What is a company structure?
A company structure, also known as an organizational structure, refers to the framework or design that outlines how a company is organized and how its various components, such as departments, roles, and responsibilities, are arranged and interact within the organization. The company structure defines the hierarchy, relationships, and communication channels among employees and different parts of the business.
Key components of a company structure include:
Hierarchy and Chain of Command:
- The company structure typically establishes the hierarchy of authority, from top management down to lower-level employees. This hierarchy defines who reports to whom and the chain of command within the organization.
Departments and Divisions:
- Companies are often organized into different departments or divisions, each responsible for specific functions or areas of the business, such as finance, marketing, operations, and human resources.
Roles and Job Positions:
- Within each department or division, there are various job positions and roles, each with its own set of responsibilities and reporting relationships.
Reporting Relationships:
- The structure clarifies reporting relationships, indicating who supervises and manages whom. This ensures accountability and efficient communication within the organization.
Span of Control:
- The span of control refers to the number of employees or subordinates directly supervised by a manager or supervisor. It can vary depending on the organizational level and size of the company.
Centralization vs. Decentralization:
- Company structures can be centralized, where decision-making authority is concentrated at the top of the hierarchy, or decentralized, where decision-making authority is distributed across various levels and departments.
Matrix Structure:
- Some organizations use a matrix structure, where employees report to both a functional manager and a project or team manager. This structure is common in project-based or matrix organizations.
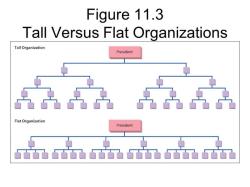
Flat vs. Tall Organizations:
- The structure also defines whether the organization is flat (few hierarchical levels) or tall (many hierarchical levels). Flat organizations tend to have a broader span of control, while tall organizations have more levels of management.
Functional vs. Divisional vs. Hybrid Structures:
- Companies can have different structural models. Functional structures group employees by their job functions (e.g., marketing, finance), divisional structures group them by products or geographical regions, and hybrid structures combine elements of both.
Organizational Chart:
- Organizational charts are visual representations of the company's structure, showing the relationships between different departments, positions, and employees.
Culture and Communication:
- The company structure influences the organization's culture and communication patterns. For example, a hierarchical structure may lead to more formal communication, while a flat structure may encourage open and informal communication.
The choice of company structure depends on various factors, including the company's size, industry, goals, and management philosophy. An effective structure aligns with the company's strategy and facilitates efficient operations, decision-making, and communication. It should also support the company's long-term objectives and adapt to changing circumstances as needed.
- What is a company structure and how does it define an organization's setup?
A company structure is the way in which a company is organized and managed. It defines the lines of authority, communication, and decision-making within the company. The company structure also determines how resources are allocated and how work is performed.
The company structure is typically defined in an organizational chart, which shows the different positions within the company and how they are related. The organizational chart also shows the chain of command within the company, which is the hierarchy of authority.
- How are company structures designed and what are the various types of organizational frameworks?
Company structures are designed to achieve the company's goals and objectives. The structure should be flexible enough to adapt to change, but it should also be stable enough to provide employees with a sense of direction and purpose.
There are a number of different types of organizational frameworks, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common types of organizational frameworks include:
- Functional structure: This is the most common type of organizational structure. In a functional structure, the company is divided into departments based on function, such as sales, marketing, finance, and accounting.
- Divisional structure: This type of organizational structure is based on product, market, or geography. In a divisional structure, each division has its own sales, marketing, finance, and accounting functions.
- Matrix structure: This type of organizational structure combines elements of functional and divisional structures. In a matrix structure, employees have two reporting managers, one from their functional department and one from their product or project team.
- Flat structure: This type of organizational structure has few or no levels of management. In a flat structure, employees have a great deal of autonomy and decision-making authority.
- How does the choice of company structure impact business operations and management?
The choice of company structure can have a significant impact on business operations and management. The structure can affect how decisions are made, how information is communicated, and how resources are allocated.
Here are some of the ways in which the choice of company structure can impact business operations and management:
- Decision-making: In a centralized structure, decisions are made at the top of the hierarchy. In a decentralized structure, decisions are made at lower levels of the hierarchy.
- Information flow: In a centralized structure, information flows up and down the hierarchy. In a decentralized structure, information flows more horizontally across the organization.
- Resource allocation: In a centralized structure, resources are allocated from the top of the hierarchy. In a decentralized structure, resources are allocated at lower levels of the hierarchy.
The choice of company structure is an important decision that should be made based on the company's goals and objectives, its size, and its industry.