What were the major effects of the Neolithic Revolution?
The Neolithic Revolution had a profound and lasting impact on human societies and marked a significant transition in human history. Some of the major effects of the Neolithic Revolution include:
Agricultural Subsistence: The shift from a nomadic, hunter-gatherer lifestyle to settled agriculture was a fundamental change. People began cultivating crops like wheat, barley, rice, and maize and domesticating animals such as cattle, sheep, and goats. This change in subsistence allowed for a more reliable and stable food supply.
Sedentary Lifestyle: With the development of agriculture, communities became more settled. People built permanent dwellings, established villages, and later, towns and cities. This shift from a mobile to a sedentary lifestyle laid the groundwork for urbanization and civilization.
Population Growth: Agriculture enabled the production of surplus food, which, in turn, supported population growth. Larger populations could be sustained, leading to increased social complexity and the growth of civilizations.
Specialization of Labor: Surplus food production allowed some individuals to specialize in occupations other than farming. This specialization gave rise to various professions, including artisans, merchants, priests, and rulers. It also facilitated the development of trade networks.
Technological Advancements: Agriculture led to the development of new tools and technologies designed for farming, such as plows, sickles, and irrigation systems. These innovations improved agricultural efficiency and productivity.
Property Ownership and Inequality: The concept of private property became more important as people staked claims to land, animals, and resources. This shift led to the development of social hierarchies and economic inequalities within communities.
Urbanization and Civilization: As agricultural communities grew and became more complex, they eventually evolved into early urban centers and civilizations. These civilizations, characterized by advanced forms of government, writing systems, and cultural achievements, emerged in various parts of the world.
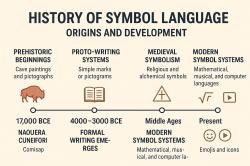
Cultural Developments: The Neolithic Revolution brought about changes in cultural practices, including the emergence of organized religions, artistic expressions, and the development of symbolic systems of communication.
Environmental Impact: The transition to agriculture also had environmental consequences. People cleared land for farming, which could lead to deforestation and soil degradation. Additionally, the domestication of animals and the concentration of populations in settlements led to the spread of diseases.
Long-Term Impact: The Neolithic Revolution set the stage for subsequent developments in human history, including the rise of more complex societies, the invention of writing, and the spread of knowledge and technology. It laid the foundation for the world's major civilizations.
The Neolithic Revolution was a pivotal moment in human history, marking the transition from a nomadic, subsistence-based existence to settled, agriculture-based societies. Its effects continue to shape our world today, influencing everything from our economic systems and social structures to our dietary habits and land use practices.
Transforming Societies: Major Effects of the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution was one of the most transformative events in human history. It was the transition from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to an agricultural lifestyle. This transition had a profound impact on human societies, including:
- Increased population: Agriculture allowed for a more reliable food supply, which led to a significant increase in population.
- Permanent settlements: Agriculture required people to stay in one place to cultivate their crops. This led to the development of permanent settlements.
- Social stratification: As societies grew larger and more complex, social stratification emerged. This was due to the need for specialized jobs and the accumulation of wealth.
- Technological advancements: Agriculture led to a number of technological advancements, such as the development of new tools, irrigation systems, and storage methods.
- Cultural changes: The Neolithic Revolution also led to a number of cultural changes, such as the development of new forms of art, religion, and government.
From Hunter-Gatherers to Farmers: The Profound Impact of the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution was a profound change in the way humans lived. Hunter-gatherers were nomadic people who moved from place to place in search of food. Farmers, on the other hand, were settled people who cultivated crops and raised animals.
The Neolithic Revolution had a number of positive effects on human societies. Agriculture allowed for a more reliable food supply, which led to a significant increase in population. This increase in population allowed for the development of more complex societies with specialized jobs and new forms of technology.
However, the Neolithic Revolution also had some negative effects. For example, agriculture led to deforestation and soil erosion. It also led to an increased risk of disease, as people were now living in close proximity to each other and to animals.
The Legacy of Change: Examining the Lasting Effects of the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution had a lasting impact on human societies. It led to the development of agriculture, permanent settlements, social stratification, technological advancements, and cultural changes.
Agriculture is still the foundation of human society today. It allows us to produce enough food to support a large population. Permanent settlements led to the development of cities and civilizations. Social stratification led to the development of complex social structures with different classes and roles. Technological advancements from the Neolithic Revolution led to the development of new tools, irrigation systems, and storage methods, which are still used today. Cultural changes from the Neolithic Revolution led to the development of new forms of art, religion, and government, which have shaped our world in profound ways.
The Neolithic Revolution was a turning point in human history. It led to the development of the way we live today.