What is treatment for left ventricular hypertrophy?
The treatment for left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) often involves addressing the underlying cause and managing associated risk factors. LVH is frequently linked to conditions such as hypertension (high blood pressure) and other cardiovascular diseases. Here are insights into the treatment options for left ventricular hypertrophy:
1. Blood Pressure Management:
- Antihypertensive Medications:
- The primary cause of LVH is often hypertension. Controlling blood pressure is a key aspect of treatment. Medications such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers are commonly prescribed.
2. Lifestyle Modifications:
Dietary Changes:
- Adopting a heart-healthy diet, such as the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which includes reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium-rich foods.
Regular Exercise:
- Engaging in regular physical activity, as exercise can help lower blood pressure and contribute to overall cardiovascular health.
Weight Management:
- Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Smoking Cessation:
- Quitting smoking, as smoking is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.
Alcohol Moderation:
- Moderating alcohol intake, as excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to hypertension.
3. Medications for Underlying Conditions:
Cholesterol-Lowering Medications:
- Statins or other cholesterol-lowering medications may be prescribed if elevated cholesterol levels are contributing to cardiovascular risk.
Diabetes Management:
- For individuals with diabetes, maintaining good blood sugar control is crucial in managing cardiovascular risk.
4. Monitoring and Follow-Up:
Regular Medical Check-ups:
- Regular monitoring of blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health through routine medical check-ups.
Echocardiography:
- Periodic echocardiograms (ultrasound of the heart) to assess the size and function of the left ventricle and monitor changes in left ventricular hypertrophy.
5. Interventional Procedures:
Catheter Ablation:
- In some cases, catheter ablation procedures may be considered, especially if left ventricular hypertrophy is associated with arrhythmias.
Valve Repair or Replacement:
- If LVH is related to aortic stenosis or other valvular disorders, surgical procedures such as valve repair or replacement may be necessary.
6. Lifestyle Changes:
Stress Management:
- Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga.
Salt Restriction:
- Limiting salt intake to help control blood pressure.
Sleep Hygiene:
- Ensuring adequate and quality sleep, as sleep plays a role in cardiovascular health.
Important Considerations:
Treatment approaches may vary based on individual health conditions and factors. A healthcare provider will tailor the treatment plan to the specific needs of the patient.
Adherence to prescribed medications and lifestyle modifications is crucial for managing left ventricular hypertrophy and preventing complications.
It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive assessment and personalized treatment plan.
The goal of treatment for left ventricular hypertrophy is to reduce the workload on the heart, manage contributing factors, and improve overall cardiovascular health. Regular communication with healthcare providers and active participation in one's own care are essential components of a successful treatment approach.
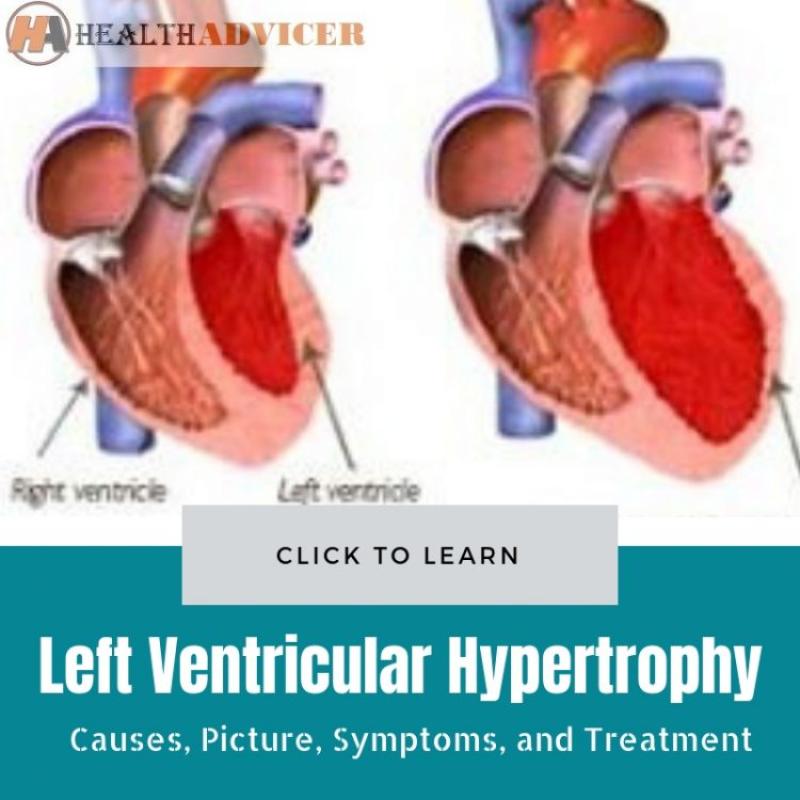
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a condition in which the walls of the left ventricle, the main pumping chamber of the heart, thicken. This thickening can occur due to various factors, including high blood pressure, aortic valve stenosis, and certain medications. Left ventricular hypertrophy can increase the risk of heart failure, arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death.
Treatment for left ventricular hypertrophy is typically aimed at addressing the underlying cause and reducing the workload on the heart. Here are some of the common treatment approaches:
Controlling Blood Pressure: High blood pressure is a major contributor to LVH, and managing blood pressure effectively is crucial for treatment. Medications such as beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) can help lower blood pressure and reduce the strain on the heart.
Managing Underlying Conditions: If LVH is caused by other conditions, such as aortic valve stenosis, addressing those conditions is essential. For example, if aortic valve stenosis is narrowing the aortic valve, surgery or valve replacement may be necessary to improve blood flow and reduce the pressure on the left ventricle.
Lifestyle Changes: Lifestyle modifications can significantly impact LVH management. These include:
Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight puts additional strain on the heart, so maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the workload on the left ventricle.
Regular exercise: Exercise helps strengthen the heart, improve blood flow, and lower blood pressure. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
Eating a heart-healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat protein can help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of LVH.
Limiting alcohol and salt intake: Excessive alcohol consumption and high salt intake can contribute to high blood pressure and LVH. Aim to limit alcohol intake and reduce salt consumption to less than 2,300 milligrams per day.
Controlling blood sugar levels: If you have diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is crucial to prevent complications, including LVH.
**Monitoring and ** Regular monitoring with your doctor is essential to assess the effectiveness of treatment and make adjustments as needed. They may also recommend additional tests, such as an echocardiogram, to monitor the thickness of the left ventricular wall and overall heart function.
In some cases, medication or lifestyle changes may not be enough to manage LVH, and additional treatments may be considered. These may include:
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT): CRT is a device therapy that coordinates the timing of the heart's contractions, improving blood flow and heart function.
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD): An ICD is a device that monitors the heart rhythm and delivers an electric shock to correct life-threatening arrhythmias.
Remember, early diagnosis and treatment of LVH are crucial to improve outcomes and prevent complications. By addressing the underlying cause, making lifestyle changes, and following your doctor's recommendations, you can effectively manage LVH and maintain a healthy heart.