What is FMLA and absence management?
FMLA (Family and Medical Leave Act):
FMLA, or the Family and Medical Leave Act, is a United States federal law that provides eligible employees with the right to take job-protected leave for specific family and medical reasons. The primary purposes of FMLA are to balance the demands of the workplace with the needs of families and to promote the stability and economic security of families.
Key features of FMLA include:
Eligibility:
- To be eligible for FMLA leave, employees must work for a covered employer, have worked for the employer for at least 12 months, and have worked a specified number of hours during the 12 months preceding the leave.
Reasons for Leave:
- FMLA allows eligible employees to take up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in a 12-month period for specific reasons, including the birth and care of a newborn child, the placement of a child for adoption or foster care, the care of a spouse, child, or parent with a serious health condition, or the employee's own serious health condition.
Job Protection:
- During FMLA leave, employers are generally required to maintain the employee's health benefits and restore the employee to the same or an equivalent position when the leave ends. Retaliation against employees for taking FMLA leave is prohibited.
Intermittent Leave:
- FMLA leave can be taken intermittently or on a reduced schedule when medically necessary. This means that eligible employees can take leave in separate blocks of time or reduce their regular working hours.
Certification:
- Employers may require certification of the need for FMLA leave, such as medical documentation for a serious health condition. Certification helps ensure that the leave is taken for a qualifying reason.
Military Family Leave:
- FMLA provides eligible employees with certain military family leave entitlements, such as leave for a qualifying exigency arising from a covered military member's active duty or for the care of a covered service member with a serious injury or illness.
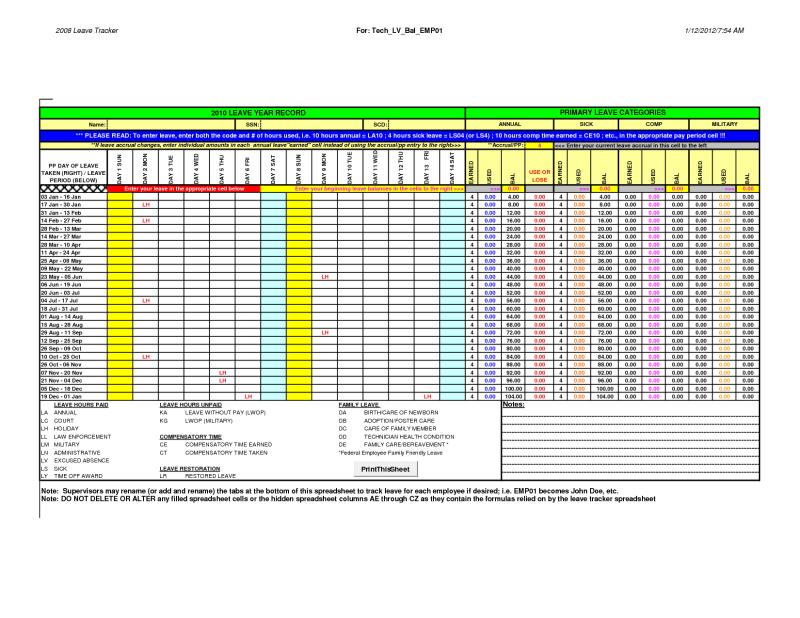
Absence Management:
Absence management refers to the strategic and coordinated approach that organizations take to manage and track employee absences from work. It involves policies, procedures, and tools designed to monitor, analyze, and address employee leave, whether for reasons covered by laws like FMLA or for other reasons such as vacation, sick leave, or personal time off.
Key aspects of absence management include:
Absence Policies:
- Organizations typically have policies in place outlining the procedures for requesting and reporting absences. This includes information on how employees should notify their employers about planned or unplanned leaves.
Tracking and Recording:
- Absence management systems or tools are used to track and record employee absences. These systems help organizations monitor attendance patterns, identify trends, and ensure compliance with relevant laws and policies.
Compliance:
- Absence management practices often involve ensuring compliance with applicable labor laws, including FMLA and other state-specific regulations. Organizations need to stay informed about legal requirements and adjust their policies accordingly.
Communication:
- Effective communication is crucial in absence management. Employers need to communicate leave policies clearly to employees and keep lines of communication open to address any issues that may arise during an absence.
Return-to-Work Programs:
- Organizations may implement return-to-work programs to facilitate a smooth transition for employees returning from leave. This may involve accommodations for employees with disabilities or phased returns to full-time work.
Technology Solutions:
- Many organizations use absence management software or integrated HR systems to automate and streamline the process of tracking employee absences. These systems can help manage leave balances, track accruals, and generate reports.
Training for Managers:
- Managers play a crucial role in absence management. Providing training to managers on leave policies, legal requirements, and effective communication can help ensure consistent application of policies across the organization.
By effectively managing absences, organizations can promote a healthy work-life balance, comply with legal requirements, and maintain productivity. Combining absence management practices with an understanding of laws like FMLA helps create a supportive and compliant work environment.
Understanding FMLA and its Impact on Absence Management:
1. The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA):
The FMLA is a federal law in the United States that entitles eligible employees to up to 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave for certain qualifying reasons, including:
- Personal medical leave for the employee's own serious health condition.
- Family leave to care for a spouse, child, or parent with a serious health condition.
- Bonding leave to care for a new child for the first year after birth or adoption.
- Military leave for certain situations involving family members serving in the Armed Forces.
2. Impact on Employee Absences and Workplace Policies:
- Reduced Absences: By providing job protection during leave, FMLA can encourage employees to return to work and reduce overall absences.
- Policy Alignment: Employers should ensure their absence management policies align with FMLA leave entitlements and procedures.
- Clear Communication: Open communication regarding leave requests and FMLA eligibility is crucial.
3. Employer Responsibilities:
- Notice and Documentation: Employers must inform employees of their FMLA rights and respond to leave requests promptly. This often involves requesting medical certification.
- Job Protection: Employers must maintain the employee's health benefits and reinstate them to their original position or an equivalent one upon return.
- Confidentiality: FMLA medical information must be kept confidential.
4. Implementing FMLA-compliant Absence Management Strategies:
- Centralized Leave Tracking: A system for tracking all leave requests, including FMLA leaves, ensures compliance and consistency.
- Flexible Work Arrangements: Consider offering options like remote work or flexible hours to accommodate employees needing leave.
- Leave of Absence Policy Review: Regularly review and update your absence policies to ensure they meet FMLA requirements.
5. Resources for FMLA and Absence Management:
- U.S. Department of Labor: https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd/fmla
- Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM): https://www.shrm.org/pages/default.aspx
- FMLASource: https://www.fmlasource.com/
- Your Legal Counsel: Consulting with an attorney specialized in employment law is recommended for complex situations.
By understanding FMLA and implementing effective absence management strategies, employers can navigate leave requests seamlessly and maintain a positive workplace environment.