Introduction
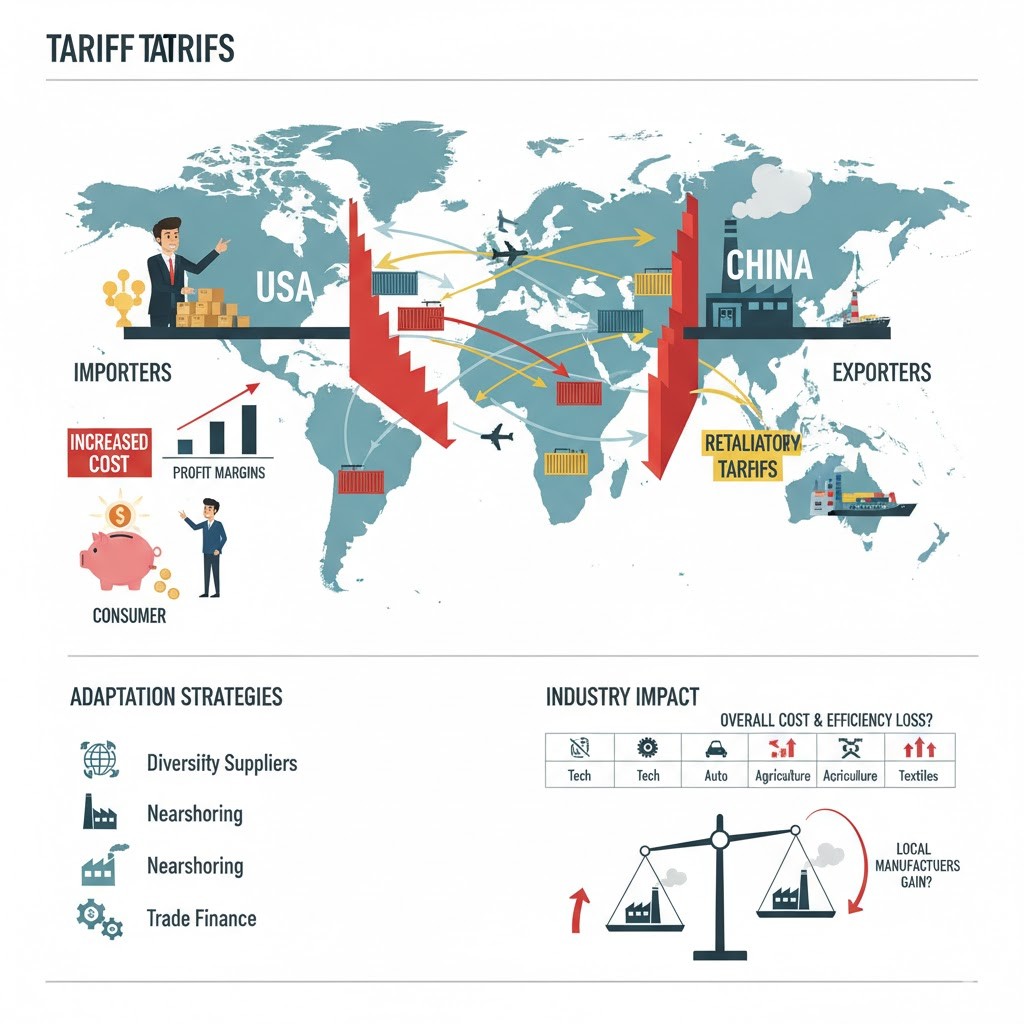
Tariffs have long been a powerful policy tool for governments to protect domestic industries, regulate trade balances, and exert economic leverage in geopolitical disputes. In the context of the US–China trade tensions, tariffs have had far-reaching effects, reshaping global supply chains, impacting corporate profitability, and influencing market behavior worldwide.
For importers and exporters, these additional costs can alter pricing strategies, reduce margins, and force businesses to rethink sourcing, manufacturing, and distribution. Meanwhile, domestic producers may benefit from reduced foreign competition. This article explores the impact of tariffs on businesses, highlights strategies for adaptation, and examines which industries are most affected.
How Do Tariffs Influence the Profit Margins of Importers and Exporters?
Tariffs directly increase the cost of imported goods, forcing importers to either absorb the added expense or pass it on to consumers. For exporters, retaliatory tariffs can reduce competitiveness in foreign markets.
Example:
A US electronics importer sourcing components from China may face a 25% tariff. If the company absorbs the cost, its profit margin shrinks; if it passes the cost to consumers, sales may decline due to higher retail prices. Conversely, Chinese exporters of agricultural goods to the US face tariffs that reduce demand and revenue.
Secondary effects include slower turnover, increased inventory holding costs, and operational inefficiencies as supply chains adjust to shifting trade rules. Businesses that fail to anticipate these changes risk margin erosion and market share loss.
Short- and Long-Term Effects of Tariffs on Global Trade
Short-term effects:
Sudden price increases for imported goods
Supply-chain disruptions as companies scramble to adjust sourcing
Shifts in trade flows to avoid high-tariff markets
Long-term effects:
Structural realignment of global production networks
Diversification of suppliers to reduce dependence on high-tariff countries
Potential decoupling of trade relationships, particularly in sensitive sectors like technology
Case Study: During the US–China trade war, several US tech firms relocated component sourcing from China to Vietnam and Mexico, mitigating immediate tariff exposure but requiring long-term investment in new supplier relationships.
How Can Businesses Adapt to Rising Tariff Costs?
Businesses can implement several strategies to minimize the financial impact of tariffs:
Diversify Suppliers: Source raw materials or finished goods from countries not affected by tariffs.
Relocate Production: Establish manufacturing closer to target markets or in low-tariff countries.
Adjust Pricing Strategies: Pass part of the cost to consumers where demand elasticity allows.
Seek Tariff Exemptions or Relief: Apply for special import duty exemptions, rebates, or trade incentives.
Financial Hedging: Use currency hedging and trade finance tools to protect margins from exchange-rate volatility.
Example: Some American manufacturers of furniture and electronics moved assembly operations to Southeast Asia to bypass high US tariffs on Chinese imports. This not only preserved margins but also diversified risk.
Which Industries Are Most Impacted by US–China Tariff Policies?
Several industries are disproportionately affected due to their reliance on global supply chains or high import/export volumes:
| Industry | Impact Reason | Example Products |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | High-value components imported/exported | Semiconductors, smartphones |
| Automotive | Complex, cross-border supply chains | Auto parts, assembled vehicles |
| Agriculture | Retaliatory tariffs on bulk exports | Soybeans, pork, dairy |
| Consumer Electronics | Costly imports of finished goods | Laptops, home appliances |
| Textiles & Apparel | Labor-intensive imports | Clothing, fabrics |
These sectors have had to adjust procurement, production planning, and pricing strategies to cope with tariff pressures.
Do Tariffs Create Opportunities for Local Manufacturers?
While tariffs pose challenges for importers and exporters, they can benefit domestic producers by reducing foreign competition.
Example:
US steel and aluminum tariffs led to higher domestic production and temporarily increased market share for local manufacturers. Similarly, domestic furniture producers have seen increased demand when Chinese imports faced higher duties.
However, these opportunities may be limited by:
Production capacity constraints
Higher domestic production costs
Need for quality improvements to meet consumer expectations
Businesses that quickly scale operations and adapt products to meet demand can capitalize on these openings.
FAQ Section
Q1: Can tariffs be fully passed on to consumers?
A: Not always. The ability to pass costs depends on demand elasticity and competitive market pressures.
Q2: How quickly can businesses adjust supply chains in response to new tariffs?
A: It varies. Some changes, like switching suppliers, can be done within months; relocation of production may take years.
Q3: Are SMEs more affected than multinational corporations?
A: Generally yes, because SMEs have less flexibility, fewer alternative suppliers, and smaller financial reserves.
Q4: Do tariffs always benefit local manufacturers?
A: Not necessarily. Capacity limits, higher costs, and skill gaps can limit benefits.
Q5: Which trade policies help mitigate tariff effects?
A: Exemptions, duty rebates, regional trade agreements, and investment incentives can all reduce exposure.
Conclusion
Tariffs have a profound effect on importers and exporters, squeezing profit margins, disrupting trade flows, and forcing strategic adjustments. While challenges are evident across multiple industries, proactive businesses can mitigate risks through supply-chain diversification, production relocation, and financial hedging.
Moreover, local manufacturers may seize opportunities to gain market share, but this requires capacity, quality, and strategic agility. As trade policies continue to evolve, companies that anticipate changes and respond quickly will be best positioned to navigate an increasingly complex global trade environment.

IndustryInsider
on October 13, 2025Nice inclusion of case studies showing real-world supply-chain adjustments.
TradePolicyGeek
on October 13, 2025I appreciate the section on financial hedging and tariff exemption strategies.