How do I know if I have a tumor in my ovary?
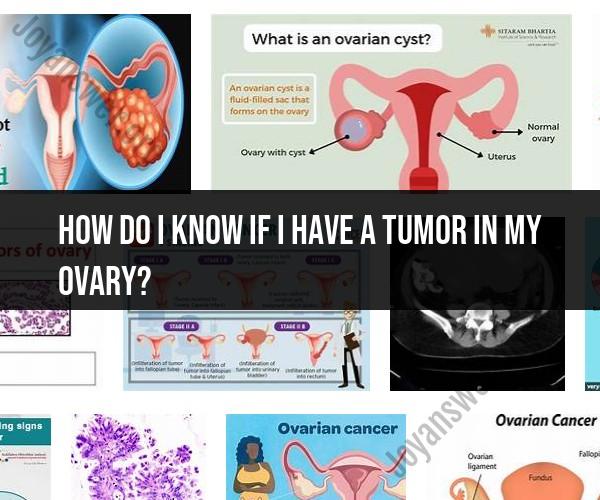
Detecting ovarian tumors involves recognizing the signs and symptoms that might indicate their presence and undergoing appropriate diagnostic tests. Ovarian tumors can be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Early detection is crucial for effective treatment. Here's an overview of signs, symptoms, and diagnosis:
Signs and Symptoms:Ovarian tumors often present with non-specific symptoms, which can make early detection challenging. Common signs and symptoms may include:
- Abdominal Discomfort: Persistent pelvic or abdominal pain, pressure, or discomfort.
- Bloating: Unexplained and persistent bloating, sometimes accompanied by a feeling of fullness even after eating small amounts.
- Changes in Bowel Habits: Changes in bowel patterns, such as constipation or diarrhea, that last for more than a few weeks.
- Urinary Symptoms: Frequent urination or a persistent urgency to urinate.
- Appetite Changes: Sudden loss of appetite or feeling full quickly while eating.
- Unexplained Weight Loss or Gain: Significant weight changes that are not related to diet or exercise.
- Fatigue: Unexplained and persistent fatigue or low energy levels.
- Back Pain: Persistent lower back pain that is not related to other known causes.
Diagnostic Process:If you experience persistent or concerning symptoms, it's important to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional will perform a thorough evaluation, which may include:
Medical History: The doctor will inquire about your symptoms, medical history, and any risk factors you may have.
Physical Examination: A pelvic exam is often conducted to assess the size and condition of the ovaries.
Imaging Tests:
- Ultrasound: Transvaginal ultrasound or abdominal ultrasound can visualize the ovaries and identify any abnormalities.
- CT Scan: A computed tomography (CT) scan provides detailed images of the pelvic area and can help detect tumors.
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide further detailed images for accurate diagnosis.
Blood Tests:
- CA-125: This blood test measures a marker called CA-125, which can be elevated in ovarian cancer. However, it's not specific to ovarian cancer and can be elevated for other reasons as well.
Biopsy or Surgery:
- If imaging and blood tests suggest a tumor, a biopsy may be performed to obtain a sample of tissue for analysis.
- Surgical procedures, such as laparoscopy or laparotomy, may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the nature of the tumor (benign or malignant).
It's important to note that the presence of symptoms does not necessarily mean ovarian cancer. Many of these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions. However, persistent or worsening symptoms should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
If ovarian cancer is suspected or confirmed, further staging tests may be performed to determine the extent of the disease and guide treatment decisions. Early detection and prompt medical attention are crucial for the best outcomes.