What should be in a research article?
A research article typically follows a specific structure to effectively communicate the research findings and contribute to the academic or scientific community. While variations exist based on the specific requirements of journals and disciplines, the following components are commonly found in a standard research article:
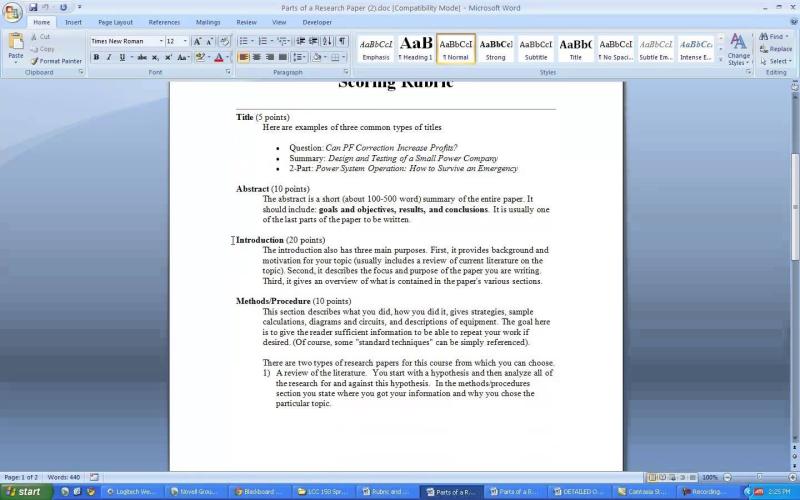
Title:
- A concise and informative title that accurately reflects the content of the research.
Abstract:
- A brief summary (usually 150-250 words) that provides an overview of the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions. The abstract should be concise yet comprehensive.
Keywords:
- A list of keywords or phrases that highlight the main concepts of the research. These help in indexing and searching for the article.
Introduction:
- An introduction that introduces the research problem or question, outlines the research objectives, and provides context by reviewing relevant literature. The introduction concludes with the research hypothesis or question.
Literature Review:
- A review of existing literature related to the research topic. This section establishes the theoretical framework, identifies gaps in the current knowledge, and justifies the need for the present study.
Methodology:
- A detailed description of the research design, methods, and procedures used to collect and analyze data. This section should provide enough information for the study to be replicable.
Results:
- Presentation of the research findings using text, tables, and figures. This section is often objective and focuses on reporting the data without interpretation.
Discussion:
- Interpretation and analysis of the results. This section relates the findings to the research question, discusses their implications, and compares them to existing literature. Limitations and potential areas for future research are often addressed.
Conclusion:
- A concise summary of the main findings and their significance. This section may also suggest practical applications or policy implications of the research.
References (or Works Cited):
- A list of all the sources cited in the article. Follow a specific citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago) as required by the journal.
Acknowledgments:
- A section where authors express gratitude for funding, support, or assistance received during the research.
Appendices (if applicable):
- Supplementary materials, data sets, or additional details that support the research but are not included in the main body of the article.
Remember that the structure and requirements may vary based on the guidelines of the specific journal or publication venue. Authors should carefully read and follow the submission guidelines provided by the target journal when preparing a research article for publication.
What essential components should be included in a research article to ensure its quality and completeness?
A research article must contain several essential components to ensure its quality and completeness. These components provide a clear and structured framework for presenting research findings and contributing to the existing body of knowledge. Here are the most crucial elements:
1. Title and Abstract:
- Title: Captures the essence of the research in a concise and informative way.
- Abstract: Provides a brief overview of the research problem, methodology, key findings, and conclusions.
2. Introduction:
- Background: Establishes the context of the research by reviewing relevant literature and highlighting existing knowledge gaps.
- Research Problem: Clearly defines the specific problem or question addressed in the study.
- Objectives: Outlines the specific goals and aims of the research.
3. Methodology:
- Research design: Describes the specific research approach used, such as experimental, qualitative, or quantitative methods.
- Participants or samples: Identifies the population or sample studied, including selection criteria and demographic information.
- Data collection instruments and procedures: Explains how the data was collected, including details of instruments and data collection procedures.
- Data analysis: Describes the methods used to analyze the collected data.
4. Results:
- Presents the findings of the research in a clear and concise manner, often using tables, figures, and charts.
- Reports statistical results accurately and interprets their meaning.
- Avoids speculation and focuses on presenting the data objectively.
5. Discussion:
- Interprets the results in the context of existing literature and previous research.
- Discusses the limitations of the study and potential alternative explanations for the findings.
- Identifies the implications of the research for theory, practice, and future research.
6. Conclusion:
- Summarizes the key findings of the research and restates the research objectives.
- Provides clear and concise conclusions based on the evidence presented.
- Highlights the significance of the research and its contribution to the field.
7. References:
- Lists all sources cited in the research article in a consistent and accurate format.
- Provides sufficient information to enable readers to locate the cited sources.
Additional components:
- Keywords: Identify relevant keywords for indexing and searching purposes.
- Appendices: Include supplementary information such as raw data, detailed procedures, or additional analyses.
- Author information: Provide details about the authors' affiliations and contact information.
By ensuring the inclusion of these essential components, researchers can contribute to the production of high-quality research articles that advance knowledge in their respective fields. Each component plays a vital role in presenting a comprehensive and transparent account of the research process and findings.