What is a myxoid soft tissue tumor?
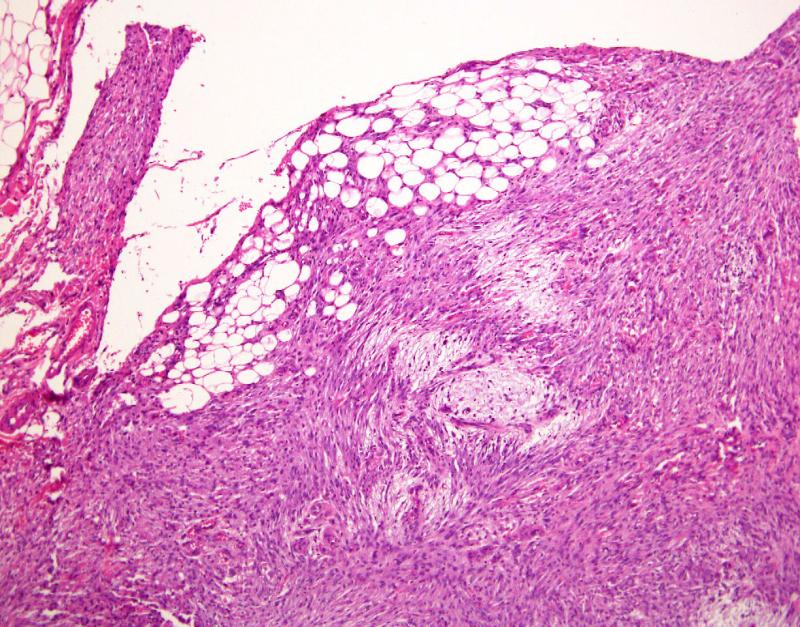
Myxoid soft tissue tumors are a group of neoplasms, or abnormal tissue growths, that have a distinctive microscopic appearance characterized by the presence of a myxoid stroma. "Myxoid" refers to a mucous or gelatinous consistency, and the tumors in this category typically exhibit abundant extracellular matrix material that gives them a gelatinous appearance under a microscope.
These tumors can occur in various soft tissues throughout the body, including muscles, tendons, and connective tissues. Myxoid soft tissue tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and their behavior and prognosis can vary widely.
Several types of soft tissue tumors fall under the category of myxoid tumors, and some common examples include:
Myxoma: Myxomas are generally benign tumors that often occur in the heart, skin, or other soft tissues. Cardiac myxomas are the most common primary heart tumors, and they usually occur in the atria.
Myxoid Liposarcoma: This is a malignant soft tissue tumor that typically arises in deep soft tissues, most commonly in the extremities, especially the thighs. It is a subtype of liposarcoma characterized by the presence of a myxoid matrix.
Myxofibrosarcoma: This is a type of soft tissue sarcoma that often occurs in the extremities of older adults. It has a tendency to recur locally and can be intermediate to high-grade in terms of malignancy.
Extraskeletal Myxoid Chondrosarcoma: This is a rare soft tissue sarcoma that can occur in various locations, including the extremities and trunk. Despite its name, it does not typically involve bone.
The diagnosis and classification of myxoid soft tissue tumors often require a combination of clinical, radiological, and pathological assessments. Additionally, molecular studies, such as cytogenetic analysis, may be performed to better understand the genetic characteristics of these tumors.
Treatment and prognosis vary based on the specific type of myxoid tumor, its location, and whether it is benign or malignant. Surgical removal is a common approach for localized tumors, and additional treatments such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy may be considered, especially for malignant variants.
It's important to consult with medical professionals for accurate diagnosis, appropriate management, and to understand the specific characteristics of any myxoid soft tissue tumor.
What defines a myxoid soft tissue tumor?
A myxoid soft tissue tumor is a type of tumor that arises from mesenchymal cells, which are the cells that make up the connective tissues of the body. These tumors are characterized by the presence of a large amount of mucinous extracellular matrix, which gives them a gel-like or jelly-like appearance. Myxoid soft tissue tumors can be benign or malignant.
How are myxoid soft tissue tumors characterized in medical contexts?
Medical professionals characterize myxoid soft tissue tumors based on their appearance, behavior, and genetic makeup.
Appearance: Myxoid soft tissue tumors typically have a lobulated or round appearance and are often soft and rubbery to the touch. They can range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
Behavior: Myxoid soft tissue tumors can be benign, locally aggressive, or malignant. Benign myxoid tumors do not spread to other parts of the body and are unlikely to recur after treatment. Locally aggressive myxoid tumors may invade nearby tissues, but they do not spread to the lymph nodes or distant organs. Malignant myxoid tumors, also known as myxoid sarcomas, are cancerous and can spread to other parts of the body.
Genetic makeup: Recent advances in molecular biology have led to the identification of several genetic alterations that are associated with myxoid soft tissue tumors. These genetic alterations can help to classify tumors and predict their behavior.
Are there different subtypes or variations of myxoid soft tissue tumors?
Yes, there are several different subtypes or variations of myxoid soft tissue tumors. Some of the most common subtypes include:
Intramuscular myxoma: This is the most common type of benign myxoid soft tissue tumor. It typically occurs in the muscles of the arms, legs, and trunk.
Myxoid liposarcoma: This is a type of malignant myxoid soft tissue tumor that arises from fat cells. It is typically found in the deep soft tissues of the arms, legs, and trunk.
Myxoid chondrosarcoma: This is a type of malignant myxoid soft tissue tumor that arises from cartilage. It is typically found in the bones and joints of the arms, legs, and trunk.
Myxofibrosarcoma: This is a type of malignant myxoid soft tissue tumor that arises from fibrous connective tissue. It can occur in any part of the body.
Ossifying fibromyxoid tumor: This is a type of intermediate-grade myxoid soft tissue tumor that can arise from a variety of tissues. It is typically found in the extremities, but it can also occur in the head and neck, trunk, and abdomen.