What was daily life like for the Neolithic Age?
The Neolithic Age, also known as the New Stone Age, was a period of significant transformation in human history. During this time, people transitioned from a nomadic lifestyle to settled agricultural communities. Here's a glimpse into daily life during the Neolithic Age:
1. Agriculture and Farming:One of the most significant changes was the shift from hunting and gathering to agriculture. People began to cultivate crops such as wheat, barley, rice, and millet, as well as domesticating animals like cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs. This transition allowed for a more stable and reliable food supply.
2. Settlements and Housing:With the development of agriculture, people started living in permanent settlements rather than constantly moving in search of food. These settlements often consisted of mud-brick houses with thatched roofs, surrounded by protective walls or ditches.
3. Division of Labor:As communities grew, there was a greater division of labor. Some people specialized in farming, while others focused on activities like pottery-making, tool crafting, and weaving. This specialization led to the emergence of trade and barter.
4. Tools and Technology:Neolithic people continued to use stone tools, but these tools became more sophisticated due to improved techniques. Stone axes, sickles, and grinding stones were vital for farming and food preparation.
5. Pottery:Pottery became more prevalent during the Neolithic Age. People used pottery for cooking, storing food, and carrying water. This technological advancement improved food storage and preparation methods.
6. Clothing and Textiles:As people began to domesticate animals, they could access animal fibers like wool and leather. This allowed for the production of clothing and textiles for clothing, blankets, and other essentials.
7. Social Organization:As communities settled down, social structures and hierarchies emerged. Leadership roles, religious figures, and communal decision-making systems became more defined.
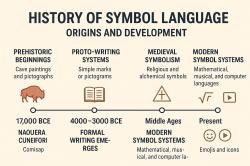
8. Art and Symbolism:The Neolithic Age saw the creation of various forms of art, including pottery decorations, sculptures, and cave paintings. These artistic expressions often had symbolic meanings related to spiritual beliefs, rituals, and daily life.
9. Religion and Beliefs:Neolithic people developed spiritual beliefs and engaged in rituals related to nature, fertility, and the cycles of life. They often created megalithic structures like Stonehenge, which might have served as ceremonial and astronomical sites.
10. Domestication of Animals:The domestication of animals not only provided food but also helped with labor, transportation, and clothing. Animals also played a significant role in religious and cultural practices.
11. Health and Medicine:While medical knowledge was limited, people had a basic understanding of using plants and natural remedies for healing purposes. Life expectancy varied, but improvements in food security likely contributed to longer lifespans compared to the Paleolithic Age.
Overall, life in the Neolithic Age marked a significant transition from a nomadic and hunter-gatherer lifestyle to settled agricultural communities. This transition led to the establishment of more complex societies, the development of various technologies, and the emergence of cultural and religious practices that laid the foundation for the civilizations that followed.