
Becoming a surgeon is a challenging yet rewarding journey that requires dedication, resilience, and a commitment to excellence in patient care. This article provides an overview of the stages involved in pursuing a career as a surgeon, from educational prerequisites to specialized training and beyond.
1. Undergraduate Education:
- Pre-Medical Studies: The path to becoming a surgeon typically begins with a bachelor's degree in a pre-medical or related field. Students focus on science and math courses to build a strong foundation for medical school.
2. Medical School:
Medical College Admission Test (MCAT): Aspiring surgeons must take the MCAT exam to gain admission to medical school. High scores are essential for competitive programs.
Medical Degree (MD or DO): Medical school involves four years of intensive study and clinical training. Students learn about various medical specialties, including surgery, during their coursework.
3. Residency Training:
- General Surgery Residency: After earning a medical degree, aspiring surgeons must complete a general surgery residency program, which typically lasts 5-7 years. This phase involves hands-on surgical training, patient care, and progressively increasing responsibilities.
4. Specialty Training:
- Fellowship Programs: Many surgeons choose to pursue additional fellowship training to specialize in a specific surgical field, such as cardiothoracic surgery, neurosurgery, or orthopedic surgery. Fellowships typically last 1-2 years.
5. Certification and Licensure:
Board Certification: Surgeons must become board-certified by passing examinations specific to their chosen specialty. Board certification demonstrates expertise and commitment to maintaining high standards of care.
State Licensure: Surgeons must obtain a medical license to practice in their respective states or countries. Requirements vary by location but typically involve passing a licensing exam.
6. Establishing a Career:
Academic or Private Practice: Surgeons can choose to work in academic medical centers, private practices, or a combination of both. Academic surgeons often teach medical students and residents in addition to clinical work.
Hospital Privileges: Surgeons must secure privileges at hospitals where they plan to operate. This process involves a thorough review of their training and credentials.
7. Continuing Education:
- Maintenance of Certification (MOC): Surgeons must participate in ongoing education and assessment to maintain board certification. MOC ensures that surgeons stay up-to-date with advancements in their field.
8. Patient Care and Research:
Clinical Practice: Surgeons provide surgical care to patients, including pre-operative assessment, surgery, and post-operative follow-up. Communication and empathy are crucial in patient interactions.
Research: Some surgeons engage in clinical or laboratory research to advance medical knowledge and improve surgical techniques.
9. Career Advancement:
Leadership and Advocacy: Experienced surgeons may take on leadership roles in healthcare organizations or engage in advocacy efforts to shape healthcare policies.
Mentorship: Many established surgeons find fulfillment in mentoring the next generation of surgical professionals.
10. Lifelong Learning:
- CME (Continuing Medical Education): Surgeons continue to engage in CME activities throughout their careers to stay informed about the latest medical advancements and best practices.
Becoming a surgeon is a multi-stage journey that requires years of education, training, and dedication. It's a path characterized by continuous learning and the unwavering commitment to providing the highest quality of surgical care to patients. Surgeons play a vital role in healthcare, and their contributions are essential to improving the well-being of individuals and communities.