What is a bacterial identification database?
A bacterial identification database, also known as a microbial identification database, is a comprehensive collection of genetic, biochemical, and phenotypic information about various bacterial species and strains. These databases serve as valuable resources for researchers, microbiologists, and healthcare professionals who need to identify and characterize bacteria. These databases are essential for taxonomic classification, diagnostic purposes, research, and quality control in fields such as clinical microbiology, environmental science, and industrial microbiology.
Key components of a bacterial identification database include:
Genomic Data: Genetic information, such as DNA sequences, ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene sequences (e.g., 16S rRNA), and whole-genome sequences, is a fundamental part of bacterial identification databases. These data are used for molecular identification and phylogenetic analysis.
Phenotypic Data: Information on bacterial phenotypes, including morphological characteristics, growth conditions, metabolic properties, and susceptibility to antibiotics, is included in the database. Phenotypic data are particularly important for clinical microbiology and diagnosing infections.
Biochemical Profiles: Many databases include results from biochemical tests commonly used for bacterial identification, such as the API system and various enzyme assays.
Mass Spectrometry Profiles: In clinical and research settings, bacterial identification databases may contain mass spectrometry profiles, such as MALDI-TOF (Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight) mass spectrometry, which is a rapid and highly accurate method for bacterial identification.
Taxonomic Information: Information on the taxonomic classification of bacteria, including their family, genus, and species, is an integral part of the database. Taxonomic data help users understand the evolutionary relationships among different bacterial species.
References and Citations: Bacterial identification databases often include references to published research and literature that support the identification and characterization of specific bacteria.
Search and Query Tools: Databases typically provide search and query tools that allow users to input data (e.g., DNA sequences, biochemical test results) for comparison with entries in the database. These tools assist in identifying unknown bacteria.
Bacterial identification databases are essential in various fields:
Clinical Microbiology: In clinical laboratories, these databases are used to identify bacterial pathogens responsible for infections and diseases. Accurate identification is crucial for determining appropriate treatment.
Environmental Microbiology: Researchers and environmental scientists use these databases to classify bacteria in environmental samples, study microbial diversity, and understand ecological roles.
Food and Industrial Microbiology: Food safety and quality control rely on accurate identification of bacteria, especially in industries such as dairy, brewing, and fermentation.
Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical QC: Bacterial identification databases are valuable for quality control in biotechnology and pharmaceutical manufacturing to ensure product safety and compliance.
Research and Taxonomy: Researchers studying bacterial diversity, evolution, and taxonomy use these databases to compare and classify new and known bacterial species.
Common bacterial identification databases include the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) GenBank, the Ribosomal Database Project (RDP), the Integrated Microbial Genomes (IMG) database, and commercial databases like the BioMerieux VITEK MS database for mass spectrometry-based identification.
These databases are continuously updated as new bacterial species are discovered, and the information they provide plays a pivotal role in the field of microbiology and related disciplines.
Understanding the Role of a Bacterial Identification Database
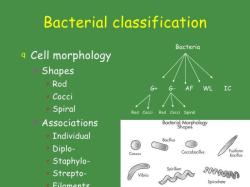
A bacterial identification database is a collection of information about different types of bacteria, including their morphology, staining characteristics, biochemical test results, and genetic sequences. Bacterial identification databases are used by microbiologists to identify bacteria that have been isolated from clinical samples, environmental samples, or food and water samples.
How is a Bacterial Identification Database Used in Microbiology?
Bacterial identification databases are used in microbiology in a variety of ways, including:
- Identifying unknown bacteria: When a microbiologist isolates an unknown bacterium from a sample, they can use a bacterial identification database to identify the bacterium by comparing its characteristics to the characteristics of the bacteria in the database.
- Confirming the identity of bacteria: If a microbiologist has already identified a bacterium using traditional methods, such as microscopy and biochemical testing, they can use a bacterial identification database to confirm the identity of the bacterium.
- Tracking the spread of bacteria: By comparing the genetic sequences of bacteria in a bacterial identification database, microbiologists can track the spread of bacteria and identify outbreaks of disease.
- Developing new diagnostic tests and treatments: Bacterial identification databases can be used to develop new diagnostic tests and treatments for bacterial infections.
Key Features of Bacterial Identification Databases
Bacterial identification databases should have the following key features:
- Comprehensive: The database should contain information about a wide variety of bacteria, including both common and rare bacteria.
- Accurate: The information in the database should be accurate and up-to-date.
- Easy to use: The database should be easy to use and navigate.
- Accessible: The database should be accessible to microbiologists around the world.
Challenges and Limitations in Bacterial Identification Using Databases
There are a few challenges and limitations associated with bacterial identification using databases:
- Databases can be incomplete: Even the most comprehensive bacterial identification databases may not contain information about all known bacteria.
- Databases can contain errors: The information in bacterial identification databases can sometimes contain errors. This is why it is important to confirm the identity of bacteria using multiple methods.
- Databases can be expensive: Some bacterial identification databases can be expensive to access.
Advancements in Bacterial Identification Technology
There have been a number of advancements in bacterial identification technology in recent years. One of the most significant advancements is the development of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology. NGS technology allows microbiologists to quickly and accurately sequence the genomes of bacteria. This information can then be used to identify bacteria using bacterial identification databases.
Another advancement in bacterial identification technology is the development of mass spectrometry (MS) technology. MS technology can be used to identify bacteria based on their unique protein profiles. MS technology is particularly useful for identifying bacteria that are difficult to identify using other methods.
These advancements in bacterial identification technology are making it easier and more accurate for microbiologists to identify bacteria. This is leading to improved diagnosis and treatment of bacterial infections.