What does it mean to be OSHA compliant?
Being OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) compliant means that a workplace has implemented and maintains a set of practices and procedures that comply with the regulations and standards set forth by OSHA. OSHA is a federal agency within the United States Department of Labor that is responsible for ensuring safe and healthful working conditions for employees.
Key elements of OSHA compliance include:
Adherence to OSHA Standards:
- Employers must follow OSHA regulations and standards relevant to their industry and specific workplace hazards. These standards cover a wide range of topics, including general safety, hazard communication, electrical safety, machine guarding, respiratory protection, and more.
Development of Safety Programs:
- Employers are often required to develop and implement safety programs tailored to their workplace's specific hazards. This may include written safety plans, training programs, and procedures for addressing potential workplace dangers.
Employee Training:
- Providing employees with proper training on workplace hazards, safe work practices, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) is a crucial aspect of OSHA compliance. Training should be ongoing and cover new hazards as they arise.
Recordkeeping:
- Employers must maintain accurate records of workplace injuries and illnesses. OSHA's recordkeeping requirements include the recording and reporting of workplace injuries and illnesses on the OSHA 300 Log.
Inspections and Audits:
- Periodic workplace inspections and safety audits help identify and address potential hazards. Employers should conduct self-audits and be prepared for inspections by OSHA compliance officers.
Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Employers must assess workplace hazards and provide appropriate PPE to employees as necessary. This includes items such as safety glasses, gloves, respiratory protection, and other equipment to mitigate specific risks.
Hazard Communication:
- Employers must have a hazard communication program that includes the labeling of hazardous chemicals, the provision of safety data sheets (SDS), and employee training on the potential hazards of workplace chemicals.
Emergency Preparedness:
- Establishing and implementing emergency response and evacuation plans is essential for OSHA compliance. Employers must have procedures in place to address potential emergencies such as fires, chemical spills, or other disasters.
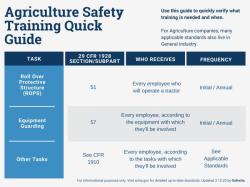
Machine Guarding and Equipment Safety:
- Ensuring that machines and equipment are properly guarded and maintained is a key component of OSHA compliance. This includes regular inspections and preventive maintenance.
Fall Protection:
- Compliance with fall protection standards is critical, especially in industries where employees may be exposed to fall hazards. This may involve the use of guardrails, safety nets, personal fall arrest systems, or other protective measures.
Anti-Retaliation Protections:
- OSHA prohibits employers from retaliating against employees who exercise their rights under the OSH Act. Employees have the right to report unsafe conditions to OSHA without fear of reprisal.
Achieving and maintaining OSHA compliance is an ongoing process that requires a commitment to workplace safety. Employers should stay informed about changes in OSHA regulations, assess and address workplace hazards, provide continuous training, and actively involve employees in the safety process. Non-compliance with OSHA regulations can result in penalties, fines, and potential legal consequences for employers.
Achieving and maintaining OSHA compliance is crucial for every company or organization in the United States. It ensures a safe and healthy work environment for employees, prevents accidents and injuries, and avoids hefty penalties. Let's dive into the specifics:
1. What Encompasses OSHA Compliance?
- Adherence to OSHA Regulations: Following specific safety standards established by OSHA for different industries and hazards. These cover various aspects like workplace hazard identification, exposure limits, personal protective equipment, emergency procedures, and recordkeeping.
- Developing and Implementing Safety Programs: Creating a comprehensive safety program tailored to your organization's workplace and unique hazards. This includes training employees on safety procedures, conducting regular inspections, and fostering a culture of safety awareness.
- Maintaining Proper Documentation: Regularly updating and maintaining records related to accidents, injuries, inspections, and safety training. This ensures transparency and provides evidence of compliance during potential OSHA inspections.
2. Fundamental Requirements for Compliance:
- General Duty Clause: This overarching principle requires employers to provide a workplace free from recognized hazards that can cause serious injury or death.
- Specific Standards: Various specific standards exist for different industries and hazards, covering topics like exposure limits to chemicals, machine guarding, fall protection, and electrical safety.
- Employee Training: Providing appropriate training to employees on specific job hazards, safety procedures, and emergency response protocols is mandatory.
3. Measuring and Assessing Compliance:
- Self-Evaluation: Companies can conduct internal audits and hazard assessments to identify potential risks and ensure compliance with relevant standards.
- OSHA Inspections: OSHA randomly or in response to complaints, conducts inspections to assess compliance and may issue citations for violations.
- Injury and Illness Rates: High rates of work-related injuries and illnesses can indicate potential compliance issues and raise red flags for OSHA.
4. Continuous Compliance Steps:
- Invest in Safety Culture: Build a strong safety culture by actively engaging employees in safety programs, encouraging open communication about hazards, and recognizing safe work practices.
- Regularly Review and Update Procedures: Adapt your safety programs and procedures as your workplace or processes change to maintain effectiveness.
- Seek Expert Guidance: Utilize industry resources, consultants, and safety professionals to ensure your understanding and implementation of evolving OSHA regulations.
5. Penalties for Non-Compliance:
- Fines: OSHA can impose significant fines for violations, ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars per violation, depending on the severity and nature of the non-compliance.
- Citations: Citations require corrective action within specified timelines and can escalate to further fines if not addressed promptly.
- Criminal Charges: In extreme cases of willful negligence or repeated violations, criminal charges may be filed against company officials.
Remember, OSHA compliance is not just about avoiding penalties; it's about creating a safe and healthy work environment for your employees. By prioritizing safety, building a strong safety culture, and actively maintaining compliance, you can boost employee morale, productivity, and long-term success.