What are the Army MOS codes?
In the United States Army, MOS stands for "Military Occupational Specialty," and it is a code that designates a specific job or career field for military personnel. These codes help the Army organize and categorize its personnel based on their roles and responsibilities. Army MOS codes consist of a combination of letters and numbers. Here are some examples of Army MOS codes and the roles they represent:
11B - Infantryman: These soldiers are the backbone of the Army's combat forces. They engage in ground combat and are responsible for closing with and destroying the enemy.
68W - Combat Medic: Combat medics provide medical care to wounded soldiers on the battlefield. They are trained in both combat and medical skills.
25U - Signal Support Systems Specialist: These soldiers are responsible for maintaining and installing communication equipment and networks, ensuring that units can communicate effectively.
31B - Military Police: Military police are responsible for enforcing laws and regulations on military installations and providing security services.
35F - Intelligence Analyst: Intelligence analysts collect and analyze information to provide commanders with critical intelligence for decision-making.
91B - Wheeled Vehicle Mechanic: These soldiers maintain and repair Army vehicles, ensuring they are in working order for missions.
15T - UH-60 Helicopter Repairer: Soldiers in this MOS repair and maintain UH-60 Black Hawk helicopters, a critical asset for Army aviation.
19K - M1 Armor Crewman: Armor crewmen operate and maintain the M1 Abrams tank, a powerful armored vehicle.
12N - Horizontal Construction Engineer: These soldiers are involved in construction and engineering projects, such as building roads, bridges, and airstrips.
74D - Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear (CBRN) Specialist: CBRN specialists are trained to detect and respond to chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear threats.
These are just a few examples of Army MOS codes. Each code represents a specific job or specialty within the Army, and soldiers receive training and education related to their designated MOS to perform their duties effectively. The Army regularly updates and adds new MOS codes to adapt to evolving roles and technologies within the military.
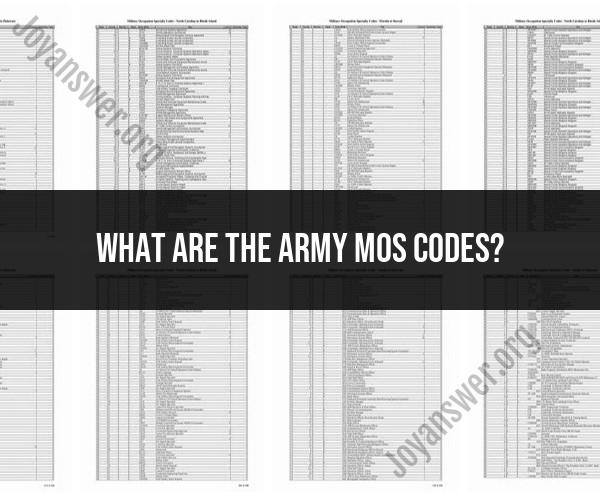
An Army MOS code, or Military Occupational Specialty code, is a nine-digit code that identifies a soldier's specific job. MOS codes are used to classify soldiers into different career fields and to determine their training and assignment requirements.
MOS codes are made up of three parts:
- The first two digits indicate the career field. For example, MOS code 11B is for infantry soldiers.
- The third digit indicates the subspecialty. For example, MOS code 11B1P is for infantry squad leaders.
- The last four digits indicate the additional qualifications that the soldier has, such as airborne training or language proficiency.
There are over 190 different MOS codes in the Army, and they cover a wide range of jobs, from combat specialties to support specialties. Some examples of MOS codes include:
- 11B: Infantryman
- 19D: Cavalry Scout
- 31B: Military Police
- 91A: Combat Medic
- 17C: Cyber Network Defender
- 25B: Information Systems Operator
Soldiers are typically assigned an MOS code during their initial military training. However, soldiers can also change their MOS code later in their careers if they meet the requirements.
MOS codes are important for soldiers because they determine their job duties, training, and assignment requirements. MOS codes also play a role in determining a soldier's pay and benefits.
Here are some tips for decoding Army MOS codes:
- The first two digits of the MOS code indicate the career field. You can find a list of Army career fields on the Army website.
- The third digit of the MOS code indicates the subspecialty. You can find a list of subspecialties for each career field on the Army website.
- The last four digits of the MOS code indicate the additional qualifications that the soldier has. You can find a list of additional qualifications on the Army website.
If you are interested in learning more about Army MOS codes, you can visit the Army website or talk to an Army recruiter.