What can you do with a mathematics degree?
A mathematics degree opens doors to a wide range of careers because it builds strong analytical, problem-solving, and quantitative reasoning skills. Employers value math graduates for their ability to think logically, work with data, and solve complex problems. Here are some top career paths:
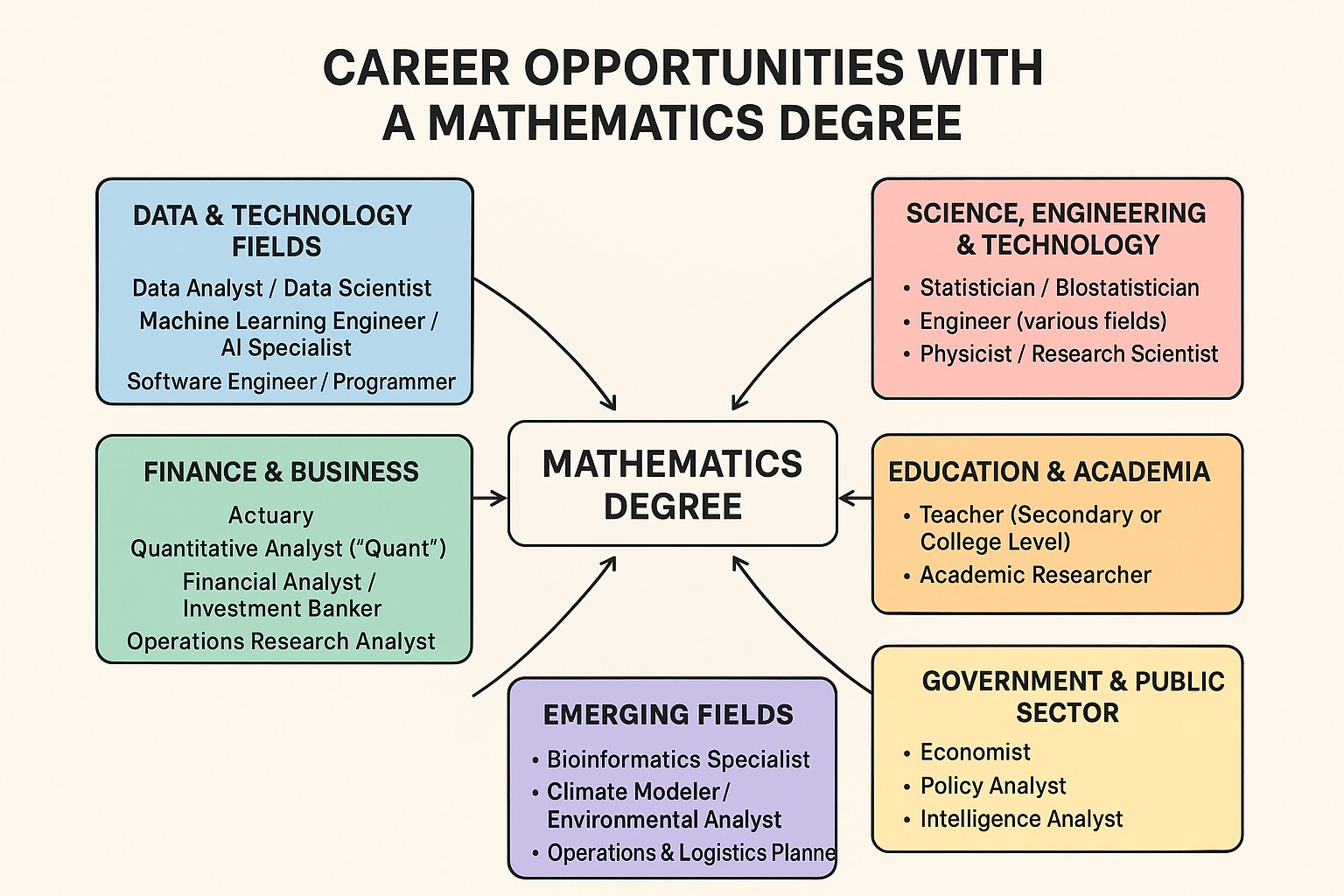
Career Opportunities with a Mathematics Degree
1. Data & Technology Fields
Data Analyst / Data Scientist – Analyze and interpret complex data to help businesses make decisions.
Machine Learning Engineer / AI Specialist – Apply mathematical models in artificial intelligence and predictive analytics.
Software Engineer / Programmer – Develop algorithms, applications, and systems.
Cryptographer / Cybersecurity Analyst – Use advanced math to secure data and networks.
2. Finance & Business
Actuary – Assess financial risks using statistics and probability, often in insurance and pensions.
Quantitative Analyst ("Quant") – Build models for trading, investment, and risk management.
Financial Analyst / Investment Banker – Apply math to forecast trends, value companies, and manage portfolios.
Operations Research Analyst – Optimize business processes, logistics, and decision-making.
3. Science, Engineering & Technology
Statistician / Biostatistician – Design experiments and analyze data in fields like healthcare, government, and research.
Engineer (various fields) – Apply mathematical modeling in mechanical, civil, electrical, or aerospace engineering.
Physicist / Research Scientist – Use advanced math for modeling and experimental design.
4. Education & Academia
Teacher (Secondary or College Level) – Teach mathematics, statistics, or related subjects.
Academic Researcher – Conduct research in pure or applied mathematics.
5. Government & Public Sector
Economist – Use math to analyze economic data and trends.
Policy Analyst – Apply statistics and models to evaluate government programs.
Intelligence Analyst – Work in national security using cryptography and data analysis.
6. Emerging Fields
Bioinformatics Specialist – Apply math and statistics to genetics and biology.
Climate Modeler / Environmental Analyst – Use mathematical models to study weather, climate, and sustainability.
Operations & Logistics Planner – Improve supply chain efficiency using optimization methods.
Key Takeaway
With a mathematics degree, you’re not limited to teaching or academia — you can enter finance, tech, research, government, or industry. The versatility of math skills makes graduates highly employable across many sectors.
A mathematics degree equips you with a versatile set of analytical and problem-solving skills, opening doors to a wide range of careers across numerous industries. These skills are highly valued in fields that require logical reasoning, data analysis, and abstract thinking.
Career Options with a Mathematics Degree
A mathematics degree can lead to diverse career paths, from traditional roles to emerging fields:
Actuary: Analyzes the financial costs of risk and uncertainty for insurance companies and other businesses. This is consistently one of the top-paying math careers.
Statistician: Designs surveys and experiments, collects, analyzes, and interprets data to solve problems in various fields, including business, engineering, and medicine.
Data Scientist/Analyst: Uses advanced mathematical and statistical methods to investigate complex business issues, identify inefficiencies, and inform strategic decisions through data.
Financial Analyst: Evaluates investment opportunities, manages portfolios, and assesses economic trends for banks, investment firms, and other financial institutions.
Computer Programmer/Software Developer: Writes, tests, and updates code for computer applications and software programs, often leveraging mathematical logic and algorithms.
Economist: Analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services, often using mathematical models and theories to understand economic behavior and policy.
Mathematician: Conducts fundamental research in mathematics or applies mathematical techniques to solve problems in science, management, and other areas.
Operations Research Analyst: Uses advanced mathematical methods to help organizations solve problems and make better decisions, particularly in optimizing processes and resource allocation.
Teacher/Professor: Teaches mathematics at various educational levels, from secondary school to university.
Cryptographer: Develops algorithms and security systems to encrypt sensitive information, a critical role in cybersecurity.
Skills Gained from a Mathematics Program
A mathematics program is not just about numbers; it's about developing a powerful set of transferable skills that are highly sought after by employers:
Quantitative Reasoning: The ability to use mathematical concepts and data to make sound conclusions.
Problem-Solving: Tackling complex issues with confidence, creativity, and logical application of mathematical principles.
Analytical Thinking: Breaking down intricate problems into manageable parts, analyzing them systematically, and identifying underlying patterns.
Logical Reasoning and Proof Construction: Developing the ability to construct rigorous logical arguments and solve problems through proof techniques, fostering precision in thought.
Data Analysis and Interpretation: Collecting, organizing, interpreting, and effectively presenting data, often using statistical methods and software.
Abstract Thinking: Dealing with highly abstract concepts and applying them to real-world situations.
Attention to Detail and Precision: Mathematics demands accuracy and meticulousness, which translates into careful work in any profession.
Computer Proficiency: Often includes skills in programming languages (e.g., Python, C++, Java) and software like Excel, MATLAB, or Maple, crucial for data manipulation and modeling.
Communication: Clearly presenting mathematical and logical arguments, and explaining complex ideas to both technical and non-technical audiences.
Adaptability and Independent Learning: The continuous evolution of mathematical fields encourages self-directed learning and adapting to new challenges.
Industries That Value Math Graduates
Mathematics graduates are valued in almost every sector due to their strong analytical and problem-solving capabilities. Key industries include:
Finance and Insurance: Banking, investment firms, actuarial science, credit analysis, and risk management.
Technology and Computing: Software development, data science, cybersecurity (cryptography), information security, and systems analysis.
Government and Public Service: Federal government agencies (e.g., Department of Defense, NSA), public policy, and research institutions.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals: Biostatistics, healthcare analytics, medical research, and pharmaceutical companies.
Consulting: Management consulting, operational research, and specialized analytical consulting.
Education: Teaching at secondary schools, colleges, and universities, as well as educational research.
Engineering: Designing algorithms, developing mathematical models, and solving complex technical problems in various engineering disciplines (e.g., aeronautical, mechanical).
Market Research: Analyzing market conditions and consumer behavior to inform business and marketing strategies.
Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Optimizing supply chains, inventory management, and delivery routes.
Advanced Studies and Certifications in Mathematics
To specialize or advance further, mathematics graduates can pursue various educational and certification opportunities:
Graduate Degrees:
Master's (M.A. or M.S.) in Mathematics, Applied Mathematics, Statistics, Data Science, or Financial Engineering: These degrees provide deeper specialization and are often required for higher-level analytical roles, research, or university teaching.
Doctorate (Ph.D.) in Mathematics or related fields: Essential for academic research and professorships, and highly valued in advanced R&D roles in industry and government.
Professional Certifications:
Actuarial Exams: A series of rigorous exams (e.g., offered by the Society of Actuaries or Casualty Actuarial Society) required to become a fully qualified actuary.
Financial Certifications: Certifications like the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) are beneficial for financial analyst roles.
Data Science Certifications: Various certifications in data analysis, machine learning, and specific programming languages (e.g., Python, R) enhance marketability.
Graduate Certificates in Mathematics: Programs designed for professionals to update or deepen their mathematical content knowledge, often to teach dual enrollment or undergraduate courses.
Tips to Leverage a Math Degree for Career Growth
To maximize career potential with a mathematics degree, consider these strategies:
Gain Diverse Experience: Seek internships, co-ops, or entry-level positions in various industries to understand different applications of mathematics and identify your interests.
Develop Complementary Skills: While your math degree provides a strong foundation, enhance it with skills in:
Programming: Master languages like Python, R, or C++ for data manipulation, modeling, and software development.
Statistical Software: Become proficient in tools like R, SAS, or SPSS.
Data Visualization: Learn tools like Tableau or Power BI to effectively communicate insights.
Communication Skills: Practice presenting complex mathematical ideas clearly and concisely to both technical and non-technical audiences.
Network: Attend industry events, join professional organizations (e.g., AMS, SIAM, ASA), and connect with alumni to explore opportunities and gain insights.
Specialize: Identify a niche area of interest (e.g., quantitative finance, cryptography, biostatistics) and pursue advanced coursework or certifications in that domain.
Continuous Learning: The fields that value math are constantly evolving. Stay updated with new techniques, software, and industry trends through online courses, workshops, and further education.
Build a Portfolio: For data-oriented roles, create projects that showcase your analytical abilities and problem-solving skills, even if they are personal projects.
Emphasize Transferable Skills: When applying for jobs, explicitly highlight how your math background has equipped you with strong analytical, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities.