How to define sales cycle stages?
Defining the stages of a sales cycle is essential for understanding and managing the process of converting prospects into customers. Here is a comprehensive guide to the typical stages of a sales cycle:
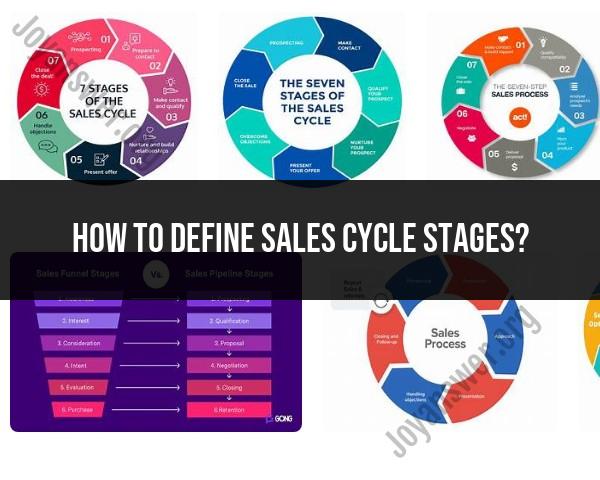
1. Prospecting
Prospecting is the first step where sales representatives identify potential customers. This involves researching and finding leads who might be interested in the product or service. Techniques include networking, social media outreach, and using lead generation tools.
2. Qualifying Leads
In this stage, the identified leads are assessed to determine if they have the potential to become actual customers. This involves evaluating whether they have the need, authority, budget, and timeline (often referred to as BANT criteria) to make a purchase.
3. Initial Contact
Once leads are qualified, the next step is to reach out and make initial contact. This can be done through emails, phone calls, or meetings. The goal here is to establish a relationship and understand the prospect’s needs and pain points.
4. Needs Assessment
This stage involves a deeper understanding of the prospect’s challenges and requirements. Sales representatives ask questions to uncover the specific needs that the product or service can address. This often involves detailed discussions and possibly demonstrations or trials.
5. Presentation/Demonstration
After understanding the prospect’s needs, the sales rep presents the product or service as the solution. This can be through a formal presentation, a demo, or providing samples. The objective is to show how the product or service meets the prospect’s needs and to highlight its benefits and value.
6. Handling Objections
Prospects often have objections or concerns that need to be addressed before they are willing to buy. This stage involves responding to questions, clarifying doubts, and overcoming any resistance the prospect may have.
7. Closing the Sale
This is the critical stage where the sales representative asks the prospect to make a purchase. This can involve negotiating terms, discussing pricing, and finalizing the deal. Techniques such as trial closes, assumptive closes, and direct asks are often used.
8. Follow-Up
After the sale is closed, follow-up is essential to ensure customer satisfaction and address any issues. This can help in building long-term relationships and may lead to repeat business and referrals.
9. Post-Sale Activities
This stage includes delivering the product or service, providing training if necessary, and offering ongoing support. It ensures that the customer is satisfied and fully understands how to use the product or service effectively.
10. Relationship Building
Ongoing relationship building is crucial for customer retention and loyalty. This involves regular check-ins, providing value-added services, and keeping the customer informed about new products or upgrades.
Additional Resources
For more detailed information, you can refer to the following sources:
- HubSpot on Sales Cycle Stages
- Salesforce on The Sales Process
- Investopedia on Understanding the Sales Cycle
By understanding and defining these stages, businesses can create a structured approach to managing their sales processes, leading to increased efficiency and higher conversion rates.
How can sales cycle stages be defined and categorized?
The sales cycle can be broken down into a series of stages, typically following a linear progression from initial contact to closing the deal. Here's how these stages can be defined and categorized:
Common Sales Cycle Stages:
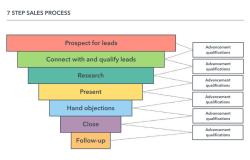
Prospecting: Identifying and generating leads who might be interested in your product or service. This involves research, market analysis, and qualifying potential customers.
Qualifying: Assessing a lead's needs, budget, and decision-making authority to determine if they're a good fit for what you offer. Not all leads are created equal, so qualification helps prioritize resources.
Connecting & Presenting: Making initial contact with qualified leads, introducing yourself and your solution, and demonstrating how your product or service addresses their needs. This could involve phone calls, emails, or in-person meetings.
Overcoming Objections: Addressing concerns and hesitations that prospects might have about your product or service. This stage requires active listening, clear communication, and effectively demonstrating the value proposition.
Closing the Sale: Guiding the prospect towards a buying decision by negotiating terms, finalizing the agreement, and securing the sale.
Post-Sale Activities: Following up with the customer after the sale to ensure satisfaction, provide ongoing support, and potentially explore upselling or cross-selling opportunities.
Categorizing Stages:
These stages can be further categorized into three main phases:
- Top of the Funnel (TOFU): Prospecting and qualifying leads (broad outreach)
- Middle of the Funnel (MOFU): Connecting, presenting, and overcoming objections (educating and nurturing leads)
- Bottom of the Funnel (BOFU): Closing the sale and post-sale activities (converting leads into customers)
Number of Stages:
The exact number of stages in a sales cycle can vary depending on the industry, product complexity, and sales methodology. Some companies might have additional stages, such as lead nurturing or contract negotiations, while others might combine some stages for simpler products or shorter sales cycles.