What is clinical psychology primarily concerned with?
Clinical psychology is primarily concerned with the assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental and emotional disorders and issues in individuals. Its primary concerns include:
Assessment and Diagnosis: Clinical psychologists are trained to assess and diagnose various psychological disorders and conditions. This involves conducting comprehensive evaluations to understand a person's mental and emotional state, symptoms, and any underlying issues that may be contributing to their difficulties.
Treatment: Once a diagnosis is made, clinical psychologists develop and implement treatment plans tailored to the individual's needs. Treatment approaches may include psychotherapy (talk therapy), medication management (in collaboration with a psychiatrist), and other therapeutic interventions.
Psychotherapy: Clinical psychologists often provide psychotherapy or counseling to individuals, couples, families, and groups. They use evidence-based therapeutic techniques to help clients manage and overcome their mental health challenges.
Prevention: Clinical psychologists are also concerned with the prevention of mental health issues. They may work in schools, communities, or organizations to develop programs and strategies aimed at reducing the risk of mental health problems and promoting overall well-being.
Research: Clinical psychologists engage in research to advance our understanding of mental health and psychological disorders. They conduct studies to identify effective treatment methods, risk factors, and prevention strategies.
Consultation: Clinical psychologists may consult with other healthcare professionals, such as physicians, social workers, and educators, to provide expertise on mental health issues and contribute to holistic patient care.
Assessment Tools: They develop and utilize psychological assessment tools and tests to evaluate cognitive, emotional, and behavioral functioning. These assessments help in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Crisis Intervention: Clinical psychologists often work with individuals experiencing acute psychological crises, such as trauma, grief, or severe stress, to provide immediate support and interventions.
Client Education: They educate clients about their mental health conditions, coping strategies, and techniques for improving their emotional well-being.
Ethical and Legal Considerations: Clinical psychologists must adhere to ethical guidelines and legal regulations in their practice, ensuring the well-being and confidentiality of their clients.
In summary, clinical psychology is primarily concerned with the mental health and well-being of individuals. Clinical psychologists play a vital role in assessing, diagnosing, and treating mental and emotional disorders, as well as promoting mental health through prevention and research efforts.
Exploring the Domains of Clinical Psychology: Its Primary Concerns
Clinical psychology is a broad field that encompasses the study, assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental disorders. Clinical psychologists are concerned with a wide range of issues, including:
- Psychological well-being: Clinical psychologists are interested in promoting and enhancing psychological well-being. This includes helping people to develop coping skills, manage stress, and build resilience.
- Mental disorders: Clinical psychologists diagnose and treat mental disorders such as anxiety, depression, schizophrenia, and eating disorders. They also develop and implement prevention programs to reduce the risk of developing mental disorders.
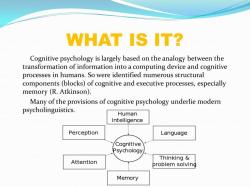
- Cognitive processes: Clinical psychologists study cognitive processes such as attention, memory, and problem-solving. They use this knowledge to develop and implement cognitive therapies, which are designed to help people change their thoughts and behaviors.
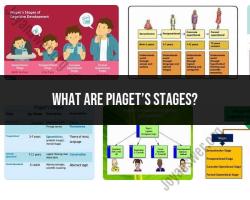
- Human development: Clinical psychologists study human development throughout the lifespan. They are interested in how people change over time and how these changes can impact their mental health.
- Social and cultural factors: Clinical psychologists recognize that social and cultural factors play a role in mental health. They consider these factors when diagnosing and treating mental disorders, and when developing and implementing prevention programs.
The Multifaceted Field of Clinical Psychology: Areas of Emphasis and Expertise
Clinical psychologists can specialize in a variety of areas, including:
- Child and adolescent psychology: Clinical psychologists who specialize in child and adolescent psychology focus on the mental health needs of children and adolescents. They work with children and adolescents who are experiencing a variety of challenges, including anxiety, depression, and behavioral problems.
- Adult psychology: Clinical psychologists who specialize in adult psychology focus on the mental health needs of adults. They work with adults who are experiencing a variety of challenges, including anxiety, depression, relationship problems, and work-related stress.
- Geropsychology: Clinical psychologists who specialize in geropsychology focus on the mental health needs of older adults. They work with older adults who are experiencing a variety of challenges, including cognitive decline, grief and loss, and chronic health conditions.
- Neuropsychology: Clinical psychologists who specialize in neuropsychology focus on the relationship between the brain and behavior. They work with people who have neurological disorders, such as stroke, brain injury, and dementia.
- Forensic psychology: Clinical psychologists who specialize in forensic psychology work with the legal system. They provide assessments, evaluations, and treatment to people who are involved in the legal system, such as criminal defendants and victims of crime.
Psychological Well-Being and Beyond: What Clinical Psychology Addresses
Clinical psychology addresses a wide range of issues, including psychological well-being, mental disorders, cognitive processes, human development, and social and cultural factors. Clinical psychologists work with people of all ages and backgrounds to help them improve their mental health and well-being.
Here are some specific examples of what clinical psychologists address:
- Anxiety: Clinical psychologists help people with anxiety disorders to manage their symptoms and live more fulfilling lives.
- Depression: Clinical psychologists help people with depression to overcome their negative thoughts and feelings and improve their mood.
- Trauma: Clinical psychologists help people who have experienced trauma to process their experiences and heal.
- Eating disorders: Clinical psychologists help people with eating disorders to develop healthy eating habits and body image.
- Addiction: Clinical psychologists help people with addiction to overcome their addiction and live more sober lives.
- Relationship problems: Clinical psychologists help couples and families to improve their communication and resolve conflict.
- Work-related stress: Clinical psychologists help people to manage work-related stress and improve their work-life balance.
Clinical psychology is a multifaceted field that addresses a wide range of issues. Clinical psychologists are trained to help people of all ages and backgrounds improve their mental health and well-being.