What is the history of Chinese writing?
The Evolution of Chinese Writing: A Historical Overview
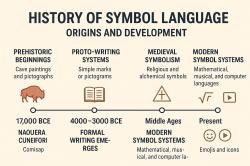
Chinese writing is one of the world's oldest and most complex writing systems, with a rich history dating back thousands of years. Understanding the evolution of Chinese writing helps us appreciate its cultural significance and the profound impact it has had on China's history and beyond.
1. Oracle Bone Script (c. 1200–1050 BCE):
- The earliest known form of Chinese writing was Oracle Bone Script. It was etched onto turtle shells and animal bones during the Shang Dynasty. These inscriptions were used for divination and record-keeping in early Chinese society.
2. Bronze Script (c. 1046–771 BCE):
- During the Zhou Dynasty, the Bronze Script emerged as a more standardized form of writing. It was engraved on bronze vessels and weaponry and served both ritual and practical purposes.
3. Seal Script (c. 221 BCE–220 CE):
- The Seal Script was widely used during the Qin Dynasty and later dynasties. It is characterized by its intricate, decorative characters, often used for official seals and inscriptions on art and architecture.
4. Clerical Script (c. 221 BCE–220 CE):
- Developed during the Han Dynasty, Clerical Script simplified characters for easier and faster writing. It became the standard script for official documents and administration.
5. Regular Script (c. 220 CE–present):
- Regular Script, also known as Kai Shu, emerged during the Wei and Jin Dynasties. It is the basis for modern Chinese writing. Regular Script is characterized by its neat and symmetrical characters, making it highly legible.
6. Cursive Script (c. 220 CE–present):
- Cursive Script, or Cao Shu, developed as a quicker and more fluid form of writing. It is known for its abbreviated, often abstract characters. It is used for informal writing and calligraphy.
7. Running Script (c. 220 CE–present):
- Running Script, or Xing Shu, is a semi-cursive style that combines the speed of Cursive Script with the readability of Regular Script. It is often used in calligraphy and artistic writing.
8. Modern Chinese (20th Century–present):
- Simplified Chinese characters were introduced in the 20th century to improve literacy rates. These simplified characters are used in mainland China, while traditional characters are still prevalent in Taiwan and Hong Kong.
Conclusion:
The evolution of Chinese writing reflects not only linguistic developments but also the changing political and cultural landscape of China. Today, Chinese writing remains a vital aspect of Chinese culture, connecting contemporary society to its rich historical roots. It continues to adapt and evolve while preserving its deep cultural significance.
Understanding the historical development of Chinese writing offers valuable insights into the complexity and enduring legacy of this ancient script.