Density Calculator
Enter the block's measurements to see the results here.
Calculated Volume
--
Calculated Density
--
How It Works
What is the formula for calculating density?
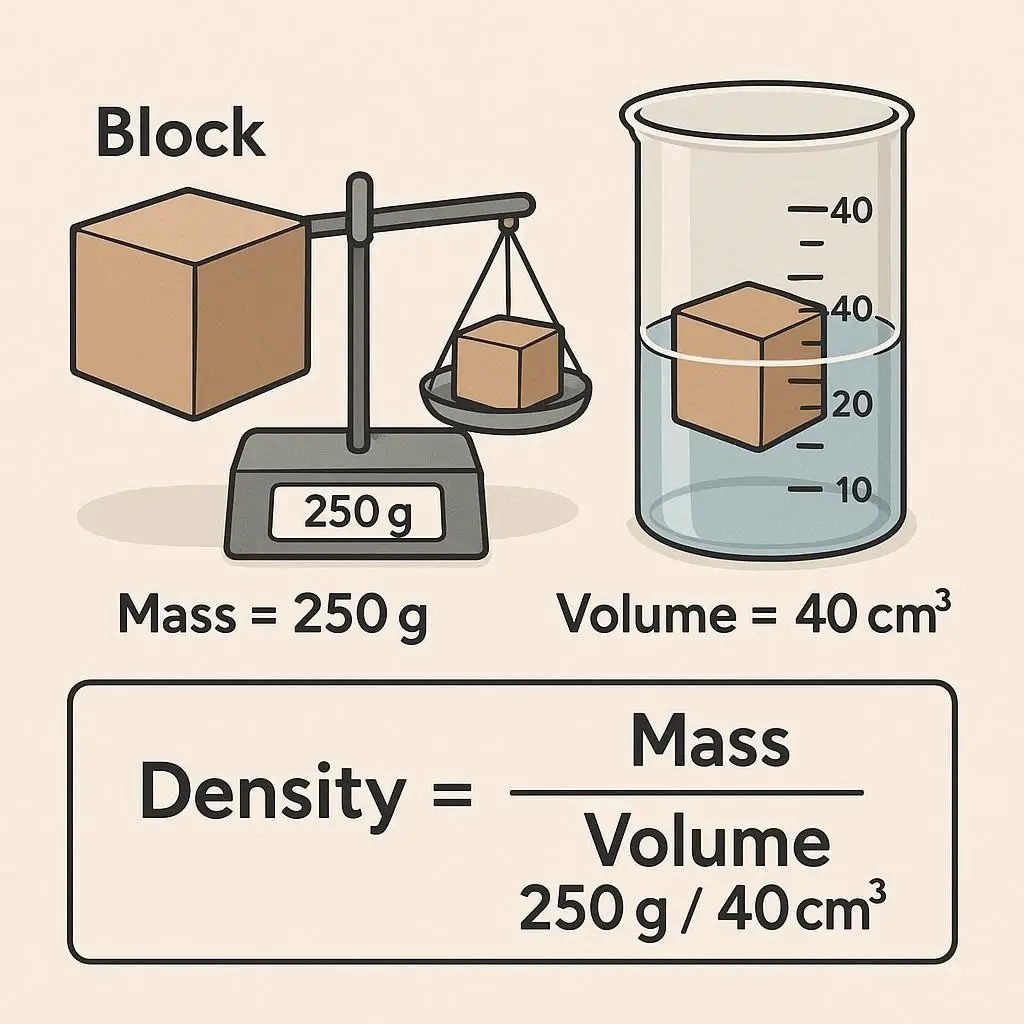
+Density is a fundamental property of matter that describes how much "stuff" is packed into a given space. The formula is:
Density (ρ) = Mass (m) / Volume (V)
- ρ (rho) is the symbol for density.
- m represents the mass of the object.
- V represents the volume the object occupies.
How do I measure the mass and volume?
+Measuring Mass (m)
To find the mass of the block, you need a scale. Place the block on the scale and record the measurement. The standard unit for mass in scientific contexts is grams (g) or kilograms (kg).
Measuring Volume (V) of a Block
For a regularly shaped object like a rectangular block, the volume is calculated by multiplying its length, width, and height. Use a ruler or calipers for accurate measurements.
Volume = Length × Width × Height
Ensure all three measurements are in the same unit, such as centimeters (cm) or meters (m).
What are the standard units for density?
+The units for density depend on the units used for mass and volume. It's crucial to be consistent. Common standard units include:
- grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³): Often used for solids and liquids. For example, the density of water is approximately 1 g/cm³.
- kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³): The standard SI unit, often used in engineering and physics. 1 g/cm³ is equal to 1000 kg/m³.
Our calculator assumes grams and centimeters, resulting in a density of g/cm³.
A Deeper Dive
Density isn't always constant. External factors, like temperature, can cause it to change. Explore the chart below to see how this works for a common substance: water.
How Temperature Affects Density (Example: Water)
As you heat most substances, they expand, increasing their volume and thus decreasing their density. Water is unique because it's densest at 4°C (39.2°F). The chart below shows this unusual behavior.