How do you calculate heparin units per hour?
Calculating heparin units per hour involves determining the infusion rate at which a patient should receive a continuous intravenous (IV) infusion of heparin to achieve a specific therapeutic effect, such as preventing or treating blood clots. Heparin is an anticoagulant medication that is administered in units per hour to maintain the desired level of anticoagulation in the blood. Here's a practical guide on how to calculate heparin units per hour:
Note: This calculation is typically performed by healthcare professionals, such as nurses or pharmacists, and should be based on the specific orders and protocols established by the healthcare provider.
Step 1: Gather Information
Heparin Order: Obtain the heparin order from the healthcare provider. This order should specify the target activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) or other relevant parameter.
Heparin Concentration: Determine the concentration of the heparin solution prescribed for the IV infusion. Common concentrations include 1,000 units/mL or 5,000 units/mL.
Patient Weight: Know the patient's weight in kilograms (kg), as dosages may be weight-based.
Step 2: Calculate the Initial Bolus (if applicable)
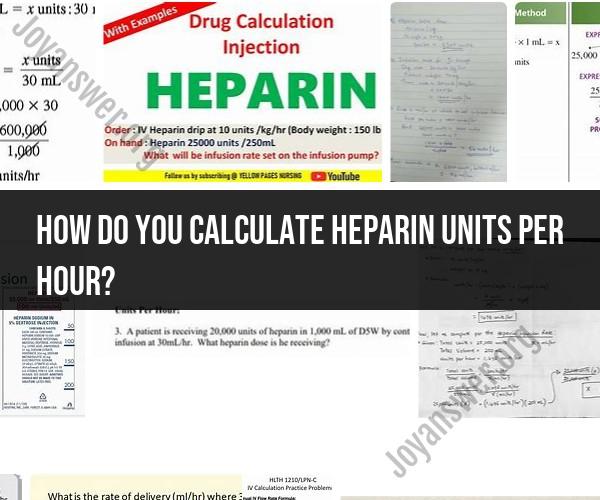
In some cases, a loading or initial bolus dose of heparin may be prescribed. If so, calculate the initial bolus based on the order. For example, if the order is for 80 units/kg as a bolus and the patient weighs 70 kg:
Initial Bolus = 80 units/kg × 70 kg = 5,600 units
Step 3: Determine the Maintenance Infusion Rate
To calculate the maintenance infusion rate in units per hour, you can use the following formula:
Target Rate (units/kg/hour): The target rate depends on the specific order and the patient's condition. For example, a common starting point for prophylaxis is 18 units/kg/hour.
Patient Weight (kg): Use the patient's weight in kilograms.
Heparin Concentration (units/mL): The concentration of the heparin solution being used for the infusion (e.g., 1,000 units/mL or 5,000 units/mL).
Step 4: Set the Infusion Pump
Program the infusion pump with the calculated maintenance infusion rate (in units per hour). Ensure that the pump is properly calibrated and set to deliver the correct dosage.
Step 5: Monitor and Adjust
Continuous monitoring of the patient's aPTT or other relevant parameters is essential to ensure that the desired therapeutic effect is achieved. The heparin infusion rate may need to be adjusted based on the patient's response and ongoing clinical assessment.
Please note that this calculation is for informational purposes and should not replace guidance from a qualified healthcare professional. The administration of heparin is a critical medical intervention that requires proper training and adherence to established protocols and guidelines. Always follow the orders and recommendations of the healthcare provider and facility-specific policies when administering medications like heparin.
To calculate heparin units per hour, you will need to know the following:
- The heparin concentration in units per milliliter (U/mL)
- The desired heparin dose in units per kilogram per hour (U/kg/hr)
- The patient's weight in kilograms (kg)
Once you have this information, you can use the following formula:
Heparin units per hour = Heparin concentration (U/mL) * Desired heparin dose (U/kg/hr) * Patient's weight (kg)
For example, if you are using a heparin solution with a concentration of 25,000 U/mL and you want to give a patient a heparin dose of 18 U/kg/hr, and the patient weighs 75 kg, then the heparin units per hour would be calculated as follows:
Heparin units per hour = 25,000 U/mL * 18 U/kg/hr * 75 kg = 1350 U/hr
Therefore, the patient would need to receive 1350 units of heparin per hour.
Nursing Protocols: Calculating Heparin Infusion Rates for Patient Care
Nursing protocols typically specify the desired heparin dose in U/kg/hr. Nurses can then use the above formula to calculate the heparin units per hour based on the patient's weight and the heparin concentration.
It is important to note that heparin is a potent medication and that it is important to calculate the heparin units per hour accurately. If the heparin dose is too high, it can lead to bleeding complications. If the heparin dose is too low, it may not be effective in preventing blood clots.
Here are some additional tips for calculating heparin units per hour:
- Always double-check your calculations.
- Use a heparin calculator if available.
- Be aware of the heparin concentration of the solution you are using.
- Take into account the patient's weight and any other relevant medical conditions.
If you have any questions or concerns about calculating heparin units per hour, please consult with a pharmacist or other healthcare professional.