What are the different types of Philosophy?
Philosophy is a diverse and multifaceted field that explores fundamental questions about the nature of reality, knowledge, ethics, existence, and more. As a result, there are various branches and subfields within philosophy. Here is a comprehensive overview of different types of philosophy:
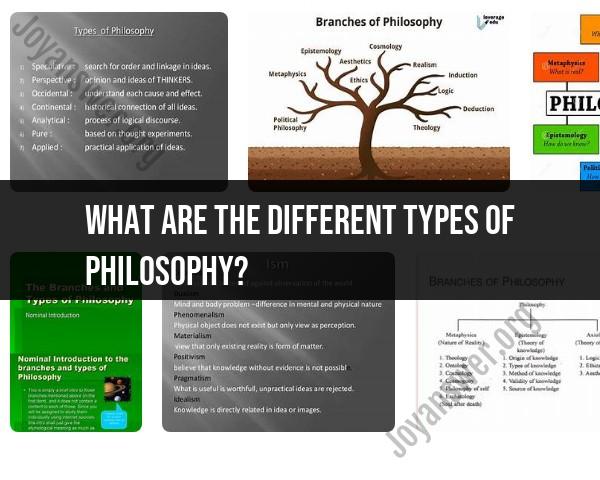
Metaphysics: Metaphysics is the branch of philosophy that explores the fundamental nature of reality, including questions about existence, the nature of being, causality, and the relationship between mind and matter.
Epistemology: Epistemology is the study of knowledge. It delves into questions about what knowledge is, how we acquire it, the limits of human understanding, and the nature of truth and belief.
Ethics: Ethics focuses on questions of morality and principles of right and wrong. It includes normative ethics (the study of ethical theories and principles) and applied ethics (applying ethical principles to real-world situations).
Aesthetics: Aesthetics is concerned with questions of beauty, art, and the nature of aesthetic experiences. It explores concepts like taste, the definition of art, and the nature of artistic expression.
Logic: Logic is the study of valid reasoning and argumentation. It deals with formal systems of reasoning, deductive and inductive reasoning, and the structure of valid arguments.
Philosophy of Mind: This subfield explores the nature of consciousness, mental states, the mind-body problem, and the relationship between the brain and mental phenomena.
Philosophy of Language: Philosophy of language examines the nature of language, meaning, communication, and the relationship between language and thought.
Political Philosophy: Political philosophy considers questions of justice, authority, power, and the structure of government. It includes theories of justice, democracy, and human rights.
Philosophy of Religion: This branch deals with questions related to the existence and nature of deities, religious experiences, the problem of evil, and the relationship between faith and reason.
Philosophy of Science: Philosophy of science explores the nature of scientific knowledge, the scientific method, the demarcation problem (distinguishing science from non-science), and scientific realism.
Moral Philosophy: Moral philosophy is a subfield of ethics that specifically focuses on questions of right and wrong conduct, moral values, and ethical decision-making.
Existentialism: Existentialism is a philosophical movement that emphasizes individual freedom, choice, and responsibility, often exploring questions of existential meaning and authenticity.
Pragmatism: Pragmatism is a philosophical tradition that focuses on the practical consequences of beliefs and actions. It stresses the importance of utility, experience, and empirical inquiry.
Feminist Philosophy: Feminist philosophy explores issues related to gender, patriarchy, and the social construction of gender roles. It seeks to address and challenge gender-based inequalities and biases.
Eastern Philosophy: This category includes philosophies and traditions from Asia, such as Confucianism, Taoism, Buddhism, and Hinduism. It explores concepts like karma, dharma, and enlightenment.
Analytic Philosophy: Analytic philosophy is characterized by its emphasis on clarity and precision in language and logic. It is often associated with formal logic and the analysis of language.
Continental Philosophy: Continental philosophy is a diverse tradition that includes existentialism, phenomenology, hermeneutics, and critical theory. It often focuses on the human experience and interpretation.
Environmental Philosophy: This subfield examines the relationship between humans and the natural environment, including ethical and philosophical issues related to environmental conservation and sustainability.
These are just some of the many branches and subfields within philosophy. Each area explores unique questions and concepts, contributing to the rich tapestry of philosophical thought. Philosophers often engage in interdisciplinary discussions and borrow ideas and methods from various branches to address complex and multifaceted philosophical questions.
An Overview of Different Types of Philosophy
Philosophy is a broad field of study that encompasses a wide range of topics and approaches. Some of the most common types of philosophy include:
Metaphysics: The study of the nature of reality, including the existence of God, the nature of time, and the relationship between mind and body.
Epistemology: The study of knowledge, including its nature, scope, and justification.
Logic: The study of correct reasoning, including the rules of inference and the structure of arguments.
Ethics: The study of morality, including the nature of right and wrong, and the justification of moral judgments.
Aesthetics: The study of beauty, including the nature of art, the value of beauty, and the relationship between art and emotion.
Political philosophy: The study of the nature of government, the relationship between the individual and the state, and the distribution of power and justice.
Social philosophy: The study of the nature of society, including the relationship between the individual and society, the distribution of wealth, and the role of social institutions.
Philosophy of mind: The study of the nature of the mind, including the relationship between mind and body, the nature of consciousness, and the free will vs. determinism debate.
Philosophy of language: The study of the nature of language, including the relationship between language and thought, the meaning of words, and the nature of truth.
Branches and Schools of Thought in Philosophy
In addition to these main types of philosophy, there are also a number of branches and schools of thought within philosophy. Some of the most well-known branches of philosophy include:
Analytic philosophy: A branch of philosophy that emphasizes the use of logic and language analysis.
Continental philosophy: A branch of philosophy that emphasizes the importance of history, culture, and existential experience.
Feminist philosophy: A branch of philosophy that examines the nature of gender and the oppression of women.
Marxist philosophy: A branch of philosophy that is based on the works of Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels.
Existentialist philosophy: A branch of philosophy that focuses on the nature of individual existence and the meaning of life.
Postmodernist philosophy: A branch of philosophy that rejects traditional notions of truth, objectivity, and meaning.
The Distinctive Characteristics of Various Philosophical Disciplines
Each of the different types of philosophy has its own distinctive characteristics. For example, metaphysics is concerned with the fundamental nature of reality, while epistemology is concerned with the nature of knowledge. Logic is concerned with the rules of correct reasoning, while ethics is concerned with the nature of morality. Aesthetics is concerned with the nature of beauty, while political philosophy is concerned with the nature of government.
How Different Types of Philosophy Address Fundamental Questions
Different types of philosophy address fundamental questions in different ways. For example, metaphysicians might ask questions about the nature of God, the existence of free will, or the relationship between mind and body. Epistemologists might ask questions about the nature of knowledge, the possibility of certainty, or the justification of beliefs. Logicians might ask questions about the validity of arguments, the nature of fallacies, or the relationship between logic and language.
Exploring Interdisciplinary Approaches in Philosophy
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in interdisciplinary approaches in philosophy. This involves bringing together insights from different branches of philosophy in order to address complex problems. For example, philosophers of science might draw on insights from metaphysics and epistemology in order to develop a better understanding of the nature of scientific knowledge. Similarly, philosophers of mind might draw on insights from ethics and aesthetics in order to develop a better understanding of the nature of consciousness.
The study of philosophy can help us to think more clearly and critically about the world around us. It can also help us to develop a deeper understanding of ourselves and our place in the universe.