What are the beneficial functions of a floodplain?
A floodplain is the flat, low-lying land adjacent to rivers and streams that naturally floods during periods of high water. While flooding can seem destructive, floodplains provide important environmental and community benefits when they are allowed to function naturally.
Here are the key beneficial functions of a floodplain:
Environmental Benefits
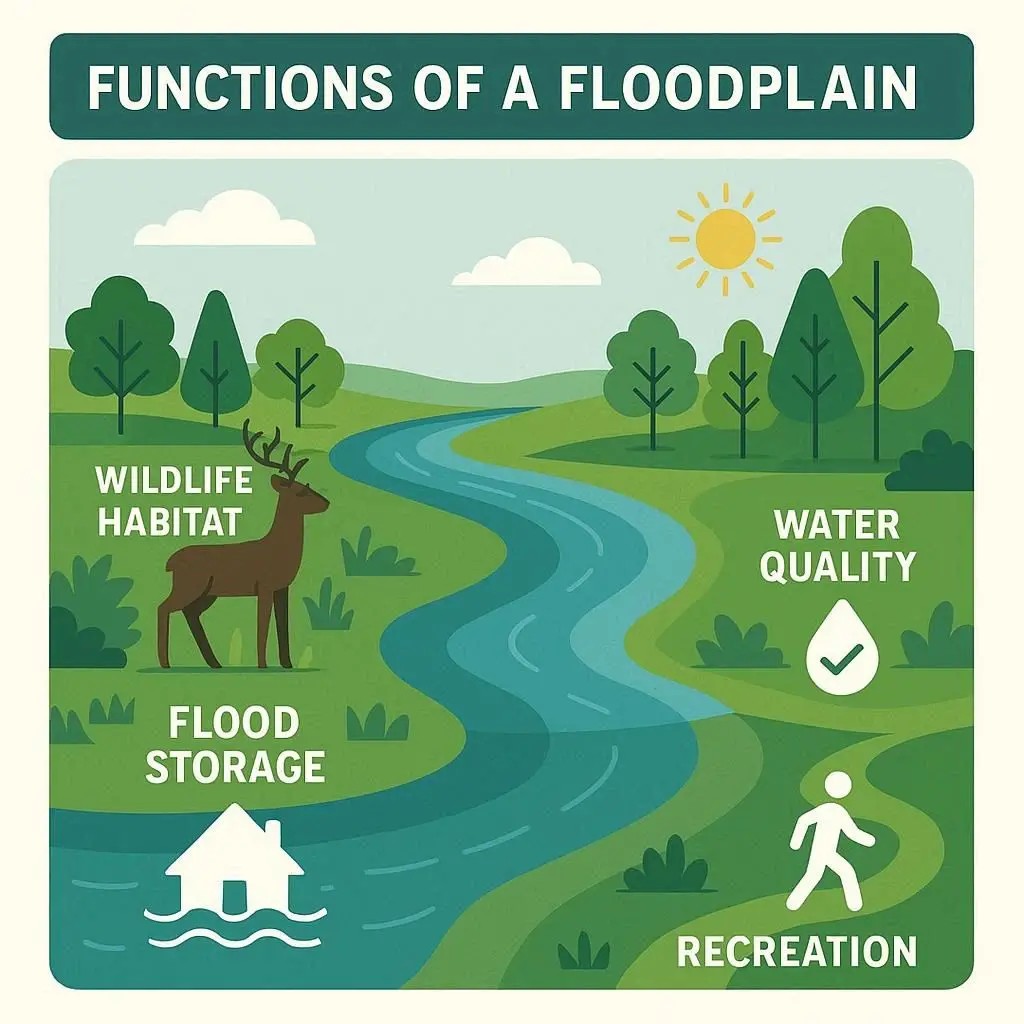
Water Storage – Floodplains act like natural sponges, storing excess water during storms and slowly releasing it back, reducing downstream flooding.
Groundwater Recharge – Water soaking into the soil helps replenish aquifers and maintain healthy water supplies.
Water Quality Improvement – Floodplains filter out sediments, nutrients, and pollutants before they enter rivers, improving water quality.
Habitat for Wildlife – They support diverse ecosystems, providing breeding and feeding grounds for fish, birds, and other species.
Erosion Control – Vegetation along floodplains stabilizes soil and reduces riverbank erosion.
Community and Economic Benefits
Flood Risk Reduction – By absorbing and slowing floodwaters, floodplains help protect downstream communities from severe flooding.
Recreational Opportunities – Many floodplains are used for parks, trails, hunting, fishing, and other outdoor activities.
Agricultural Value – Floodplain soils are fertile due to regular nutrient deposits, supporting productive farming.
Scenic and Cultural Value – They preserve open space, natural landscapes, and cultural heritage areas along rivers.
Cost Savings – Protecting and restoring floodplains is often cheaper than building artificial flood control structures like levees and dams.
In summary: Floodplains are not just “flood-prone land” — they are vital natural systems that protect communities, support biodiversity, improve water quality, and provide economic and recreational benefits.
Floodplains are essential natural systems that provide numerous benefits, including flood management, ecosystem support, and water quality improvement.
What Are the Beneficial Functions of a Floodplain?
Floodplains serve multiple beneficial functions that are crucial for both the environment and human communities.
How Do Floodplains Support Ecosystems?
Floodplains are some of the most biodiverse and productive lands on the planet.
What Role Do Floodplains Play in Flood Management?
A floodplain's role in flood management is primarily about storage and conveyance.
How Do Human Activities Impact Floodplains?
Human activities have a significant negative impact on floodplains.
How Can Floodplains Be Conserved or Protected?
Conservation and protection of floodplains are essential for maintaining their natural functions.
Zoning and regulations: Implementing strict zoning laws that limit or prohibit development in flood-prone areas.
Land preservation: Acquiring and protecting floodplain lands through conservation easements or by creating parks, greenways, and wildlife preserves.
Restoration projects: Reconnecting rivers to their floodplains by removing or setting back levees to restore the natural flow and exchange of water and sediment.
Promoting green infrastructure: Encouraging the use of green infrastructure, such as permeable pavements and rain gardens, in developed areas to help manage stormwater runoff and reduce pressure on floodplains.