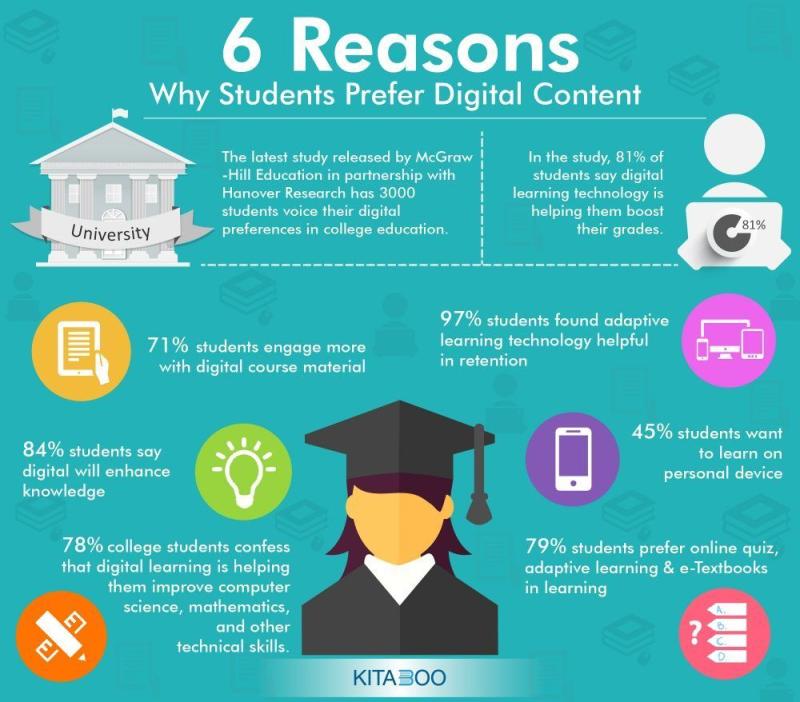
What do you need to educate people about recovery?
Educating people about recovery, particularly from substance abuse or addiction, requires a comprehensive and empathetic approach. Here are essential components and information that can contribute to effective education about recovery:
Understanding of Addiction:
- Provide information about the nature of addiction, emphasizing that it is a complex, chronic condition that affects the brain. Help dispel myths and misconceptions surrounding addiction.
Stages of Change:
- Introduce the Transtheoretical Model (Stages of Change), highlighting the different stages individuals go through when making positive changes in their lives. Understanding these stages helps individuals recognize where they are in their recovery journey.
Treatment Options:
- Explain various treatment modalities, including detoxification, counseling, therapy, medication-assisted treatment, and support groups. Discuss the importance of personalized treatment plans based on individual needs.
Role of Support Systems:
- Emphasize the crucial role of family, friends, and community support in the recovery process. Encourage the development of healthy relationships and communication.
Relapse Prevention:
- Educate about common triggers and stressors that can lead to relapse. Provide coping strategies, stress management techniques, and skills to navigate challenging situations without returning to substance use.
Holistic Well-being:
- Emphasize the importance of holistic well-being, including physical, emotional, and mental health. Encourage healthy lifestyle choices, nutrition, exercise, and stress reduction activities.
Mental Health Awareness:
- Address the intersection of substance abuse and mental health. Many individuals with addiction also experience co-occurring mental health disorders. Promote awareness and understanding of mental health issues.
Recovery Resources:
- Inform individuals about available recovery resources, including local support groups, counseling services, community centers, and online forums. Provide information about helplines and crisis intervention services.
Peer Support:
- Highlight the effectiveness of peer support in recovery. Peer support groups, led by individuals with lived experience, can provide understanding, empathy, and shared coping strategies.
Reducing Stigma:
- Challenge and combat the stigma associated with addiction. Foster empathy and understanding to create an environment that supports individuals in recovery.
Continuum of Care:
- Explain the concept of the continuum of care, emphasizing that recovery is an ongoing process. Discuss aftercare plans, relapse prevention strategies, and ongoing support options.
Cultural Competence:
- Recognize and address the cultural factors that may impact an individual's experience of addiction and recovery. Ensure that educational materials and programs are culturally competent and inclusive.
Trauma-Informed Approach:
- Acknowledge the prevalence of trauma among individuals with addiction. Promote a trauma-informed approach in recovery support, treatment, and education.
Legal and Employment Considerations:
- Educate about the potential legal and employment challenges individuals in recovery may face. Provide information about rights, protections, and resources available to support reintegration into society.
Self-Care and Personal Responsibility:
- Empower individuals in recovery by emphasizing the importance of self-care, accountability, and taking responsibility for one's actions.
Remember that effective education involves open and non-judgmental communication. Tailor information to the needs of the audience and create a supportive and inclusive environment that encourages questions and discussion.
What educational approaches are effective in informing people about recovery from substance abuse?
Effective educational approaches for substance abuse recovery should be comprehensive, tailored to the individual's needs, and delivered in a supportive environment. These approaches should incorporate:
Psychoeducation: Providing clear and accurate information about substance abuse, its effects on the body and mind, and the recovery process.
Skills training: Teaching individuals coping mechanisms, stress management techniques, and relapse prevention strategies.
Motivational interviewing: Helping individuals explore their reasons for wanting to change and develop a strong motivation for recovery.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): Addressing distorted thinking patterns and beliefs that contribute to substance abuse.
Peer support: Connecting individuals with others who are in recovery, providing a sense of community and encouragement.
What are the key messages or information needed to educate individuals about recovery?
Key messages and information for educating individuals about recovery include:
Substance abuse is a treatable disorder.
Recovery is a journey, not a destination.
There are many different paths to recovery.
Recovery is possible, regardless of the severity of addiction.
Relapse is a common part of the recovery process.
Help is available, and there are many resources to support individuals in recovery.
Are there community programs or initiatives aimed at educating people about recovery?
Yes, there are numerous community programs and initiatives aimed at educating people about recovery. These programs often provide a combination of psychoeducation, skills training, peer support, and other resources to support individuals on their recovery journey. Some examples include:
Support groups: These groups provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals to share their experiences, receive encouragement, and learn from others in recovery.
Community organizations: Many local organizations offer educational programs, workshops, and events focused on substance abuse prevention and recovery.
Rehabilitation centers: These facilities provide comprehensive treatment programs that incorporate education, therapy, and support services.
How do cultural factors influence the education and understanding of recovery?
Cultural factors significantly influence the education and understanding of recovery. Different cultures may have varying beliefs about substance abuse, its causes, and effective treatment approaches. It is crucial to consider these cultural differences when designing and delivering educational programs to ensure they are culturally sensitive and relevant to the target audience.
Can personal stories or testimonials be effective in educating people about recovery?
Personal stories and testimonials can be powerful tools for educating people about recovery. Hearing firsthand accounts of the challenges and triumphs of others in recovery can provide hope, inspiration, and a sense of connection for those struggling with substance abuse. These stories can also help to dispel myths and stereotypes about addiction and demonstrate the possibility of successful recovery.
In addition to personal stories, educational programs can also incorporate multimedia resources, such as documentaries, films, and interactive online platforms, to engage learners and provide a variety of perspectives on substance abuse and recovery.