What are the types of Applied Ethics?
Applied Ethics involves the application of ethical principles and theories to specific practical issues or domains. It addresses moral questions and dilemmas in real-world contexts. Here are some common types of Applied Ethics, each focusing on ethical considerations within a specific field:
Bioethics:
- Bioethics deals with ethical issues arising in the field of biology and healthcare. It includes considerations related to medical treatment, research ethics, genetic engineering, reproductive technologies, end-of-life decisions, and the rights and well-being of patients.
Business Ethics:
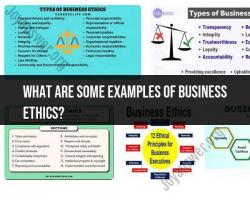
- Business Ethics explores ethical considerations within the business and corporate world. It addresses issues such as corporate social responsibility, fair business practices, ethical decision-making, corporate governance, and the social impact of business activities.
Environmental Ethics:
- Environmental Ethics focuses on ethical concerns related to the environment and the impact of human activities on the natural world. It addresses issues such as environmental conservation, sustainable development, climate change, and the ethical treatment of animals.
Information Ethics:
- Information Ethics deals with ethical issues in the use and dissemination of information and technology. It includes considerations related to privacy, data security, intellectual property, digital rights, and the ethical use of emerging technologies.
Engineering Ethics:
- Engineering Ethics addresses ethical dilemmas within the field of engineering. It includes considerations related to professional conduct, safety, environmental impact, and the ethical responsibilities of engineers in designing and implementing technology.
Media Ethics:
- Media Ethics focuses on ethical considerations in the field of journalism and media. It includes issues such as truthfulness, objectivity, freedom of the press, the public's right to know, and the ethical use of new media technologies.
Legal Ethics:
- Legal Ethics examines ethical considerations within the legal profession. It includes issues related to attorney-client privilege, conflicts of interest, confidentiality, professional conduct, and the responsibilities of lawyers in the justice system.
Political Ethics:
- Political Ethics explores ethical questions within the realm of politics and government. It addresses issues such as political corruption, transparency, accountability, human rights, and the ethical conduct of political leaders.
Educational Ethics:
- Educational Ethics focuses on ethical considerations within the field of education. It includes issues related to academic integrity, student-teacher relationships, diversity and inclusion, and ethical decision-making in educational institutions.
Military Ethics:
- Military Ethics addresses ethical questions related to the conduct of armed forces. It includes considerations such as the just war theory, rules of engagement, treatment of prisoners of war, and the ethical responsibilities of military personnel.
Sports Ethics:
- Sports Ethics examines ethical issues within the realm of sports and athletics. It includes considerations related to fair play, sportsmanship, performance-enhancing drugs, violence in sports, and the ethical responsibilities of athletes and sports organizations.
Technology Ethics:
- Technology Ethics encompasses ethical considerations in the development and use of technology. It includes issues related to artificial intelligence, automation, privacy, data ethics, and the societal impact of technological advancements.
These are just a few examples of the many subfields within Applied Ethics. Each area involves the application of ethical principles to address specific challenges and dilemmas unique to that field. Ethical frameworks within Applied Ethics provide guidance for individuals, professionals, and organizations as they navigate complex moral questions in their respective domains.
What are the branches or categories within Applied Ethics?
Applied Ethics, the branch of philosophy that analyzes practical moral problems, encompasses a vast and diverse array of subfields. While there's no single universally accepted taxonomy, some of the most commonly recognized branches or categories within Applied Ethics include:
1. Professional Ethics: This category focuses on ethical concerns specific to different professions, like:
- Business Ethics: Examines ethical dilemmas faced in business, such as corporate social responsibility, insider trading, marketing ethics, and fair labor practices.
- Medical Ethics: Deals with ethical issues in healthcare, like informed consent, euthanasia, abortion, and genetic engineering.
- Legal Ethics: Explores ethical obligations of lawyers and judges, including conflicts of interest, confidentiality, and truthfulness.
- Engineering Ethics: Addresses ethical challenges faced by engineers, such as environmental impact, safety considerations, and whistle-blowing.
2. Social and Political Ethics: This category explores ethical issues related to broader society and governance, including:
- Environmental Ethics: Investigates our moral obligations towards the environment, addressing issues like sustainability, pollution, and animal welfare.
- Bioethics: Examines ethical dilemmas arising from advancements in science and technology, such as human cloning, gene editing, and end-of-life care.
- Political Philosophy: Analyzes ethical principles underlying political systems, exploring issues like justice, equality, and freedom.
- Peace and War Ethics: Examines the morality of using violence, questioning the justification for war and exploring alternatives to conflict resolution.
3. Individual and Personal Ethics: This category focuses on ethical concerns related to individual behavior and well-being, including:
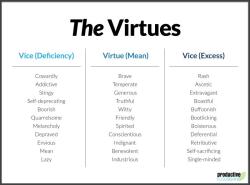
- Virtue Ethics: Investigates the role of character traits and virtues in living a good life, exploring concepts like courage, honesty, and compassion.
- Sexual Ethics: Addresses ethical questions surrounding intimacy, relationships, and reproductive choices.
- Animal Ethics: Examines our moral obligations towards non-human animals, considering issues like animal testing, factory farming, and animal rights.
- Technological Ethics: Explores the ethical implications of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, social media, and privacy concerns.
4. Global Ethics: This category examines ethical challenges arising from interconnectedness and globalization, including:
- International Ethics: Focuses on ethical considerations in international relations, such as human rights, international law, and global justice.
- Intercultural Ethics: Examines ethical issues arising from cultural differences and interactions, promoting understanding and respect for diverse moral perspectives.
- Development Ethics: Explores ethical challenges related to international development initiatives, addressing issues like poverty, inequality, and environmental sustainability.
Remember, these categories are not mutually exclusive. Many ethical issues fall within multiple branches, and the boundaries between them are often blurred. However, this categorization offers a framework for understanding the vast and diverse landscape of Applied Ethics and identifying specific areas of interest within this dynamic field.
Feel free to ask if you'd like to delve deeper into any specific branch of Applied Ethics, explore how different categories intersect, or discuss real-world ethical dilemmas within a particular area. I'm happy to share my knowledge and engage in further discussion on this fascinating subject!