How does FDA evaluate the ability of users to perform the workflow?
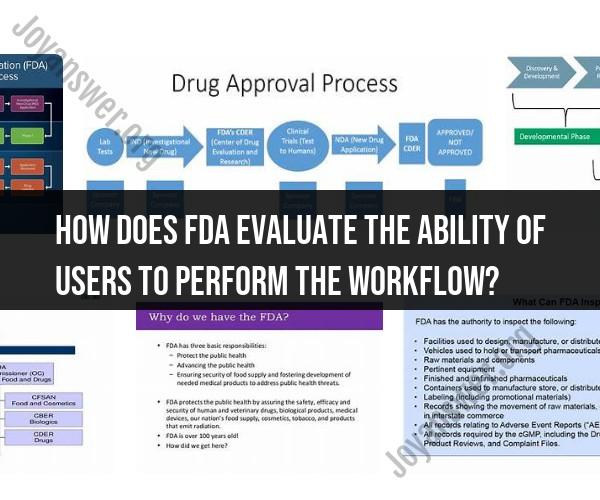
The FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) evaluates the ability of users to perform workflow tasks as part of its assessment process for medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and other products. The evaluation typically follows a rigorous methodology to ensure the safety and effectiveness of these products. Here's how the FDA evaluates user workflows:
Task Analysis:
- The FDA begins by conducting a detailed task analysis of the intended use of the product. This involves identifying all the tasks that users need to perform while interacting with the device or using the pharmaceutical product.
User Profiling:
- The FDA considers the characteristics and demographics of the intended user population, such as healthcare professionals, patients, or caregivers. Understanding the user profile is essential for tailoring evaluations to the target audience.
Usability Testing:
- Usability testing is a critical component of the evaluation process. This involves observing real users as they interact with the product to complete specific tasks. Users are typically asked to perform typical workflows that mimic real-world scenarios.
Task Success and Efficiency:
- The FDA assesses whether users can successfully complete the tasks required by the product. This includes evaluating the accuracy and efficiency with which tasks are performed.
User Satisfaction and Feedback:
- User feedback is gathered through surveys, interviews, or structured questionnaires. This information helps the FDA assess user satisfaction, as well as identify pain points, difficulties, or concerns related to the workflow.
Error Identification:
- The FDA looks for errors made by users during the workflow, including user-related errors and system-related errors. Identifying errors is crucial for improving product safety and usability.
Cognitive Workload:
- The cognitive workload imposed on users is evaluated to ensure that it is reasonable and does not lead to user fatigue, stress, or a high risk of errors.
Training Requirements:
- The FDA assesses the training required for users to effectively perform the workflow. Products should ideally have intuitive user interfaces and workflows that minimize the need for extensive training.
Human Factors Engineering (HFE):
- HFE principles are applied to the evaluation. This includes considering factors such as the layout of controls, the clarity of labeling, the intuitiveness of user interfaces, and other design elements that impact usability.
Iterative Design and Testing:
- The FDA encourages manufacturers to conduct iterative design and testing, where user feedback and usability issues are addressed through multiple design revisions and evaluations.
Documentation and Reporting:
- Manufacturers are required to document the usability evaluation process and submit this documentation as part of their regulatory submissions to the FDA.
Regulatory Compliance:
- The FDA evaluates whether the product complies with relevant regulations and standards related to human factors, usability, and user interface design.
The FDA's evaluation of user workflows is crucial in ensuring that medical devices and pharmaceutical products are safe and effective for their intended users. It helps identify and rectify usability issues, reducing the risk of user errors that could harm patients or compromise the effectiveness of the product. Manufacturers are expected to work closely with the FDA to address usability concerns and make necessary improvements based on evaluation results.